GDebi is a package installer to install Debian executable packages on Debian-based distribution of Linux. It is foreseen that while installing the Debian packages on Ubuntu, a dependency error comes; that won’t allow you to install the package; the GDebi package installer will resolve the dependency issue. Ubuntu uses the default software installer to install .deb packages; GDebi can also be used because it is more efficient and quicker as compared to the default Ubuntu installer. Ubuntu is well known for its resource consumption; that’s why it would be a good option to use GDebi as a default installer for .deb packages: inspired by this; we have compiled a detailed guide on installation and use of GDebi package installer:
How to install GDebi package installer in Ubuntu
You can install the GDebi on Ubuntu by two ways:
- Using terminal
- Using Ubuntu Software Center
How to install GDebi using terminal in Ubuntu
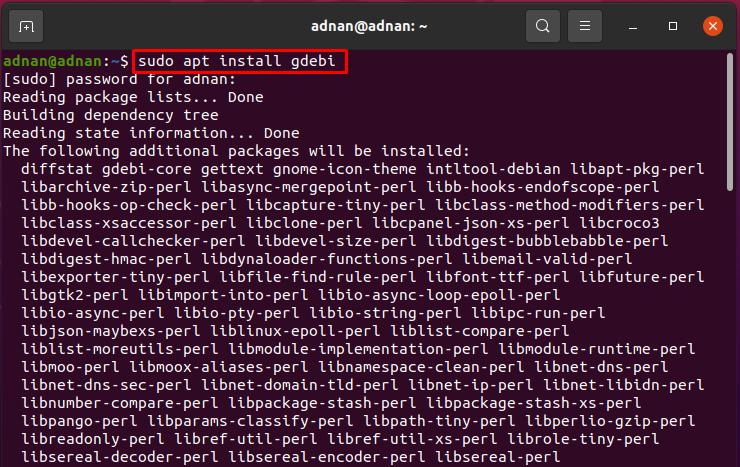
Open your Ubuntu command terminal using shortcut “Ctrl+Alt+T”; use the command given below to install the GDebi package:
