This guide will explain in-depth information on how to use the “TIME_FORMAT()” function in MySQL.
How to Use the TIME_FORMAT() Function in MySQL?
In MySQL, the “TIME_FORMAT()” is utilized to format the given time value. The syntax of the “TIME_FORMAT()” function is given below:
In the above syntax, two arguments are given to “TIME_FORMAT()”: the first is “time_value” which is the date-time value, and the second argument is “format,” which specifies the desired date-time format. The date-time format may include multiple values or any kind of format from the given below format specifier:
- %H: Hour in 24-hour format (00-23)
- %h: Hour in 12-hour format (01-12)
- %i: Minutes (00-59)
- %s: Seconds (00-59)
- %p: AM or PM
These specifiers can be utilized in various formats like “%H:%i:%s”, “%h:%i %s %p” and so on. Let’s head toward the examples to understand different use cases of TIME_FORMAT() function in MySQL.
Example 1: Formatting the Static Time Value
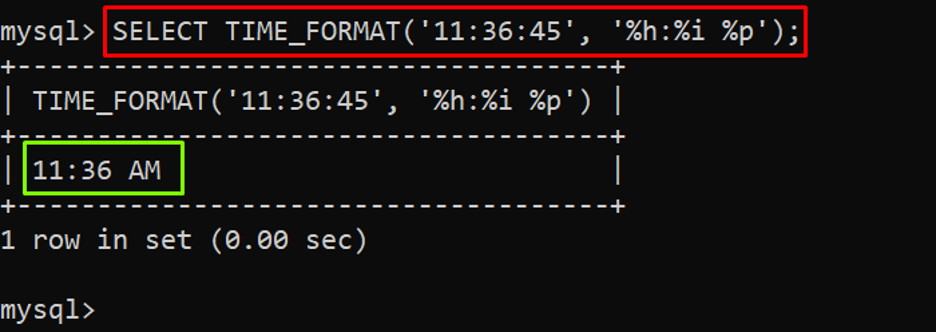
To format the static time value, use the “SELECT” statement with the “TIME_FORMAT()” function to fetch the output. Give the static time value as a first argument and a particular format as a second argument to the “TIME_FORMAT()” function as shown in the below example:
In the above example, “11:36:45” is the static time value, and “%h:%i %p” is the proper format for the given time value.
Output
The output showed that the time has been formatted in the given format “%h:%i %p” (hours:minutes PM)
Example 2: Formatting a Time Value With an Additional Symbol
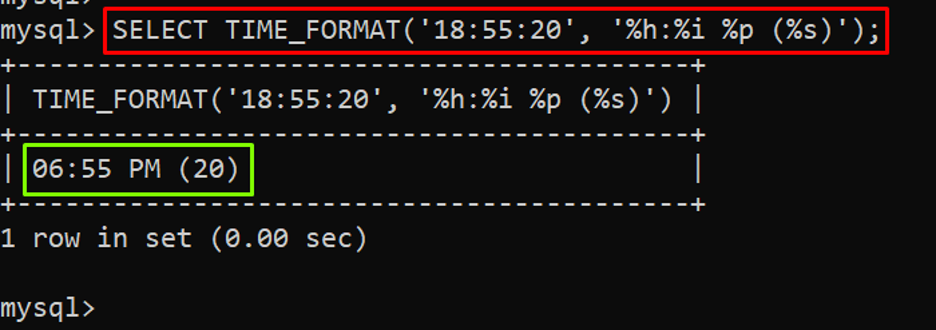
While formatting any time value you can include any symbol in the format as given below in the example:
In the above example, “18:55:20” is the time value, and the “%h:%i %p (%s)” is the format in which you can include the parentheses.
Output
The output depicts the time in the provided format and that includes seconds in the parentheses.
Example 3: Formatting the Table Data
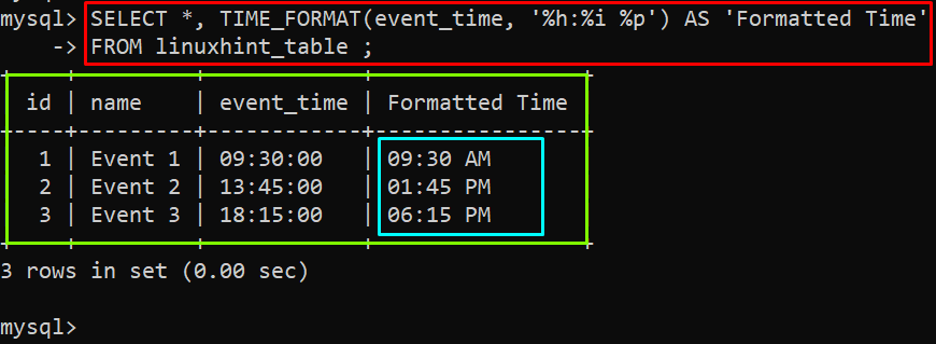
The “TIME_FORMAT()” function can be utilized to format the table’s data, by providing a particular column as a first argument to TIME_FORMAT() function. The example of formatting the “event_time” column of the “linuxhint_table” is given below:
FROM linuxhint_table ;
In the above example, the time format is “%h:%i %p”.
Output
The output showed that the “event_time” column of the “linuxhint_table” has been formatted.
Conclusion
The TIME_FORMAT() function in MySQL allows you to format date-time values according to specific formats. By specifying the time value and the desired format as arguments, you can format static time values, include additional symbols, and even format data in a table. The function provides flexibility by using format specifiers such as %H, %h, %i, %s, and %p, which represent hours, minutes, seconds, and AM/PM respectively as explained in the above guide.