This write-up will demonstrate the usage of the “implements” keyword in Java.
What is “implements” in Java?
The term “implements” corresponds to a keyword utilized to integrate the related methods by implementing the interface. These methods can be “abstract” or “default” and the interface can be implemented in the same or different file.
Syntax
void temp1();
default void temp2() {
//body
}
}
class abc implements InterfaceName {
//class body
}
In this syntax:
- “temp1” is an abstract method.
- “temp2” is the default method.
- “class abc” refers to the class that implements the “InterfaceName” interface via the “implements” keyword.
Example 1: Implementing a Default Method From an Interface in Java
In this example, an interface can be implemented from an external file using the “implements” keyword, and the default method of the interface can be imported and executed from this file via the class object.
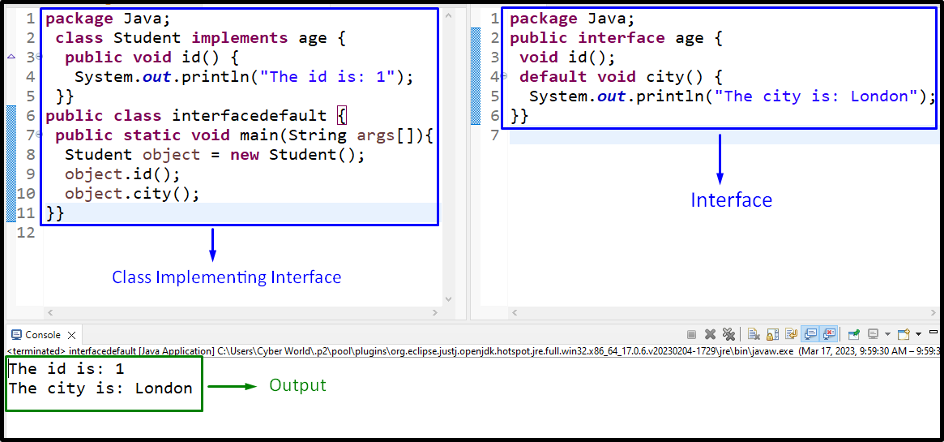
Interface Code
Go through the following code snippet:
void id();
default void city() {
System.out.println("The city is: London");
}}
In the interface file, apply the following steps:
- First, create an interface named “age”.
- Within this interface, first, specify the abstract method, i.e., “id()”.
- Note: The abstract method does not have a body.
- Now, define the default method named “city()” displaying the stated message.
Class Code
Now, follow the below-provided code:
According to the above class code, apply the below-provided steps:
- Define the class “Student” implementing the discussed interface, i.e., “age” using the “implements” keyword.
- In the class, define the method “id()” specified in the interface.
- In the “main()” method, create an object of the class named “object” using the “new” keyword and the “Student()” constructor, respectively.
- After that, invoke the abstract and default interface methods by referring to the created class object, respectively.
Output
In this output, it can be observed that the defined default method from the interface is implemented appropriately.
Example 2: Implementing Abstract Methods From an Interface in Java
In this particular example, the abstract methods, i.e., “comprising no body” in the interface can be implemented in the class.
