This blog will illustrate the implementation of the “Integer Division” in Java.
How to Perform “Integer Division” in Java?
In Java, the integer division can be carried out with the help of the “Arithmetic Operator ( / )”. This operator can return the division of the specified or the user-input integers.
Example 1: Performing Division Upon the Specified Integers
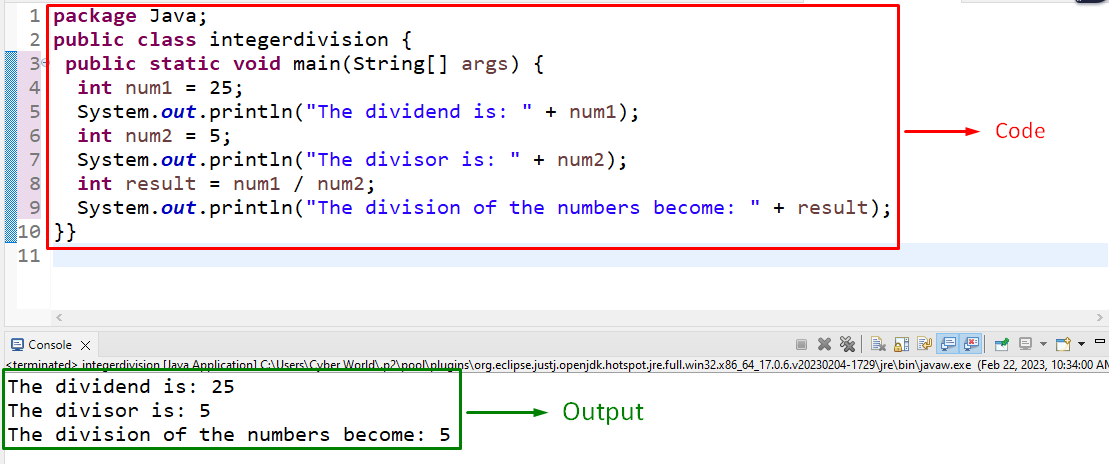
In this example, the two specified integers can be computed for division:
In the above code block, apply the following steps:
- First, initialize the first integer value, i.e., “Dividend”, and display it.
- Likewise, display the latter initialized integer, i.e., “Divisor”.
- Now, apply the “Arithmetic Operator( / )” between the dividend and divisor to compute the division and display the resultant outcome on the console.
Output
In the above output, it can be analyzed that the resultant number is displayed after division.
Example 2: Performing Division Upon the User Input Integers
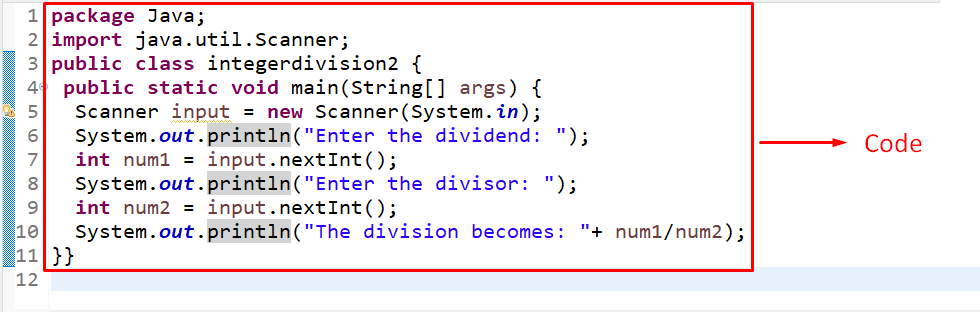
In this specific example, the user input integers can be computed for division. Before heading to the example, include the below-given library to enable user input:
Add the following code in the “main()” method:
In this code, perform the following steps:
- Create a “Scanner” object named “input” via the “new” keyword and the “Scanner()” constructor, respectively.
- Note that the “System.in” parameter refers to the user input.
- In the next step, associate the “nextInt()” method with the created object to ensure that the user input is “integer”.
- Finally, apply the “Arithmetic operator ( / )” to return the division of the user input numbers.
Output
Case 1: Remainder Equals “0”(Completely Divisible)
In this outcome, it is evident that the real-time division is returned based on the user input numbers.
Case 2: Remainder Not Equals “0”
In the case of division where the remainder is not equivalent to “0”, the final result will be rounded off to the largest divisible integer, as follows:
As observed, the largest rounded integer is returned.
Conclusion
In Java, integer division can be carried out with the help of the “Arithmetic Operator ( / )”. This is done by returning the corresponding or the largest divisible integer(in the remainder case). The division can be performed upon the specified or the user input integers. This blog discussed the implementation of the “Integer division” in Java.