In Git, developers deal with large software development projects. They work and make changes on local Git repositories. However, there is a chance of losing repository data. To avoid such a situation, it is important to create a backup of the repository as it is a good practice for developers to prevent data loss. Moreover, backing up a repository on a remote server allows multiple developers to collaborate on the same codebase.
This write-up will explain:
- Is “git push –mirror” Sufficient/Enough for Backing up a Repository?
- How to Backup a Repository Using the “git push –mirror” Command?
Is “git push –mirror” Sufficient/Enough for Backing up a Repository?
Yes, “git push –mirror” can be sufficient for backing up a repository. The “git push –mirror” is a Git command that pushes all the content of the local repository including files, tags, branches, commits messages, and many more to the remote repository.
How to Backup a Repository Using the “git push –mirror” Command?
To back up a particular repository, first, switch to the specific GitHub repository and copy its HTTP URL. Then, navigate to the local repository and add the remote repository as a remote in it. After that, run the “git push –mirror” command to create a backup of the local repository in the remote repository. Lastly, verify changes on the remote repository.
Step 1: Redirect to Remote Repository
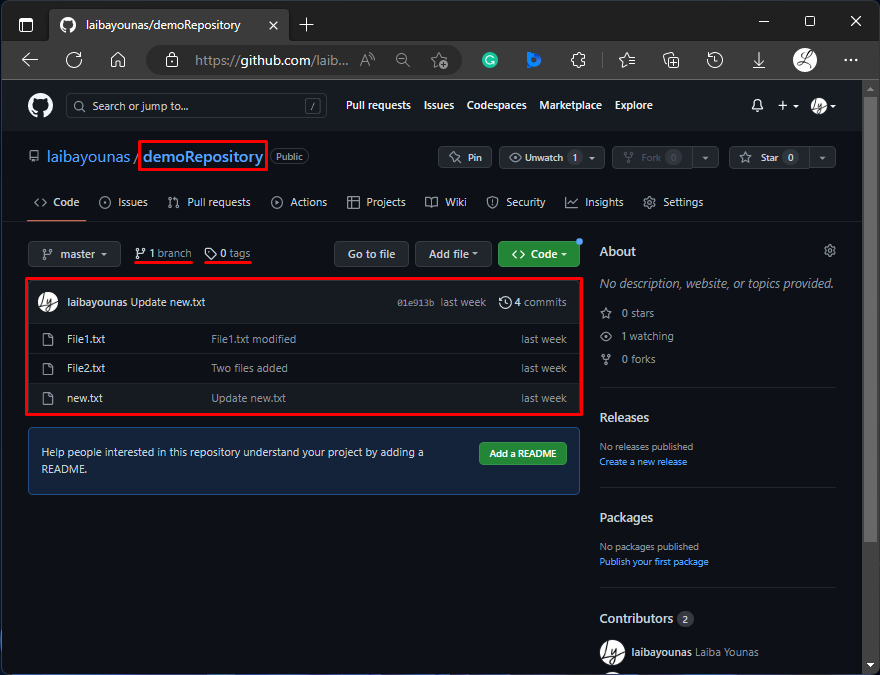
First, open GitHub and navigate to the desired remote repository:
In the above screenshot, the content, branches, and tags of the remote repository can be seen. Now, copy its HTTP URL.
Step 2: Switch to Local Repository
Then, move to the desired local repository:
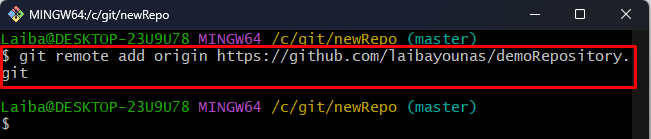
Step 3: Add Remote Origin
Next, connect the local repository with the particular remote repository using the below-provided command:
Make sure to replace “<user-name>” with your GitHub username and “<repo-name>” with the remote repository name:
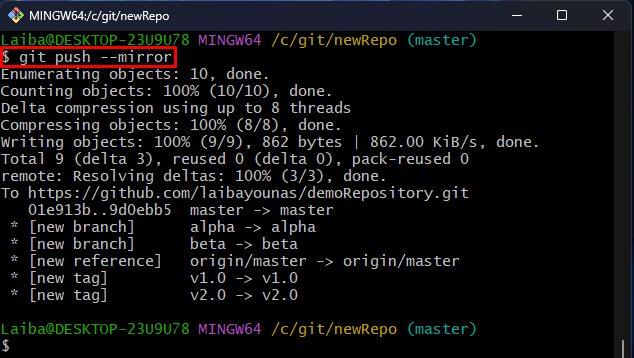
Step 4: Mirror-Push to Remote Repository
Now, write out the “git push” command along with the “mirror” option to push all the content of local repository as a mirror to the remote repository:
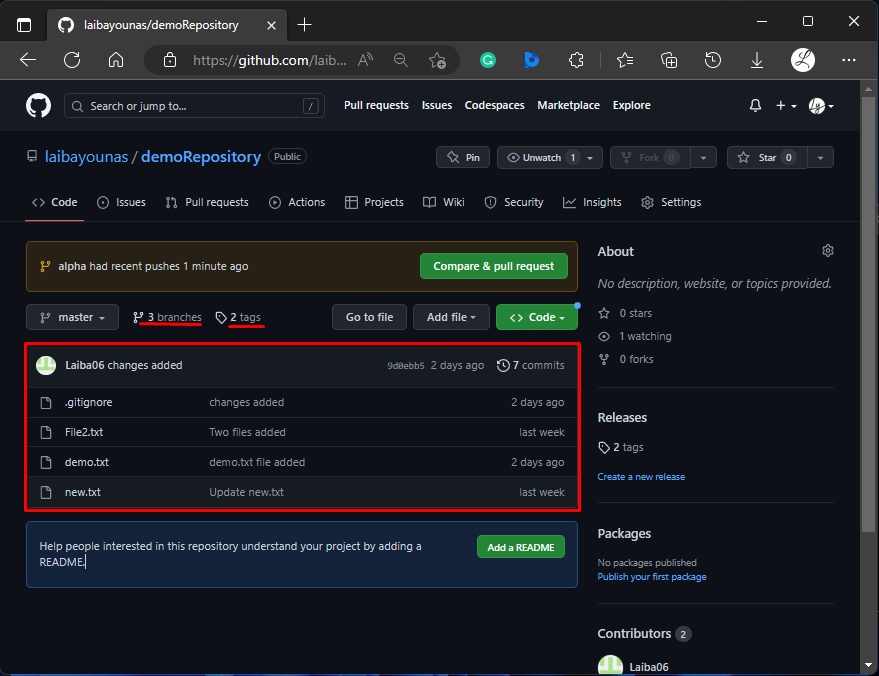
Step 5: Verify Changes on GitHub Repository
In the below screenshot, the highlighted part shows the new changes in the GitHub repository:
That was all about backing up the repository using the “git push –mirror” command.
Conclusion
“git push –mirror” is a Git command that can be sufficient for backing up a repository. It pushes all the content of the local repository including files, commits messages, tags, and branches to the GitHub repository. To create a backup of a local repository, first, link the local repository with the remote repository by adding the GitHub repository as a remote in it. Then, utilize the “git push –mirror” command and view changes on the remote Git repository. This write-up explained the method of backing up the Git repository using the “git push –mirror” command.