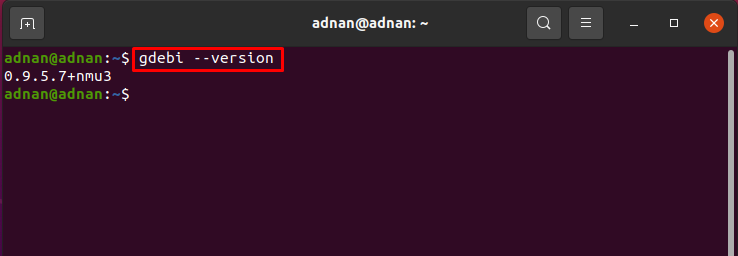
Once it is installed; you can verify the installation by checking the version of the package using command given below:
How to install GDebi installer using Ubuntu Software Center
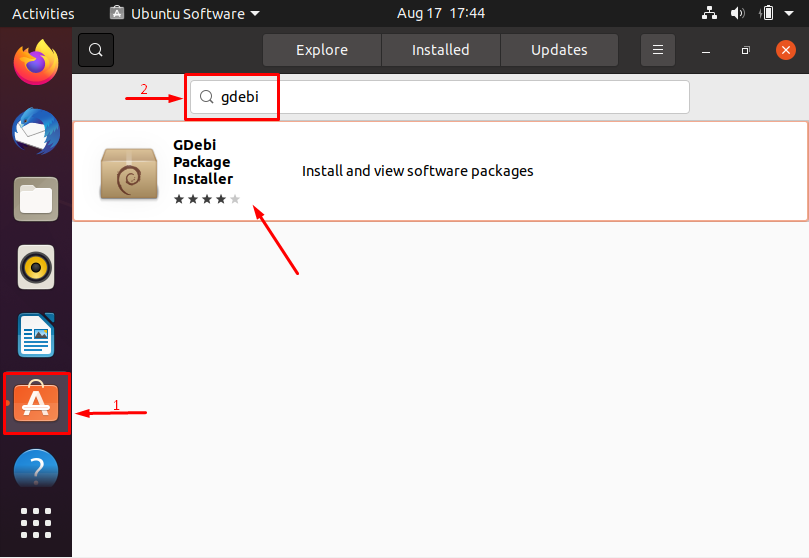
Open the Ubuntu Software Center app; and search for “gdebi”; you will see the required result in few moments:
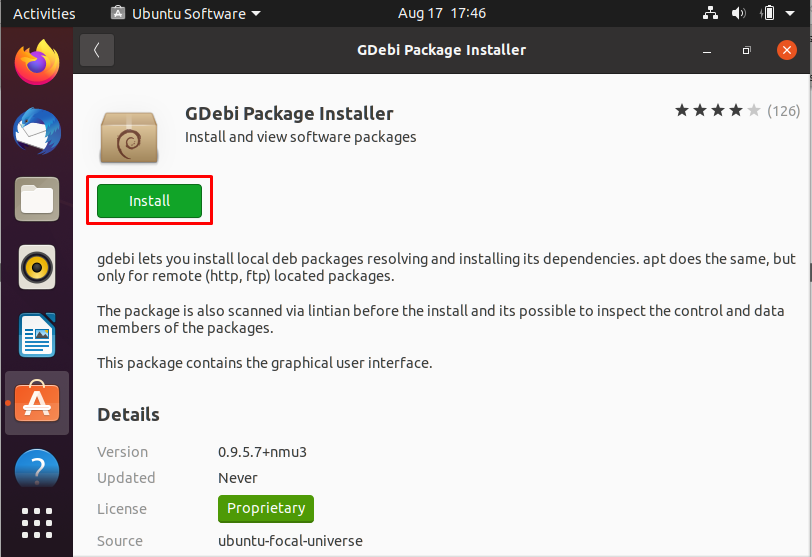
Click on the package installer; the next window contains the green “Install” button; click on that button to start the installation:
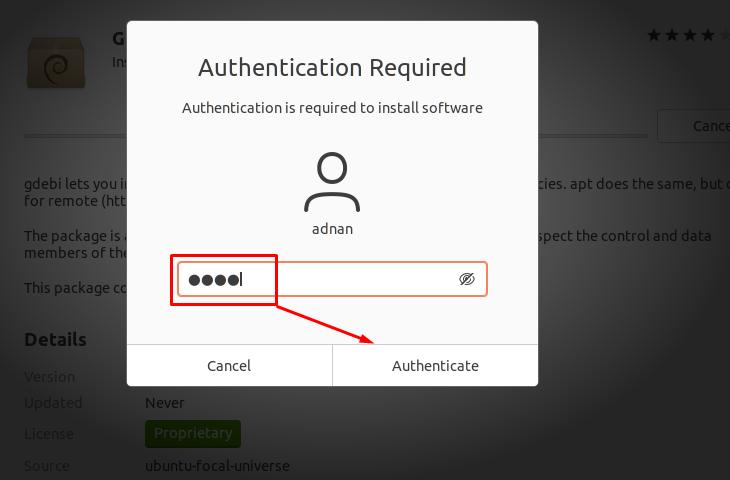
The time you click on “Install”; it confirms your decision by asking for Ubuntu user password as shown below:
Enter the password and click on “Authenticate” to move forward:
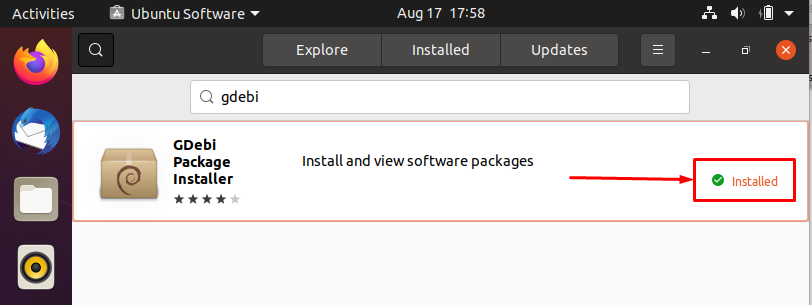
After Authentication; installation will take few minutes to complete; once the installation is finished you can observe that the status of GDebi package is changed to “Installed”:
How to use GDebi package installer in Ubuntu
