This write-up will explain:
- Is There a Way to Rollback/Revert the Last Push to Git?
- How to Rollback/Revert the Last Push to Git?
Is There a Way to Rollback/Revert the Last Push to Git?
Yes, there is a way to roll back to the last push to Git. Developers are permitted to perform this operation in Git.
How to Rollback/Revert the Last Push to Git?
To roll back the last push to Git, follow the below-provided instructions:
- Switch to the local repository.
- Generate a new file.
- Track the newly created file.
- Commit changes.
- Verify remote origin.
- Push changes to the remote repository.
- Rollback the last push using the “git reset –hard HEAD~1” command.
- Update remote repository.
Step 1: Move to Git Local Directory
First, write out the following command along with the repository path and switch to it:
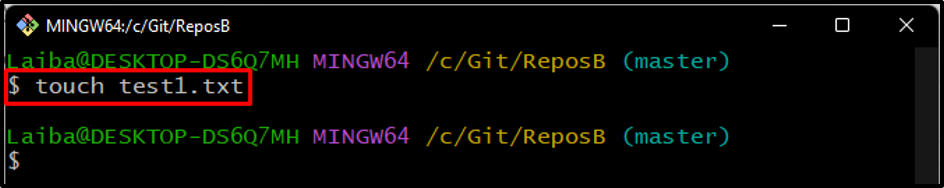
Step 2: Create a New File
Next, make a new file in the working repository using the “touch” command:
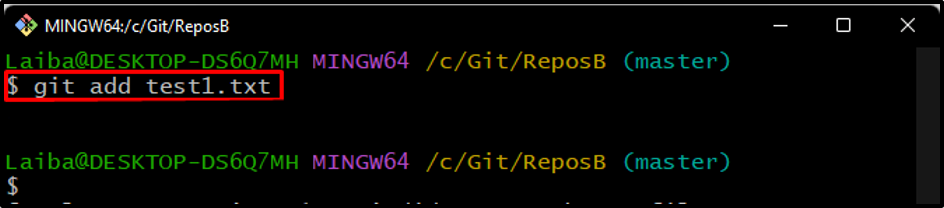
Step 3: Track New File
Then, run the “git add” command along with the newly created file name to stage this file:
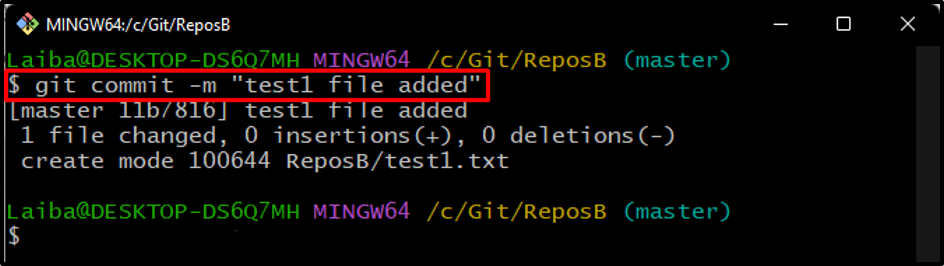
Step 4: Commit File
Commit the new file to save the added changes using the below-provided command:
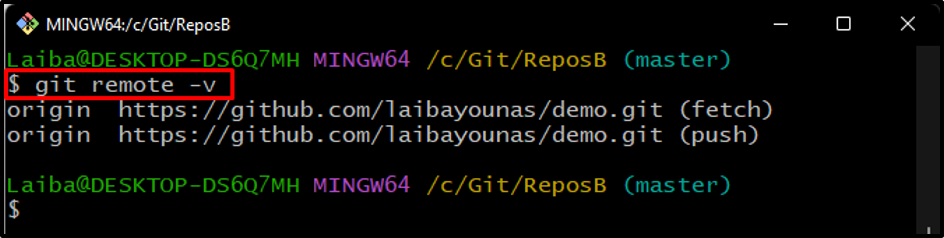
Step 5: Check Remote Origin
After that, verify whether the local directory is connected to the remote:
Step 6: Push Changes to Remote Repository
Then, push the local repository’s content to the remote repository:
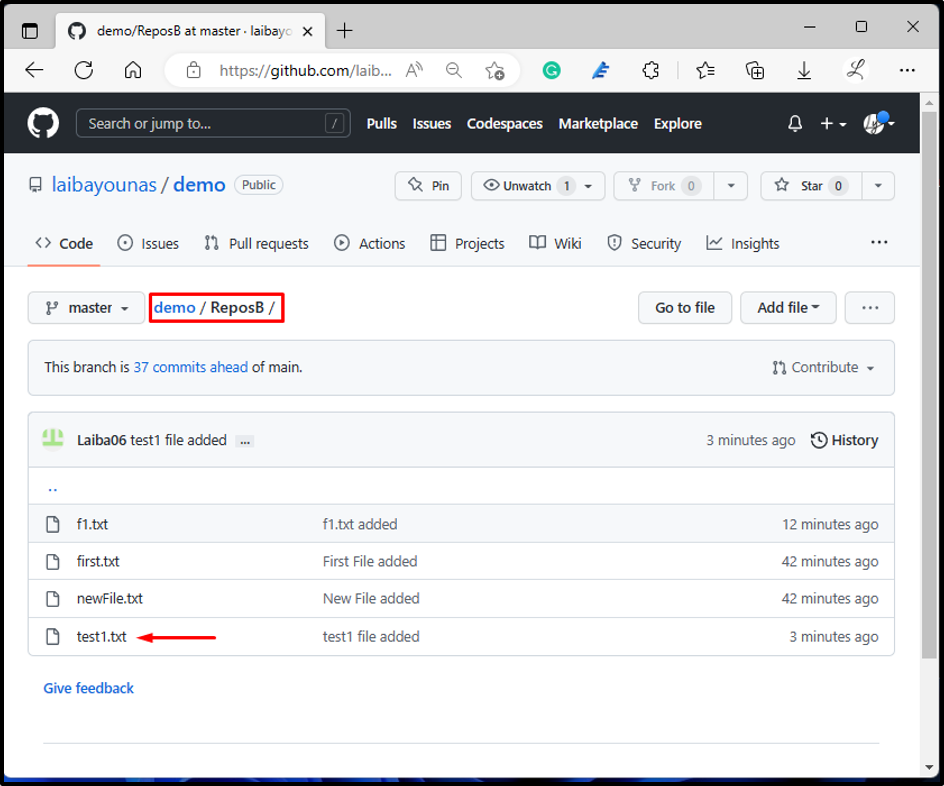
