This tutorial explains how to install PIP for Python 3 and Python 2 on Debian 11 and other Debian-based Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu.
PIP (Pip Installs Packages) is a Python written packages manager used to install software from repositories. If you don’t know PIP, you can think of it as a similar tool to the Debian apt command. Basically, the syntax to install packages using the PIP packages manager is pip install <package>.
This tutorial covers PIP installation, both for Python 3 and Python 2, despite Python 2 isn’t supported on default by Debian repositories. This article also explains how to get both PIP versions with just a command. Additionally, I added instructions to keep PIP up-to-date and to use it to install the software.
Installing PIP3 on Debian 11
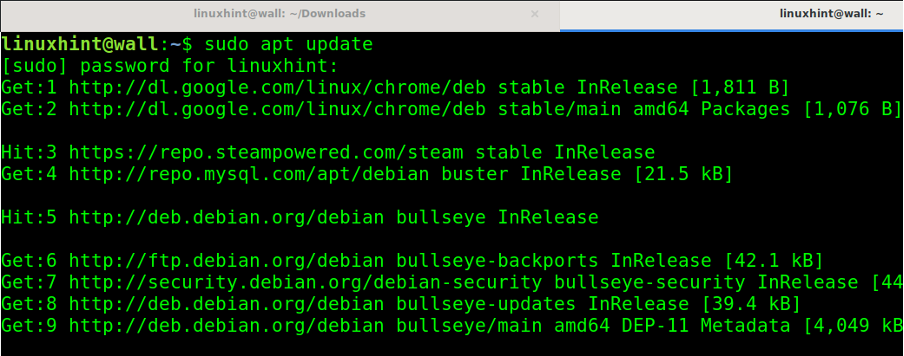
To begin, update your package repositories by running the apt command, followed by the update option as shown below:
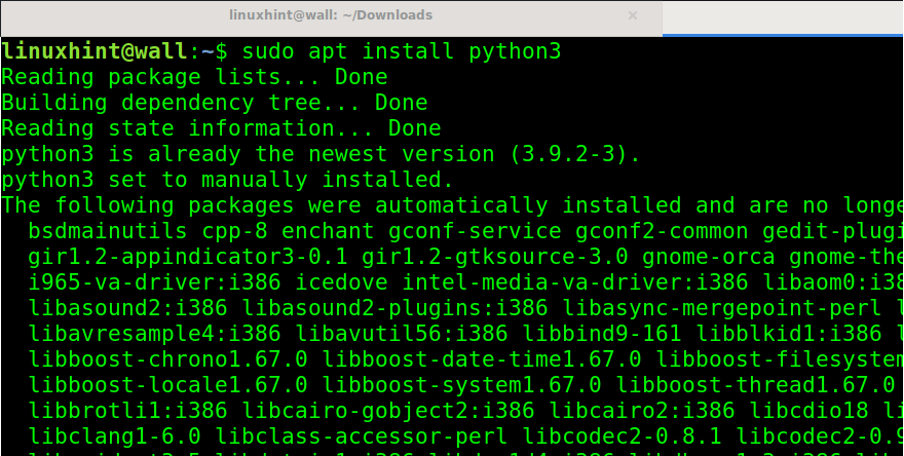
You can install Python (3) also using the apt command followed by the install option as shown below:
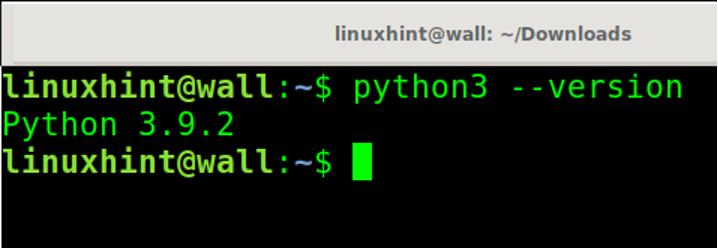
To check your Python 3 version, you can run the command below:
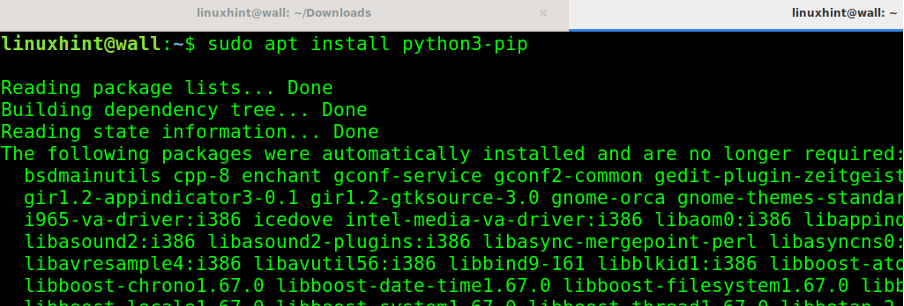
Then, install PIP3 by running the following command:
To check your PIP version, run the following command:
As you can see, PIP for Python 3 is installed.
