Tail is a program in Linux which is used to read a few lines from the end of a large file. You can also use tail to follow a file. That is, if a file is followed, the last few lines are shown in the terminal, and if any changes to the file occurs, that is shown in the terminal instantly. It is used to monitor log files.
Multi-tail is a similar program to Tail. The only difference is that with Multi-tail, you can read multiple files (usually log files) at once. It also displays every opened file in a single terminal window nicely. You can also follow multiple files for changes at once. With Multi-tail you can open different file with different colors. It is a very useful tool for Linux System Administrators.
In this article, I will show you how to install and use Multi-tail on Ubuntu 17.10 Artful Aardvark. Let’s get started.
Installing Multi-tail
Multi-tail is available in the official package repository of Ubuntu 17.10 Artful Aardvark.
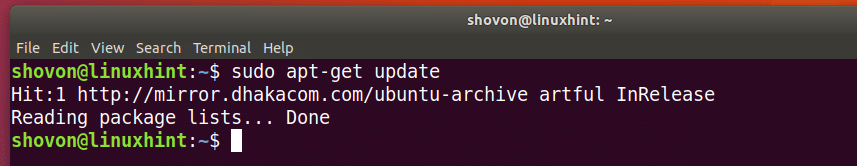
First update the package repository cache of your Ubuntu operating system with the following command:
The package repository cache should be updated.
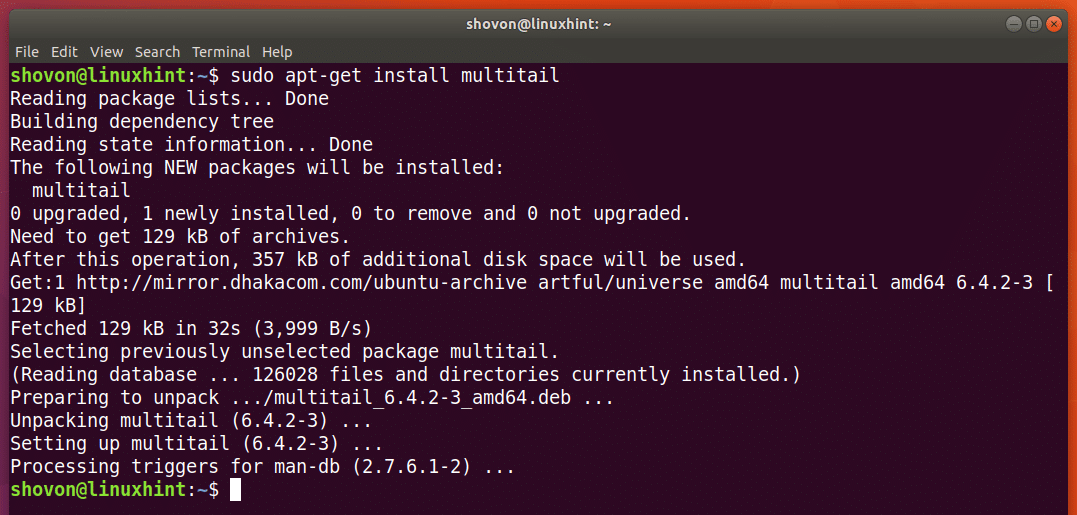
To install Multi-tail, run the following command:
Multi-tail should be installed.
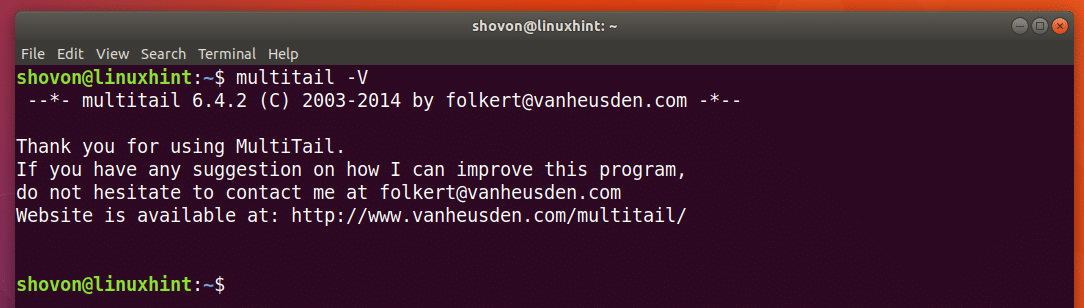
Now run the following command to check whether Multi-tail is working.
