Therefore programming languages offer the concept of scope which says not all variables/methods exist everywhere in the program instead these variables and methods will be accessible in the area where they are created.
This write-up presents a profound understanding of the following concepts:
- Scope of Variable in Java
- Class-level Scope in Java
- Method-level Scope in Java
- Block-level Scope in Java
So let’s get started!
Scope of Variable in Java
It determines whether the variable will be accessible within the entire program, within a method, or it’s accessible across the other classes as well. So in simple words, the scope of the variables determines that the variables are accessible only within the area where they are created.
Example
The below snippet will provide a better understanding of variable scope
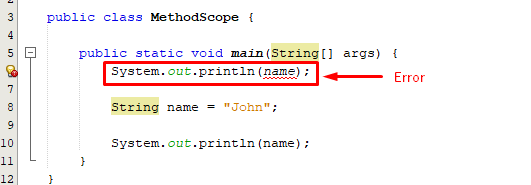
Let’s consider an example to test what will be the output, if we try to access a variable before it’s declaration:
The above snippet authenticates that the variable before its declaration can’t be accessed.
Class-level Scope in Java
The variables declared inside a class can be accessed by all the functions in that class depending on its access modifier/specifier i.e. public, private, etc. In some cases (i.e. in public access modifiers and using objects of that specific class), we can access and call the variables and methods outside the class as well.
Example
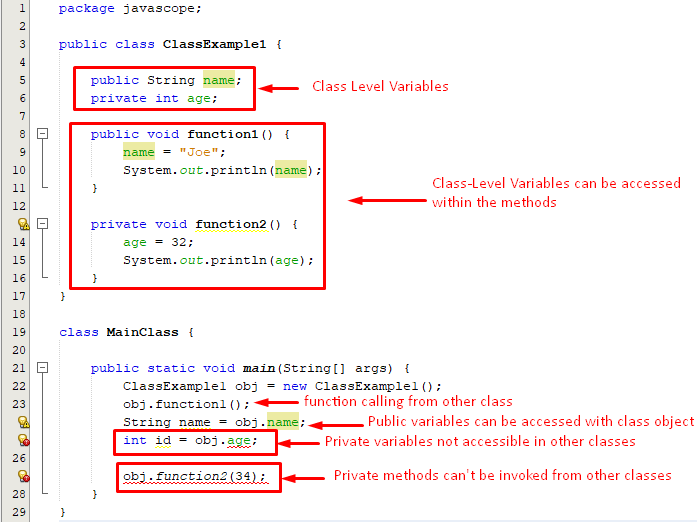
For the profound understanding of the concepts consider the below code snippet:
class ClassExample1{
public String var1;
private int var2;
public void function1(String var1, int var2) {
// var1, var2 can be accessed here
System.out.println("function1");
}
private void function2(int var3) {
// var1, var2 can be accessed here
System.out.println("function2");
}
}
public class MainClass{
public static void main(String[]args) {
ClassExample1 obj = new ClassExample1();
// public variables can be accessed in this class
// public methods/functions can be called from here
function1("Scope", 5);
String name = obj.var1;
// private variables can be accessed in this class
int id= obj.var2; //Throws an error, can't access private variables of other class here
// private methods/functions can't be called from here
obj.function2(4);
}
}
The complete code snippet will look like this:
From the above snippet we have seen that the public variables and methods can be accessed and called in other classes as well using the class’ object. However, we can’t access the private variables of one class to other class even with the help of a class object.
Method-level Scope in Java
The variable declare/created within the method will be accessible anywhere in that method after its declaration, however, it wouldn’t be accessible before its declaration. Moreover, accessing the variable of one method within the other method is not possible and if we talk about methods specifically, we can call one method within other methods as well.
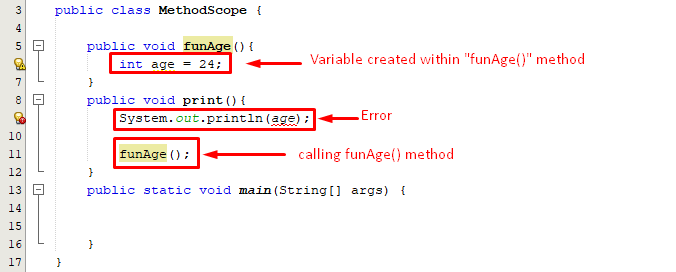
The below snippet will provide a better understanding of method scope in Java:
Example
Let’s consider the below screenshot for a profound understanding of method-level scope:
From the above snippet it is clear that we can’t access the variable of one method within other methods however, we can call a method from other methods.
Block-level Scope in Java
Everything that comes within the curly brackets {} is referred as block scope and the variables created within the block of code will be accessible by the code that comes between the curly braces. The variables declared within the block scope wouldn’t be accessible outside of the block scope.
Example
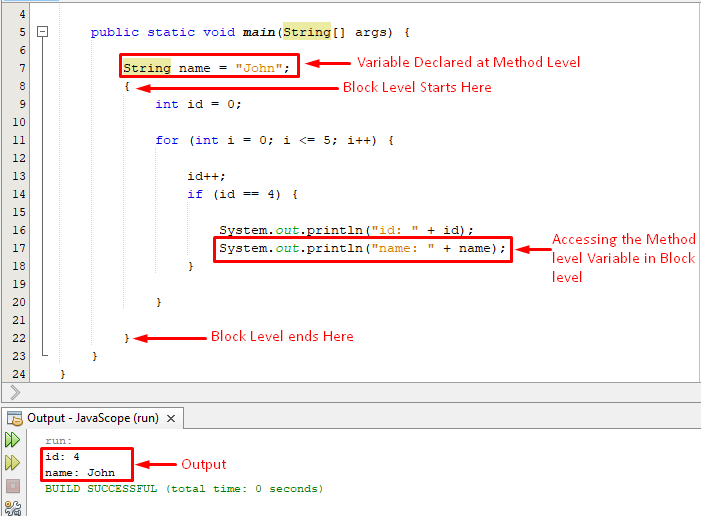
In this example we create two variables having the method-level scope and initialize them some values:
We utilize the for loop which will iterate five times and prints the name when “id = 4”. The below-snippet will provide a complete understanding of the scope and displays the output as well:
The snippet verifies that it successfully accesses both the variables i.e. name, id.
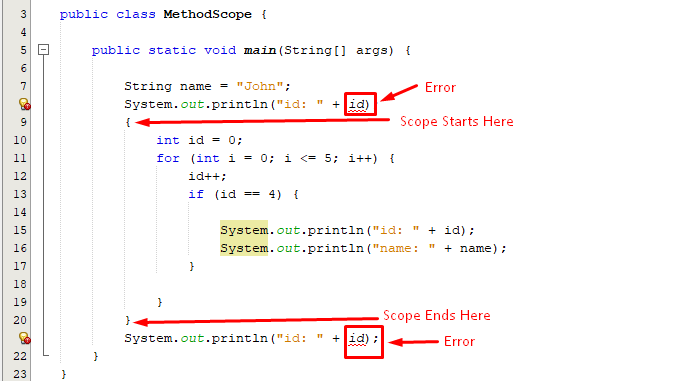
The variables created at block level wouldn’t be accessible before the start or after the end of block-level scope as shown in the below-given screenshot:
The above snippet verifies that an error occurs when we try to access the variable of block-level outside the block scope.
Conclusion
A variable declared within the method scope will be accessible only inside the method and a variable declared within the block scope will be accessible within the block scope. We can’t access a variable before its declaration and accessing the variables outside of the scope will result in an error. This write-up presents a comprehensive guide for the scope of variables and methods in Java.