This article will elaborate on the method to kill processes currently using a port on localhost in Windows:
- Using Command Prompt
- Using PowerShell
- Using CurrPorts
Let’s get started!
Method 1: Use Command Prompt to Kill the Windows Process Currently Using a Port on localhost
To kill the Windows process currently using the localhost port through Command Prompt, follow the below-listed steps.
Step 1: Open Command Prompt
First, press the “Window+R” key to open the Run box. Type “cmd” in the dropdown menu and hit the “OK” button to open a command prompt:
Step 2: Check the localhost Port Running Process
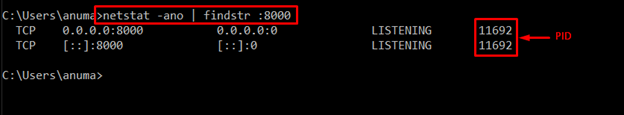
Utilize the “netstat” command to find out the currently running process on the localhost port:
Step 3: Kill Process Using PID
Then, use the “taskkill” command and specify the PID of the process currently running on localhost and kill it:

Step 4: Verify the Process State
Again run the “netstat” command to verify that the port on the localhost is running any process or not:
As no output is shown, which indicates that the specified process is killed successfully:

Step 5: Kill Process by Specifying localhost Port
You can kill a process by specifying a localhost port using the “npx kill-port <port no>” command:
We have successfully terminated the process that is running using a port on localhost:
Let’s check out the method to kill the Windows process currently using a port on localhost through PowerShell.
Method 2: Use PowerShell to Kill the Windows Process Currently Using a Port on localhost
To kill the Windows process currently using the localhost port with the help of Powershell, utilize the below provided steps.
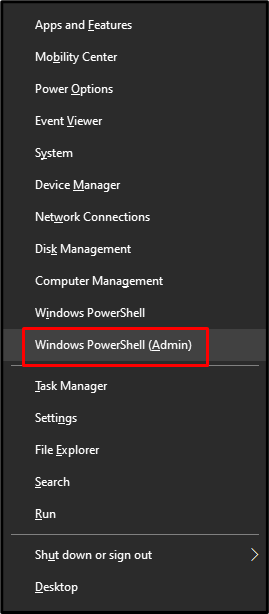
Step 1: Open Windows PowerShell
Use the “Window+X” key, then choose “Windows PowerShell” as admin from the list of options that appears to open Windows PowerShell:
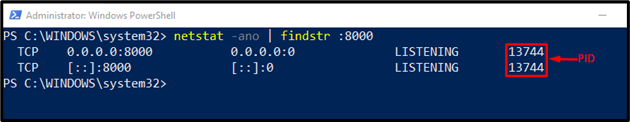
Step 2: Find localhost Port Running any Process
Firstly, find any process that is currently using a port on localhost by executing the provided command:
Step 3: Kill Process Using PID
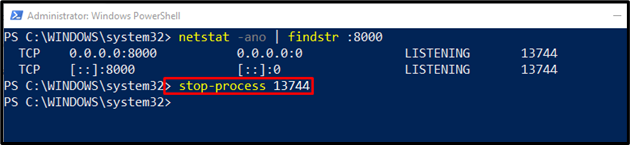
To terminate a process utilizing a localhost port, issue the “stop-process” command with the PID number:
Step 4: Kill Process by Specifying localhost Port
The localhost port number can also be used by the user to terminate the process. To do so, use the “Get-Process” command and pass its output to the “Stop-Process” command using the pipe operator “|”. This action will kill the process that is currently running on the specified port:
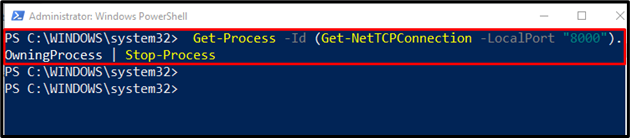
Run the “netstat” command once again to confirm that the specified process has killed:

