This article will demonstrate the method of creating a Git fork manually.
How to Manually Create a Git Fork?
To manually create a fork in Git, look at the following steps:
- Open GitHub and redirect to the target repository that requires to be forked.
- Click on the “Fork” button.
- Create a fork by hitting the “Create fork” button.
- Copy the HTTP URL of the forked repository.
- Navigate to the local repository and clone the forked repository in it.
- Add remote origin.
- Pull changes from the forked repository.
- Verify changes.
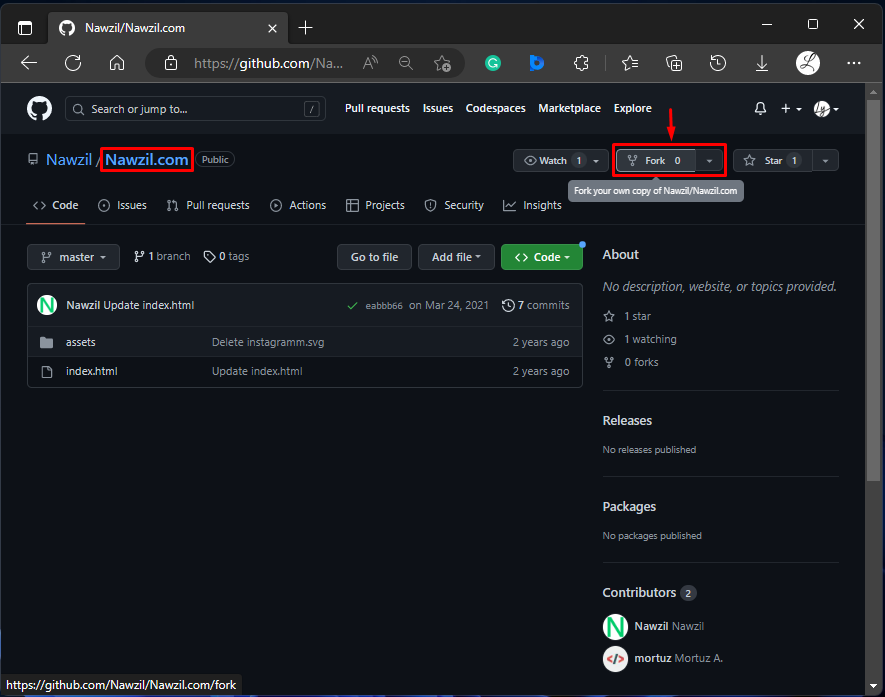
Step 1: Navigate to Target Repository
First, open GitHub and redirect to the target repository that is supposed to be forked. For instance, we want to fork the “Nawzil.com” repository.
Step 2: Create Fork
Then, click on the “Fork” button to create a copy of the target repository into your GitHub account:
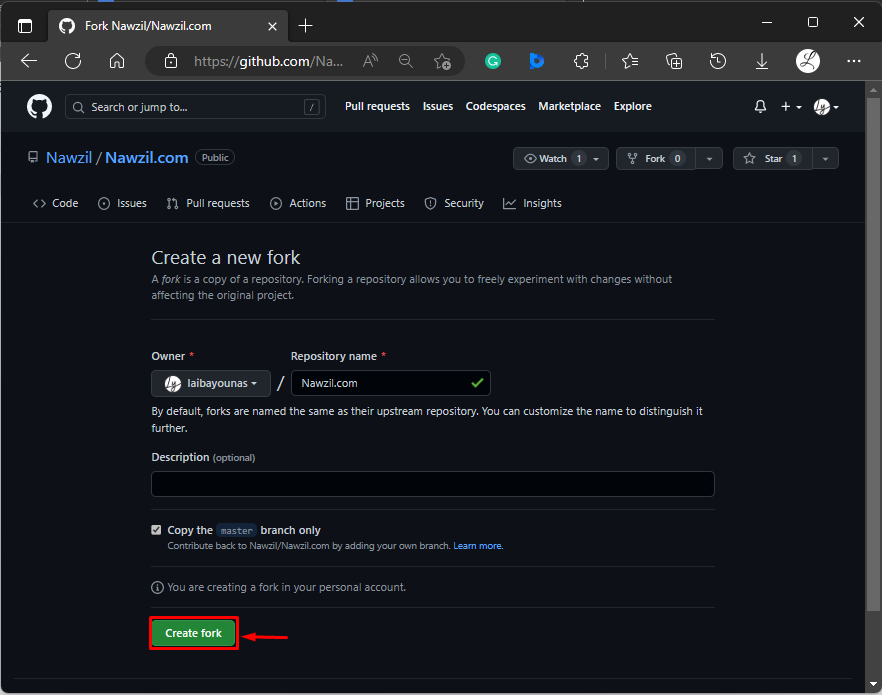
After that, change the repository name and description if needed. Next, hit the “Create fork” button:
Upon doing so, the target remote repository will be forked successfully.