After performing the above operation, switch back to your remote repository and view the changes. For instance, it can be seen that our local repository’s file “test1.txt” has been pushed successfully:
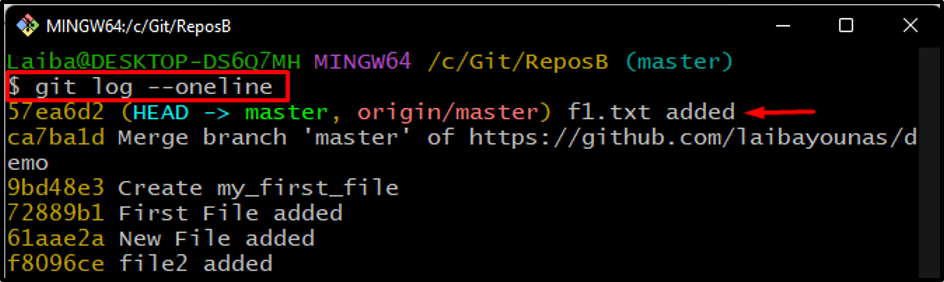
Step 7: Check Git Log
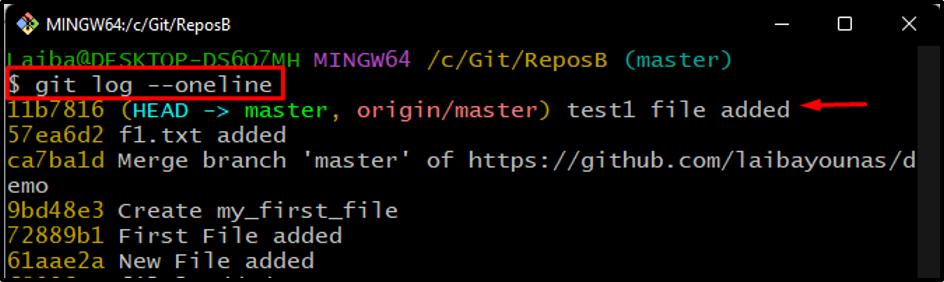
Next, display the commit history to check the current position of HEAD:
It can be observed that the HEAD is pointing to the most recent committed file:
Step 8: Rollback to Last Push
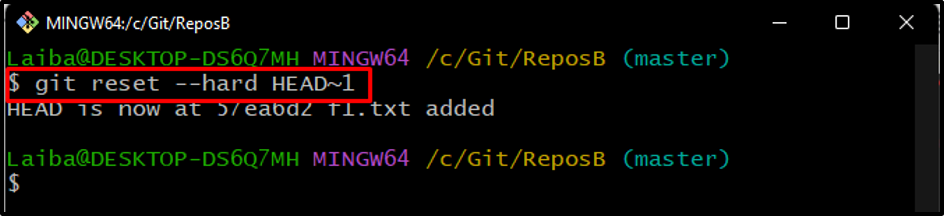
Now, execute the “git reset” command with the “–hard” option and specify the HEAD to rollback the last push:
Here, the “–hard” option is used to reset the position of HEAD, and the “HEAD~1” is used to move the HEAD pointer to the most recent commit:
Step 9: Update Remote Repository
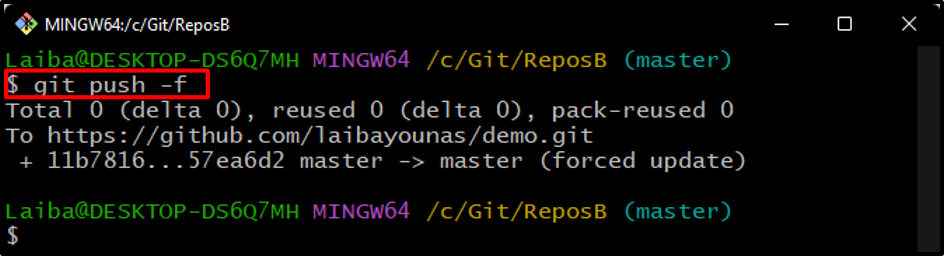
Then, again push the content of the local repository to the remote copy for updating its content:
In the above command, the “-f” option is used to push forcefully:
It can be seen that the previously pushed content has been deleted from GitHub and the remote repository is up-to-date:
Step 10: Verify Changes
Finally, verify changes by viewing the commit history:
Now, the HEAD is moved back to the previous commit:
We provided the easiest way to roll back to the last push in Git.
Conclusion
To roll back to the last push to Git, first, switch to a particular directory. Then, run the “git reset –hard HEAD~1” command to undo the most recent push. After that, update the remote repository using the “git push -f” command and verify changes. This article explained the procedure for rolling back the last push to Git.