Once the package manager is installed successfully, you can use it in multiple ways to install Debian files on your Ubuntu: this section contains the following ways to use the GDebi package manager:
Method 1: Using package manager app to install program
Method 2: Directly open the Debian file using “GDebi” package manager
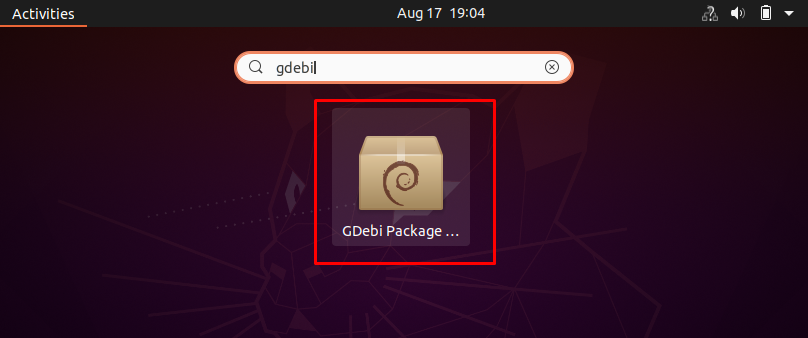
Method 1: Locate the GDebi in your applications; and click on it to open:
Once it is opened, move to the directory where .deb file is saved and click on it to open the file:
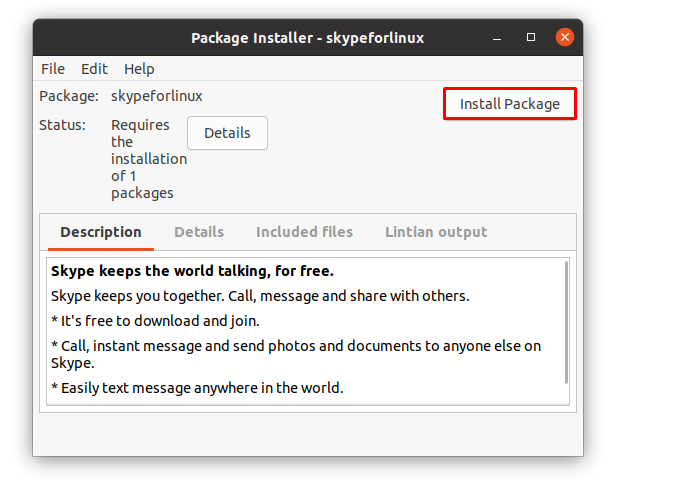
You will notice that the files of the .deb files will be loaded, and you can click on “Install Package” to start the installation using GDebi manager.
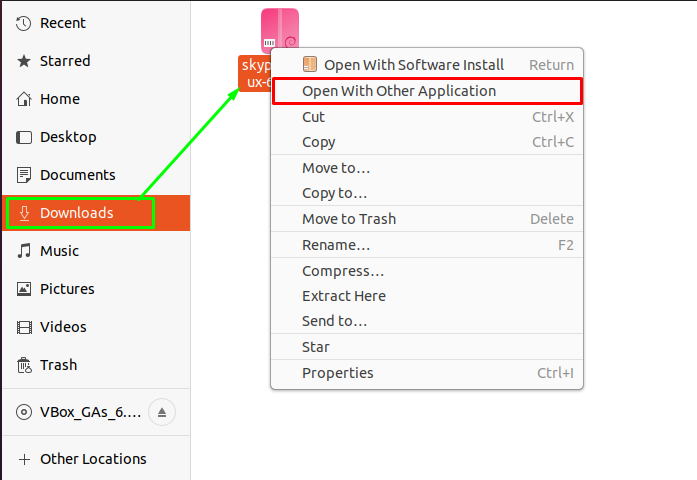
Method 2: This method refers to opening the installation file in GDebi manager. For that purpose, and select “Open With Other Application” to navigate to the list of available package managers:
After clicking that, you will see the possible installing managers, choose “GDebi Package Installer” and click on “Select” to continue:
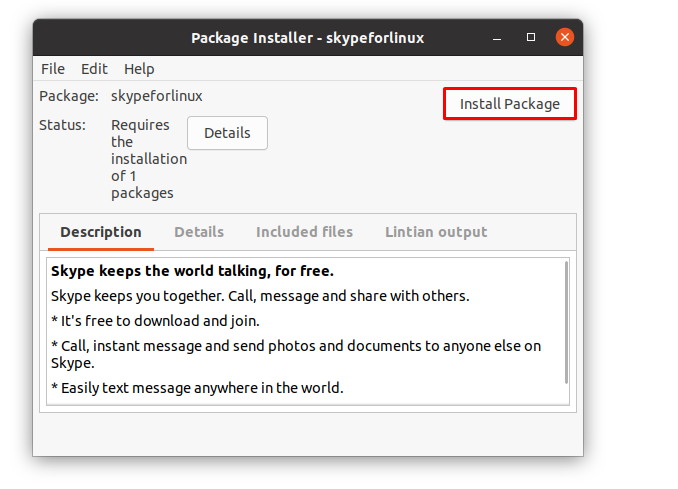