Installing PIP2 on Debian 11
As discussed, while Python 2 is still available for Debian 11, it doesn’t support PIP2 in the packages manager. However, you can get it installed by following the steps explained below:
Use the apt command to install the python2 package as shown below:
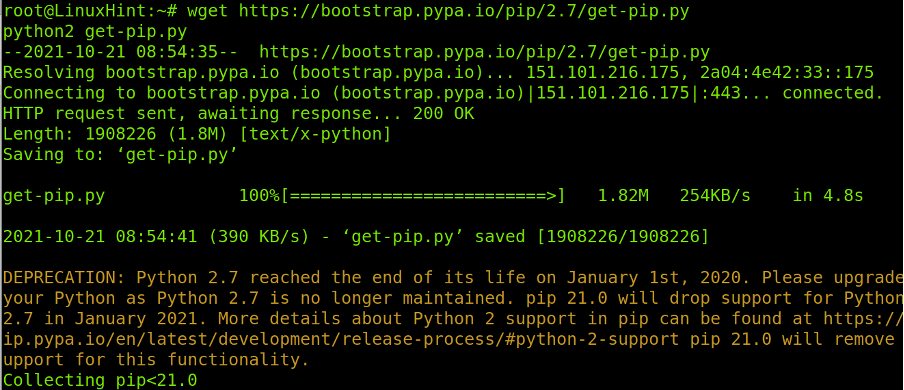
Once Python 2 is installed, download and execute the pip installer for Python 2 by running the following command:
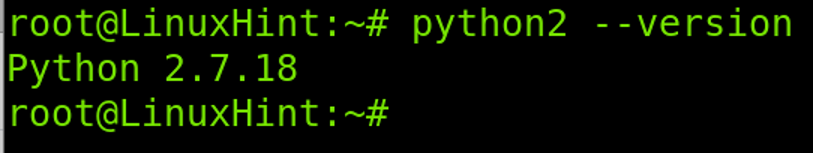
You can check your Python 2 version by executing the command below:
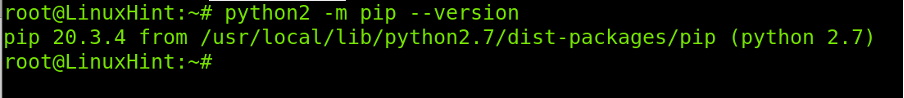
To check both Python 2 and pip versions run the following command:
As you can see, PIP for Python 2 is installed.
Keep PIP Updated
You can use the command shown in the following screenshot to keep PIP up-to-date:
Now, PIP and its components are up to date.
Using PIP to Install Software
As mentioned previously, PIP is a packages manager used to install the Python written software. The syntax to install packages is pretty simple. Just execute PIP followed by the install option and the package’s name. The syntax to install a package is the same as with the apt command.
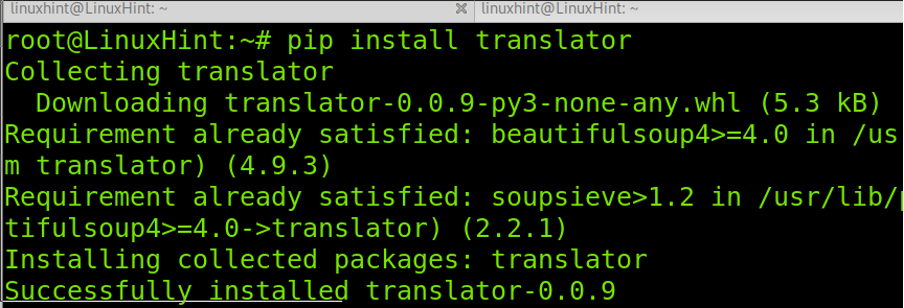
For example:
As you can see, the package was properly installed.
You can find available projects to download at https://pypi.org.
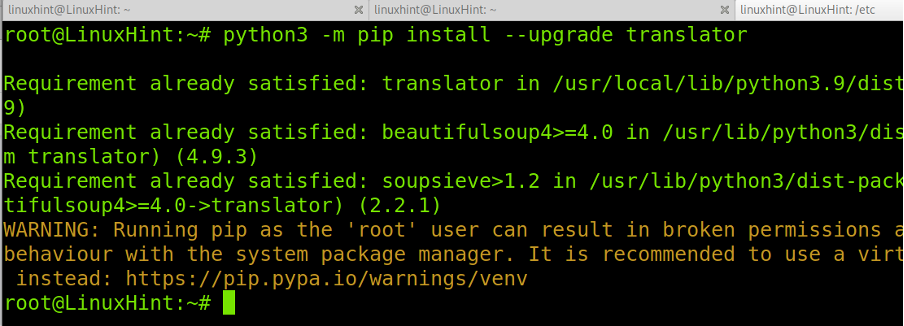
To upgrade packages using PIP, run the following command:
In this case, the software was already up-to-date.
Uninstalling Packages Using PIP
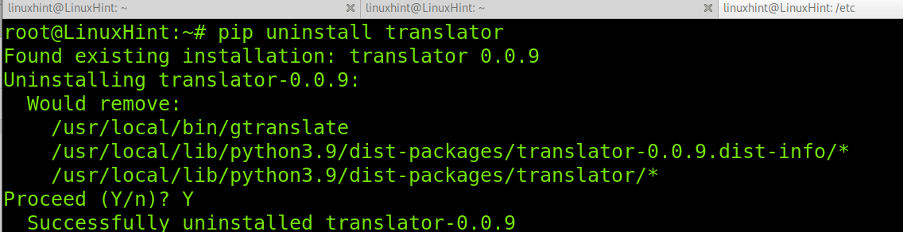
To remove packages using PIP, use the following syntax. When asked for confirmation, press Y.
To remove the translator package, run the following command. When asked for confirmation, press Y.
And as you can see in the screenshot below, the package was properly removed:
Conclusion
Thank you for reading this tutorial explaining how to install PIP on Debian 11 Bullseye. As you can see, installing both PIP for Python 3 and Python 2 is pretty easy. Any Linux-level user can get it done by following a few steps explained in this article.
Despite this tutorial showing PIP for Python 2 installation, it isn’t recommended. Instead, use Python 3. Also, remember to keep PIP and its components up-to-date using the commands explained for that purpose.
Thank you again for learning from Linux Hint. Keep following us for additional tips and tutorials.