Java provides a concept of methods that assist us in time management by means of code reusability. If we talk about the user-defined methods, we have to create/write them once and can utilize them again and again. In java, a method is nothing but a set of instructions that comes into action only when someone calls it.
In this write-up, we are going to explore the following essential concepts of user-defined java methods:
So, let’s start!
What is a Method in Java
A method also known as a function is a block of code/instruction which may or may not take the input data as parameters/arguments and returns some output. The specified block of code will execute only when someone calls/invokes it. In java, a method must be created/declared inside the class.
Syntax of Java Method
Following will be the syntax of declaring a method:
statement(s);
}
Here, in the above code snippet, public is an access modifier/ access specifier, static is a keyword, void is a return type, and firstFunction() is the name of the user-defined method.
Java offers several access modifiers such as default, private, public, and protected. These modifiers specify the access type of a function as listed below:
- The public access modifier determines that the function is accessible to all classes/subclasses.
- The protected access modifier stipulates that the method is accessible only within the specific package.
- The private access modifier determines that the function is accessible to only those classes where it is specified
- The default access modifier determines that the function is accessible to the classes of the same package.
Java has a wide range of keywords that have some special meanings and are used for some specific purposes for example the static keyword defines that the function can access the static data.
Return type determines the type of data that will be returned by the function; for example, void is used when no data type is returned.
How to Create a Method in Java
In Java, a method can be created by specifying its name, and we have to follow the camelcase naming convention.
For a profound understanding, let’s consider an example that will let you understand how to create a user-defined java method:
Example
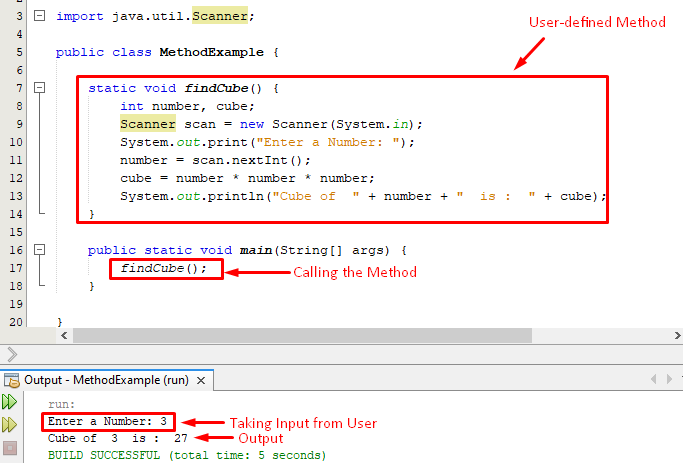
In this example, we are going to calculate the cube of the user-entered number.
We have a class “MethodExample”, and within the class we created a method findCube(). Next, we utilized the built-in Scanner class to get the user’s input. Afterward, we have a variable “cube” which will store the cube of the number.
How to Call a Method in Java
Once the method creation is done, we can call it with its method name followed by () as we did in the following snippet:
For better understanding, let’s consider the complete code-snippet and its output:
Use of the scanner class assists us to take the input from the user and when we run the code the user enters a number “3” and consequently, we get the cube of that number i.e. “27”. It shows the appropriateness of the user-defined method.
Conclusion
A method also known as a function is a block of code/instruction which may or may not take the input data as parameters/arguments and returns some output. Moreover, the specified block of code will execute only when someone calls/invokes it. In java, a method can be created by specifying the access modifier, its return type followed by the user-defined method name. And to call a method, we need to specify the method name followed by small brackets(). This write-up presents a detailed overview of what is a method and how to call a method in Java and for a profound understanding, it provides an example along with a descriptive screenshot.