The time you click on “Select”, the installer will load the files and you can click on “Install Package” to start the installation:
How to make GDebi a default installer for .deb files
There is another interesting way to avoid long steps for installation as above; you can set the “GDebi Installer” as a default install manager for .deb files. To do this, right click on any of the .deb files and click on the properties:
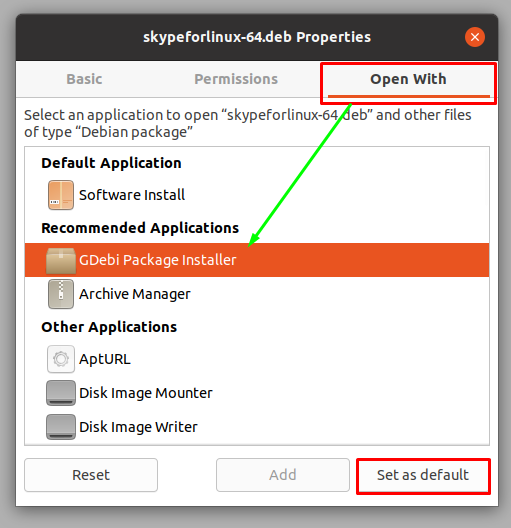
The properties options contain three tabs, you have to click on the “Open With” tab. This tab contains the available applications that can be used to install .deb files.
Choose “GDebi Package Installer” and click on “Set as default” to set it as default installer for .deb files. Now whenever you double click on .deb files, it will open with “GDebi manager”.
How to remove GDebi package installer in Ubuntu
You can remove the installed version of GDebi by two means:
Remove GDebi using terminal in Ubuntu : Open the terminal and execute the following command to remove the package:
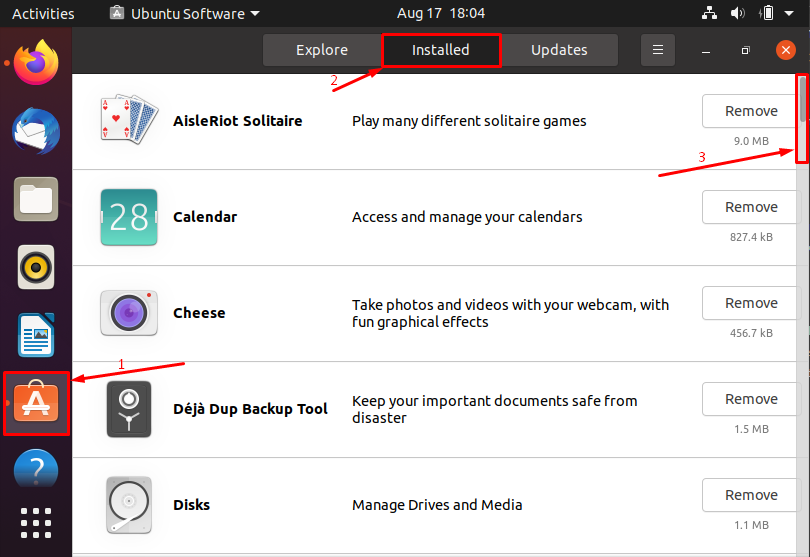
