Route Methods
Some common route methods used in Laravel to handle HTTP requests are explained below.
A. Route::get($uri, $callback_function)
The basic Laravel route, mainly used to display static pages.
B. Route::post($uri, $callback_function)
Used to create any new item.
C. Route::put($uri, $callback_function)
Used to update or replace database record.
D. Route::patch($uri, $callback_function)
Used to update or modify database record.
E. Route::delete($uri, $callback_function)
Used to delete database record.
F. Route::any($URI, $callback)
Used to handle all types of HTTP requests.
Uses of the get() Route Method
Default Route
When you create a new Laravel project, the following default route is found by default in the web.php file. This displays the content of the welcome view file for the base URL of the project.
return view('welcome');
});
Run the base URL of the Laravel project from the browser.
The following output will appear.
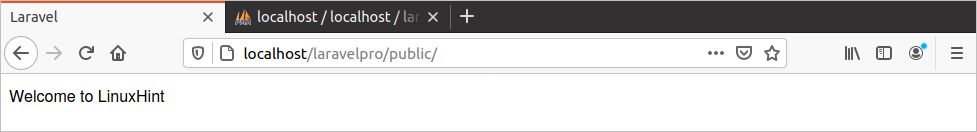
If you change the output of the base URL with the following route, then it will display the simple text “Welcome to LinuxHint” in the browser.
return 'Welcome to LinuxHint';
});
Again, run the base URL to check the output.
Basic get() Route
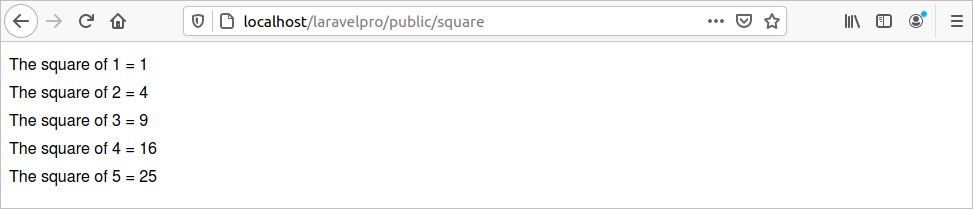
The following route will iterate a for loop 5 times and print the square values of the numbers from 1 to 5.
for($i =1; $i <= 5; $i++){
echo "The square of $i = ".pow($i,2)."<br>";
}
});
Run the following URL from the browser.
http://localhost/laravelpro/public/square
The following output will appear.
Route Using Route Parameter
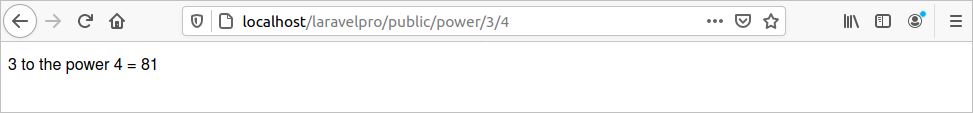
You can use the parameter with the request URL to pass as the function argument. In the following route, two parameters are used that are passed in the function as $x and $n. Here, $x is used as a base and $n is used as an exponent. $x to the power $n will be printed in the browser after executing the route.
Run the following URL from the browser. Here, the base value is 3 and the exponent value is 4.
http://localhost/laravelpro/public/power/3/4
The following output will appear.
Route Using the Optional Parameter
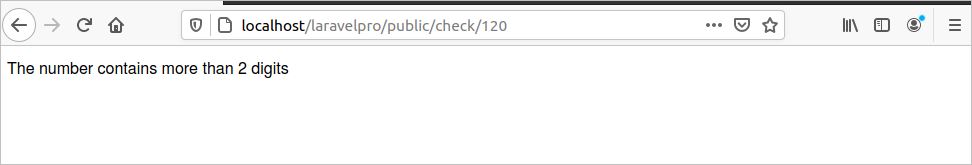
You can use the optional route parameter by using the ‘?’ symbol. This means that if you pass the route parameter value, then it will be used in the function argument, and if the parameter is omitted, then the default value of the function argument will be used. If the parameter value is more than 99, then it will print the message: “The number contains more than 2 digits.” If the value is more than 9, then it will print the message: “The number contains 2 digits.” If the parameter value is less than 9 or omitted, then it will print the message: “The number contains 1 digit.”
if($number > 99)
return "The number contains more than 2 digits";
else if($number >9)
return "The number contains 2 digits";
else
return "The number contains 1 digit";
});
Run the following URL from the browser. Here, 120 is given as the number value.
The following output will appear.
If you omit the number value from the URL, then the following output will appear.
Route with a Regular Expression
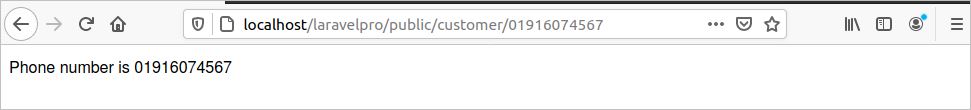
You can use any regular expression pattern to validate the route parameter value. In the following route, the phone parameter is validated using the pattern, ‘^0[0-9]{10}.’ The pattern indicates that the value of the phone will start at 0 and will contain any other 10 digits.
echo "Phone number is $phone";
})->where('phone', '^0[0-9]{10}');
Run the following URL from the browser. Here, ‘01916074567’ is given as the value of the phone parameter.
http://localhost/laravelpro/public/customer/01916074567
The following output will appear.
Routes for Controller
Run the following command to create a controller named BookController.
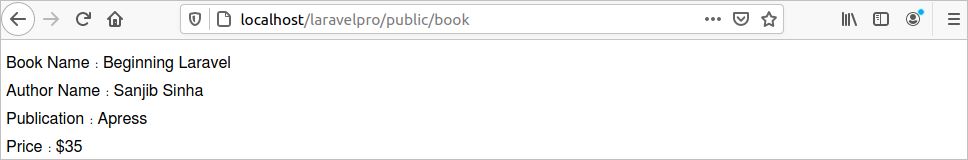
Add the following index() method inside the controller to print the details of a book.
{
echo "Book Name: Beginning Laravel<br/>";
echo "Author Name: Sanjib Sinha <br/>";
echo "Publication: Apress<br/>";
echo "Price: $35";
}
A. Simple route for controller
Now, add the following route in the web.php file to call the index() method of BookController.
Run the following URL from the browser.
http://localhost/laravelpro/public/book
The following output will appear.
B. Named route for controller
The named route is used to provide an alternative name to a route, which allows you to redirect the route to a particular route. Add the following line at the end of the index() method of BookController to create a hyperlink.
Add the anotherBook() method with the following code inside the Bookcontroller to access this method using the named route.
{
echo "book name: 'Laravel 5 Essentials'<br/>";
echo "Author Name: 'Martin Bean' <br/>";
echo "Price: $30<br/>";
echo "Publication: PAKCT<br/>";
}
Now, add the following named route in the web.php file.
'as' => 'other', 'uses' => 'BookController@anotherBook'
]);
Run the following URL again from the browser and click on the Next Book link.
http://localhost/laravelpro/public/book
The following output will appear after clicking the link.
Conclusion
This tutorial covered the various uses of the get() method in routing to clarify the concept of this method in Laravel routing. In this article, basic routing, routing with parameters, routing with the regular expression, and routing with the controller were explained through various examples. I hope that this tutorial has helped you understand the routing basics of Laravel.