As you can see from the screenshot below, the version of Multi-tail installed is 6.4.2
View Single Log File with Multi-tail
Though Multi-tail is used to view multiple log files in a single terminal window, you can also use it to view a single log file.
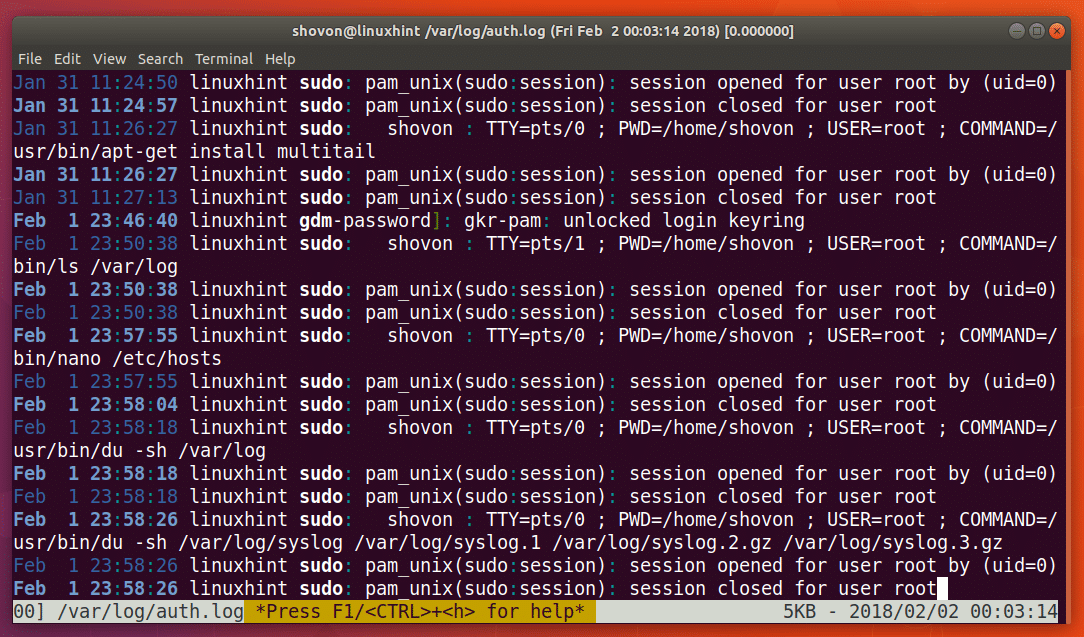
Run the following command to open a log file /var/log/auth.log:
As you can see from the screenshot below, a single log file /var/log/auth.log is opened with Multi-tail. The view is updated as the file changes as well.
You can exit Multi-tail by pressing ‘q’
View Multiple Log Files with Multi-tail
You can view multiple log files in a single terminal window. The files should be placed vertically by default.
