Types of Groups in Linux
Linux has two types of groups that contain several users:
- Primary or Login Group: it is the group associated with the files created by a specific user. The name for that primary group has the same name as the user’s name that will create that specific file. Each user must belong to exactly a single group.
- Secondary or Supplementary Group: you can use this type of group to grant privileges to a set of users that belong to that group. A user can be assigned to no or more secondary groups.
Listing Users on Linux
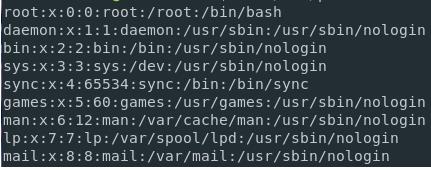
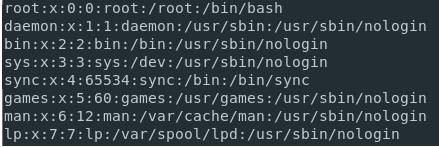
For listing all the users present on the Linux system, you can run the cat command on the ‘/etc/passwd” file. This command will help in returning the number of users that are present on the Linux system.
Also, use the “less” or “more” command for navigating within the user’s list.
$ less /etc/passwd
$ more /etc/passwd
Listing Users Using the /etc/passwd File
For listing the usernames on the Linux system, you can use the “cat” command and then pipe the output to the “cut” command to isolate the usernames available in the first column in the list. Run the below-mentioned command as shown below.
Listing Usernames Using awk
For listing the usernames on the Linux system, use the “cat” command and then pipe the output to the “awk” command that works similar to the “cat” command.
Here we are using the “awk” interpreter, as shown below.
Listing Usernames Using getent
Use the getent command along with the “passwd” argument for listing the usernames available on Linux. Also, you can mention the optional user that you want to be displayed on the screen.
The getent command retrieves the entries from the Name Service Switch databases. It is a Unix utility for retrieving entries from various data sources. Check the list of the data sources available from the nsswitch.conf, which is stored at /etc.
If you want to list all the users with the help of the getent function, you can run the following command.
Listing the Connected Users on Your Linux Host
To get the list of the users connected to the Linux system, you can use the following command.
Using this command, you will provide the connected users’ list and the shell they are using.
Also, you can use the “users” command to get the same result as the “who” command, as shown below.
devconnected john
Listing Groups Using /etc/group File
Use the most commonly used “cat” command to get the list of the groups available in the “/etc/group” file. When you run the command, you will get the list of the groups.
$ less /etc/group
$ more /etc/group
But if you are looking for the group names that are present in the “/etc/group” file, use the cat command and then pipe the output to the “cut” command as shown below.
Also, if you want to isolate one group to check what users belong to that group, use the below command.
Listing Groups Using getent
You can use the “getent” command for listing the users on the Linux system.
If you do not provide the key, you will get the entire group file.

Listing Groups for the Current User
Using the “group” command will display a list of groups a specific user is in.
If you do not provide any argument, you will get the list of the groups for the user that runs the command.
![]()
Conclusion
The Linux system contains users and groups in different files. Sometimes it becomes important to get the user details and to which group they belong. Thus Linux offers some commands that will help you to achieve that. You can run some commands to get the user details and the group to which they belong. You can also get the complete list of users on the Linux system, active users, and groups names.
You can go through this article to get various commands for getting the list of all the groups in Linux and understand how they work.