The “for” loop is the basic programming feature that is utilized for executing a block of code repeatedly. In TypeScript, the for loop has the same syntax as the for loop in JavaScript, with some additional features that make it more powerful and flexible. It is used to perform a variety of tasks, such as filtering, sorting, or transforming an array, or iterating over the properties of an object.
This blog will define the way to use the “for” loop in TypeScript.
How to Use “for” Loop in TypeScript?
The “for” loop can be used to iterate over arrays, objects, and other iterable data types such as Map, Set, and so on. To use the “for” loop in TypeScript, first, initialize a counter variable, specify a condition for the loop to describe the loop iteration and termination criteria, and finally, define how the counter variable should be incremented or decremented after each iteration.
Syntax
Follow the given syntax for the “for” loop which is the same as in other programming languages such as JavaScript, Python, or C++:
// loop body
}
The above syntax consists of three parts:
- Initialization means initializing a counter variable. This part is executed only once, at the start of the loop.
- Condition is evaluated/checked at the start of every loop iteration. The loop will continue/proceed as long as the condition is true, or else the loop terminates.
- Increment/Decrement takes place at the end of every loop iteration and it typically increments or decrements the counter variable.
- The body of the loop can contain one or more statements that are executed repeatedly while the condition is true. When the given condition becomes false the loop will be terminated, and the program continues/proceeds with the next statement after the loop.
Before proceeding, keep in mind that in order to execute a TypeScript file, it must be transpile into a JavaScript file and then run the JavaScript code on the terminal using the given commands:
node filename.js
Example 1: Print Even Numbers Using “for” Loop
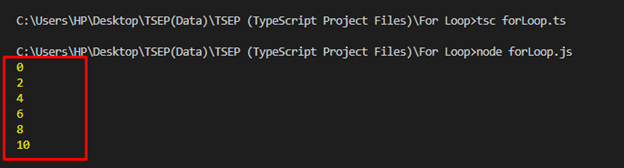
Here, we will print even numbers using the “for” loop in TypeScript. First, initialize a counter variable “i” to 0 in the loop, specify a condition for the loop to proceed as long as “i” is less than or equal to 10, and increment “i” by 1 after each iteration.
In the loop’s body, utilize the “if” statement to check if “i” is even or not using the modulus operator “%”. If “i” is even, the code block inside the if statement is executed, which prints the value of “i” to the console:
if (i % 2 === 0) {
console.log(i);
}
}
Output
Example 2: Print Array Elements Using “for” Loop
In the given example, we will print the array elements utilizing the “for” loop. First, create an array of even numbers:
Iterate the array using the “for” loop, initialize a counter variable “i” to 0, specify a condition for the loop to continue as long as “i” is less than the length of the array, and increment “i” by 1 after each iteration. In the loop body, the code block will access the current element of the array using the index “i” and display the value to the console using the “console.log()” method:
console.log(evenNumbers[i]);
}
Output
That was all about the use of for loop in TypeScript.
Conclusion
To use the “for” loop in TypeScript, first, initialize a counter variable, specify a condition for the loop to continue running, and define how the counter variable should be incremented or decremented after each iteration. It can be utilized for iterating over arrays, objects, and other iterable data types. This blog explained the way to use the “for” loop in TypeScript.