In C programming language, format specifiers are used to receive inputs and display outputs of a specific type. These specifiers are represented by the symbol % and a character to indicate to the compiler the data type of the input and output to be used. Among the different format specifiers available, the %d is the most frequently used one for integers.
In this article, we will explore the usage of the %d format specifier in C programming.
What is the %d Specifier in C?
In C programming, %d is a format specifier that accepts integer values as signed decimal integers, including both positive and negative values. However, values must be expressed in decimals, else it will print a garbage value.
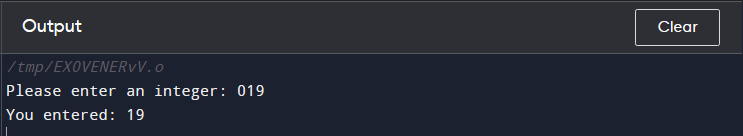
Note: If the input value is in octal format, such as 019 then %d will consider the input as 19, ignoring the zero. The format specifier %d can be used in the scanf(), printf(), or other functions that utilize a formatted string for input and output of int data type.
The syntax for %d specifier for input and output is given as:
Let’s look at some examples to demonstrate the usage of the %d.
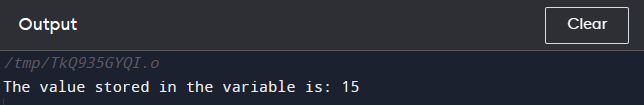
Example 1
In this example, %d is used to print an integer value using the printf() function.
int main()
{
//declare an integer value
int num = 15;
//Use format specifier %d to print the above integer value
printf("The value stored in the variable is: %d\n", num);
return 0;
}
Example 2
The given example demonstrates how the format specifier %d is used to take an integer input from the user.
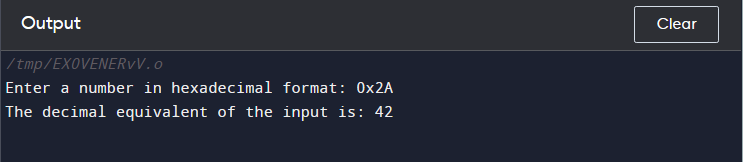
Example 3
If the input value starts with 0x or 0X, then the format specifier %d will ignore the prefix and consider the input value as a decimal integer.
Conclusion
The most commonly used format specifier in C programming is %d, which accepts integer values as signed decimal integers. This means that it can accept both positive and negative integer values. The format specifier %d can be used in the scanf(), printf(), or other functions that utilize a formatted string for output and input of int data type. This guide described the usage of the %d specifier in C language.