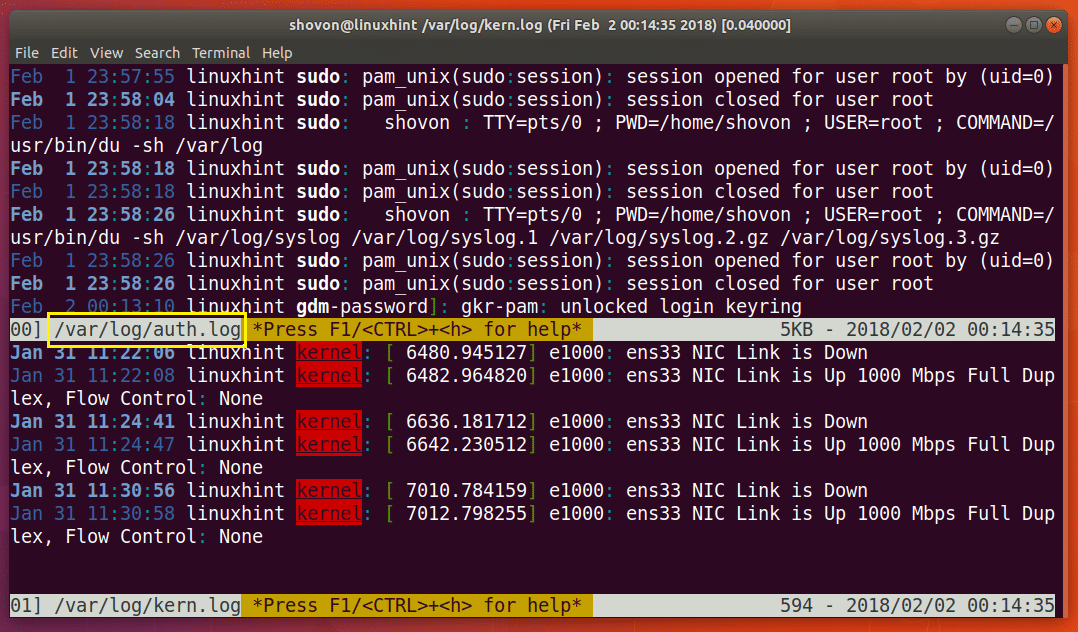
Run the following command to view /var/log/auth.log and /var/log/kern.log vertically:
The two files /var/log/auth.log and /var/log/kern.log should be opened vertically as shown in the screenshot below.
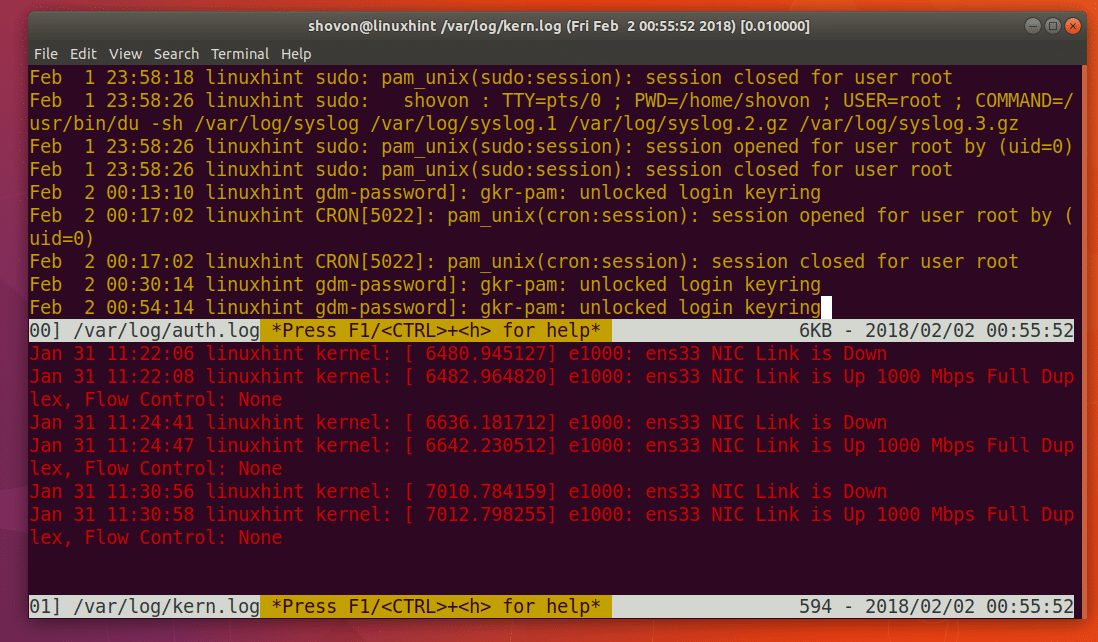
You can see from the screenshot below that the /var/log/auth.log file is opened in the top half and /var/log/kern.log file is opened in the bottom half.