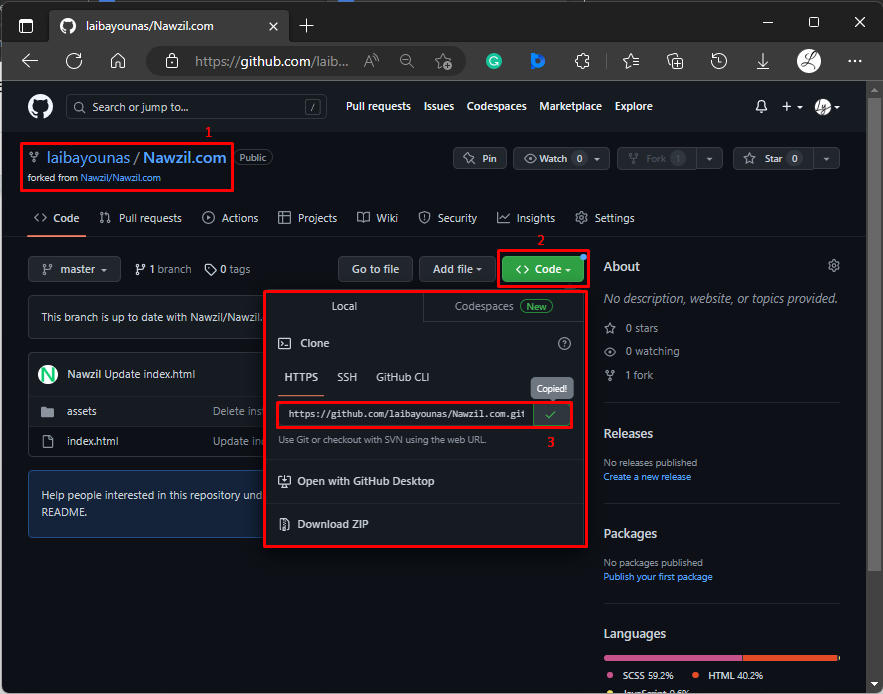
Step 3: Copy HTTP URL of Forked Repository
On the newly forked repository, click on the “Code” button and copy its HTTP URL:
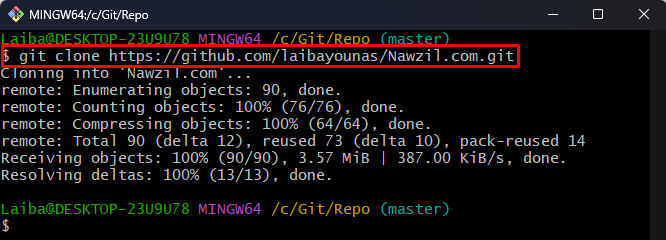
Step 4: Clone Repository
Now, create a copy of the forked remote repository into the local system using the below-listed command:
Make sure to replace the “username” with your GitHub username and “forked-repo” with the target repository name that needs to be cloned.
Here, our GitHub username is “laibayounas” and we want to clone the “Nawzil.com” repository:
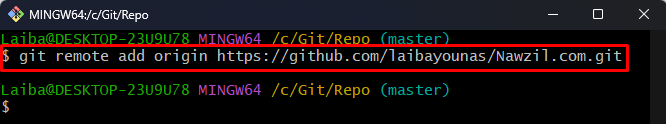
Step 5: Add Remote Origin
Utilize the “git remote add” command and specify the remote name and forked remote repository URL to link the local repository with the forked repository:
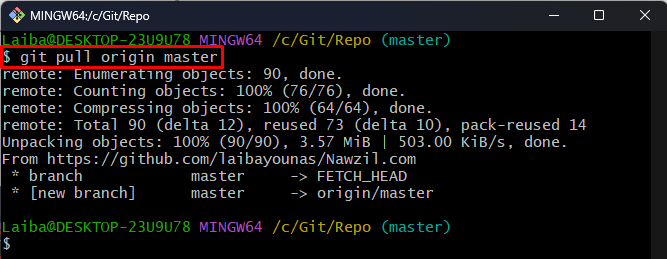
Step 6: Pull Changes
Next, pull the changes of the forked repository into the local repository:
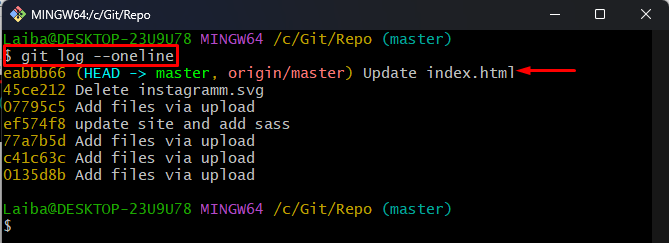
Step 7: Verify Changes
Lastly, view the Git log to ensure changes:
In the below screenshot, the content/changes of the target forked repository can be seen:
That was all about manually creating a fork in Git.
Conclusion
To manually create a fork in Git, first, open the GitHub account and switch to the target repository that needs to be forked. Then, choose the “Fork” option and create a fork by clicking the “Create fork” button. After that, navigate to the local repository and clone the forked repository in it. Lastly, pull changes from the forked repository. This article demonstrated the method to create a Git fork manually.