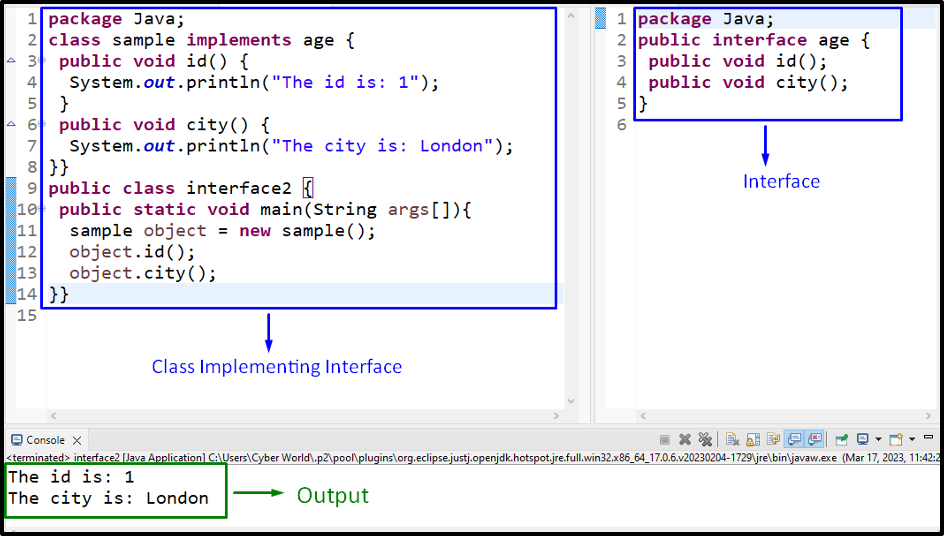
Interface Code
Consider the below-given interface code:
public void id();
public void city();
}
In this code, simply include the provided methods, i.e., “abstract” comprising no “body”.
Class Code
Let’s overview the below-provided lines of class code:
According to this code block, apply the following steps:
- First of all, declare the class “sample” implementing the allocated interface with the help of the “implements” keyword.
- Define the methods “id()” and “city()” having the stated messages, respectively.
- In the “main()” method, create a class object with the help of the “new” keyword and the “sample()” constructor, respectively.
- Lastly, invoke the defined methods via the created object.
Output
Example 3: Implementing Multiple Interfaces in Java
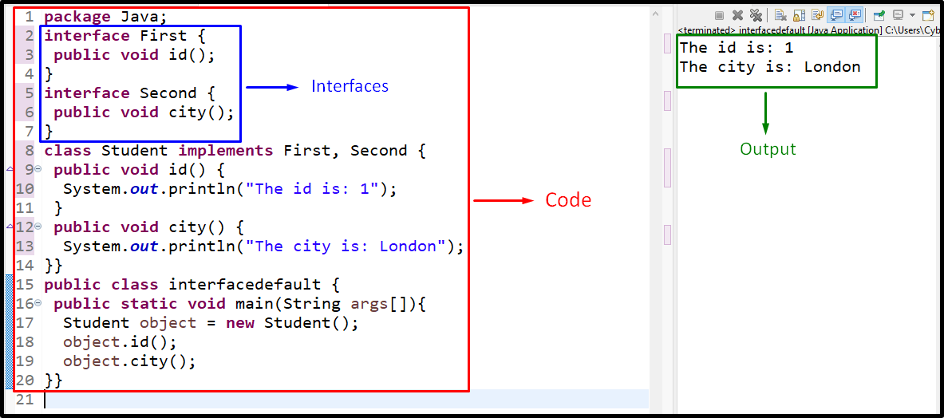
This example implements multiple interfaces via “class” by associating the methods with each of the interfaces, separately in the same file:
public void id();
}
interface Second {
public void city();
}
class Student implements First, Second {
public void id() {
System.out.println("The id is: 1");
}
public void city() {
System.out.println("The city is: London");
}}
public class interfacedefault {
public static void main(String args[]){
Student object = new Student();
object.id();
object.city();
}}
According to the above code snippet:
- Define two interfaces named “First” and “Second” accumulating the stated abstract methods, respectively.
- Now, declare a class named “Student” and implement the defined interfaces via the “implements” keyword.
- In the class definition, define the specified abstract methods previously(in the interface).
- Finally, in the “main()” method, create a class object via the discussed approach and invoke the defined methods.
Output
The above outcome indicates that the abstract methods in the interfaces are implemented successfully.
Conclusion
The term “implements” in Java corresponds to a keyword utilized to integrate the methods by implementing the interface. These methods can be “abstract” or “default”. The former method is just specified in the interface while the latter method is defined and invoked from the interface. This article guided to apply the “implements” keyword in Java.