Now, let’s head towards the next section!
Method 3: Use CurrPorts to Kill the Process Currently Using a Port on localhost in Windows
To kill the process currently running on a port on localhost using the CurrPorts tool on Windows, follow the below-listed steps.
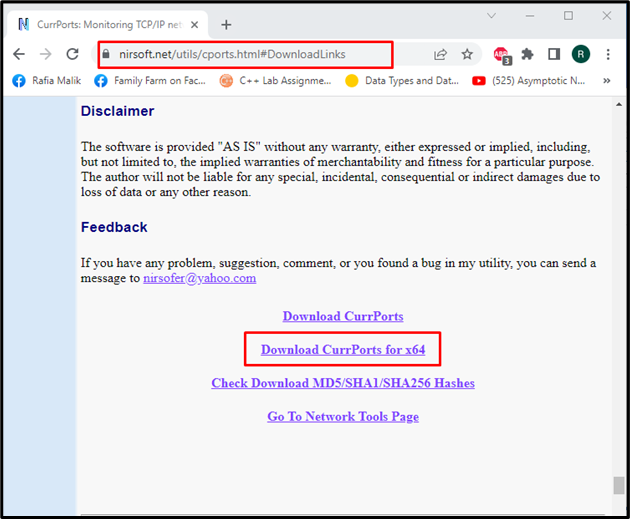
Step 1: Download CurrPorts
Visit the below-provided link and download the CurrPorts setup file:
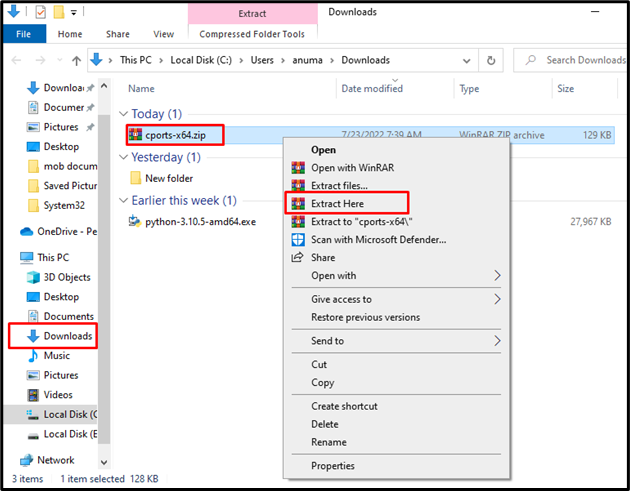
Step 2: Extract CurrPorts Setup Folder
Go to the “Downloads” directory and extract the zip folder. To do so, right-click on the file and choose the “Extract here” option:
Step 3: Run CurrPorts Execution File
Double click on the file to run the “cports.exe” file:
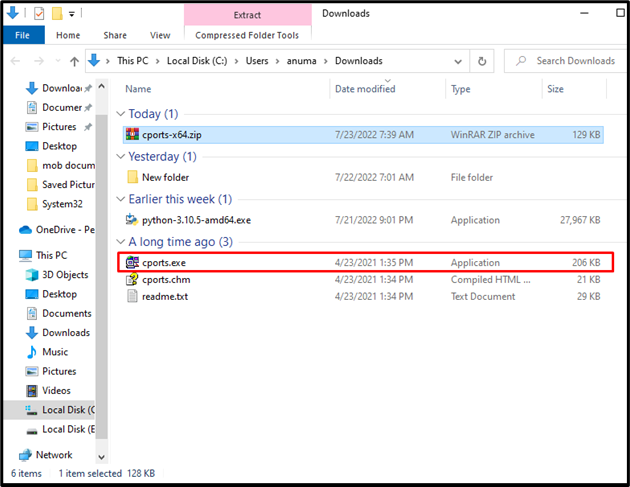
Step 4: Kill Process
Select the port, then choose the “Kill Processes Of Selected Port” option from the context menu to kill the processes:
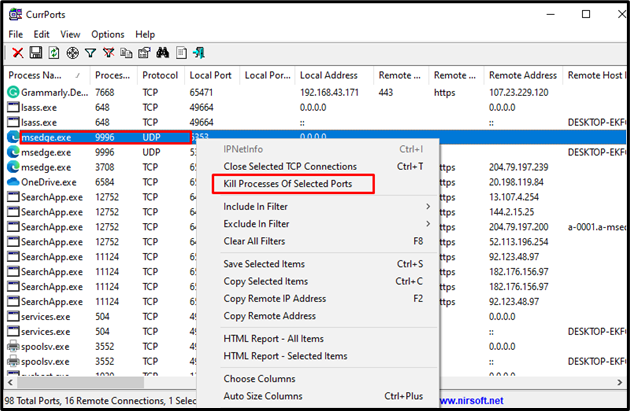
We have effectively demonstrated the methods to kill the process currently using a port on localhost in Windows.
Conclusion
To kill the Windows process currently using a port on localhost, use the “npx kill-port 8000” command on Command Prompt. On Windows PowerShell, the “Get -process” command and the “Stop-process” command to find out and end the specified processes. Lastly, the CurrPorts tools can also be utilized for the same purpose. In this blog post, we have shown how to stop Windows processes that are currently using a port on localhost.