You can also place the files /var/log/auth.log and /var/log/kern.log horizontally with the following command.
Note that, the value of -s argument is 2 because I am opening 2 files in this example. If you want to open 3 files, then the value of -s should be 3.
For example, the command above should be:
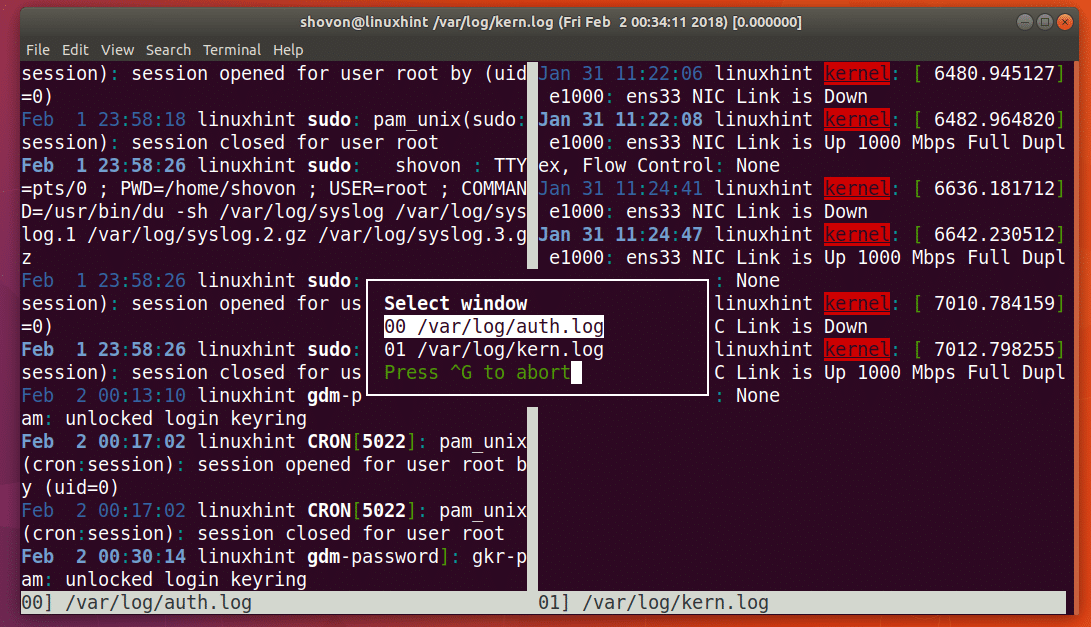
As you can see from the screenshot below, the file /var/log/auth.log is opened in the left side and the file /var/log/kern.log is opened in the right side of the terminal.
You can press ‘b’ to open a list of the opened files as shown in the screenshot below. I have 2 files opened, the first one /var/log/auth.log is numbered 00 and the second one /var/log/kern.log is numbered 01. If you don’t want to select any file, just press <Ctrl> and <g> to cancel the selection menu.
You can press <Up> and <Down> arrow keys to move the selector and press <Enter> to select the file you want.
As you can see from the screenshot below, I selected the first file /var/log/auth.log and it’s displayed in a separate section. Now you can press <Up> and <Down> arrow keys to navigate the file.
Once you’re done reading this file, you can press ‘q’ to go back to the main window of Multi-tail.
View Multiple Files with Different Colors
You can also set different color for different opened files with Multi-tail. For example, you can open /var/log/auth.log in yellow color and /var/log/kern.log in red color with the following command.
As you can see from the screenshot below that Multi-tail opened /var/log/auth.log in yellow color and /var/log/kern.log in red color.
That’s how you install and use Multi-tail on Ubuntu 17.10 Artful Aardvark. Thanks for reading this article.