Remove GDebi using “Ubuntu Software” center in Ubuntu : Open the “Ubuntu Software”; click on the “Installed” tab available at the top of the application; you will see a list of all installed packages:
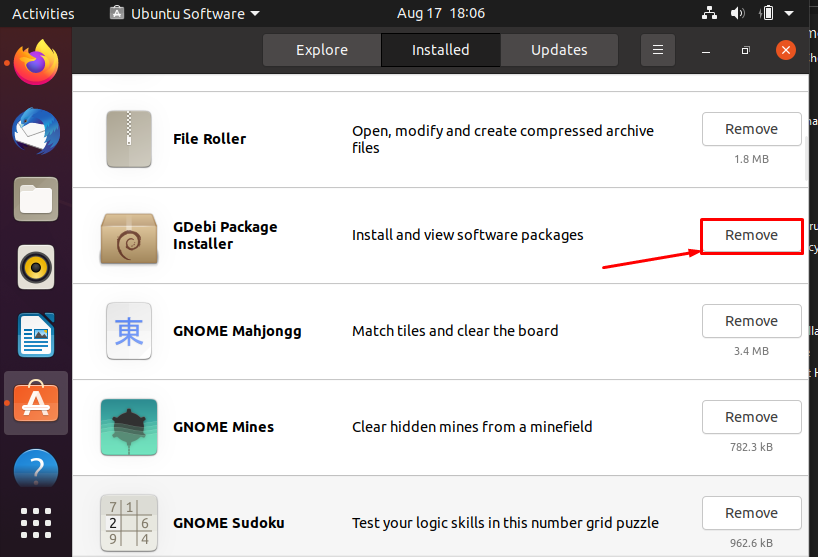
Scroll down on the window to locate “GDebi”; Once it is found; click on “Remove”:
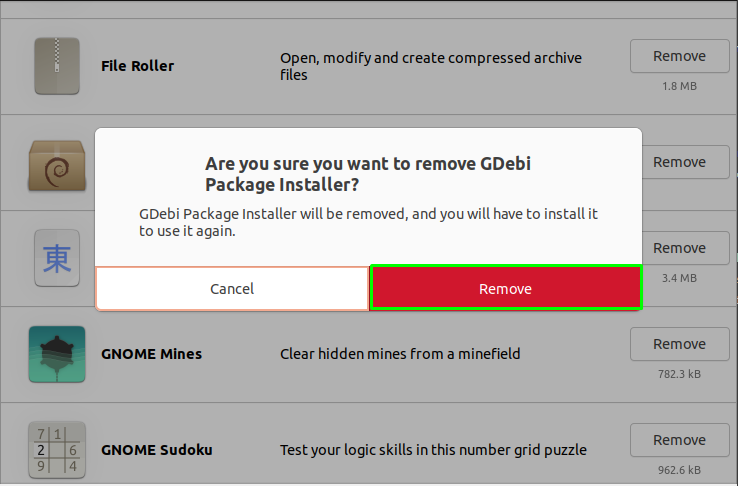
By clicking “Remove”; a prompt window will ask you for confirmation; click on “Remove”:
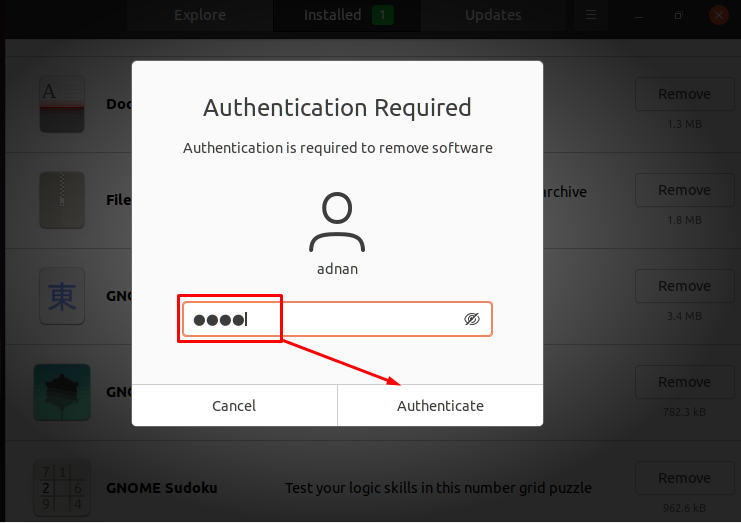
Lastly, you must put your user password and click on “Authenticate” to continue:
Conclusion
While using Debian-based distributions of Linux; you may encounter dependency issues when installing .deb executable files. One of the major reasons for acting up Ubuntu OS is the default installer as it is resource consuming, and because of this performance issue old computers may lag down. Alternate to this, we have provided the installation and usage guide of GDebi package installer. This installer helps you to install .deb files and its efficacy is better than Ubuntu’s default installer. Moreover, you can make GDebi as your default installer for .deb files.