This guide will explain how to use the “DESCRIBE” and “SHOW COLUMNS” statements in MySQL.
How to Use DESCRIBE and SHOW COLUMNS Statement in MySQL?
To use the “DESCRIBE” and “SHOW COLUMNS” statements, first you just need to log in to the MySQL server. After the login, you can use the “DESCRIBE” or “SHOW COLUMNS” statements to get information about any particular table. The information will contain the following column:
- Field: Column Name
- Type: Data Type
- Null: Nullability (whether the NULL value is allowed in that column or not)
- Key: Key information (whether the column is a primary key, foreign key, or indexed)
- Default: Default value
- Extra: Extra information (such as auto-increment, unsigned, etc.)
How to Use DESCRIBE Statement in MySQL?
The “DESCRIBE” statement can be utilized with the “DESCRIBE” keyword followed by the table name, as shown in the following syntax:
The table name can be any already existing table in a particular database.
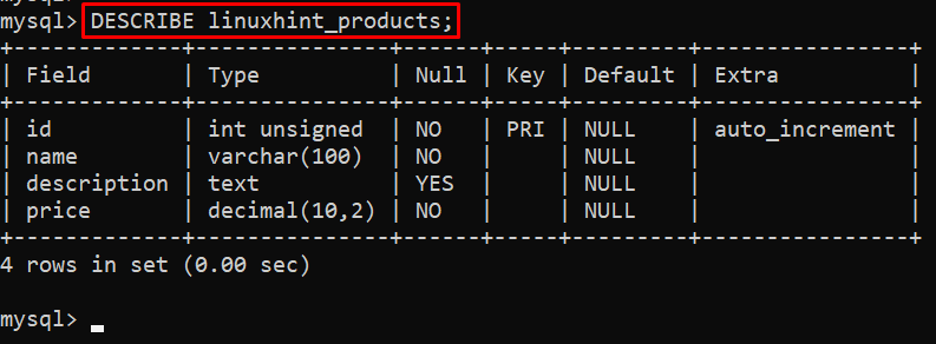
Here is an example of the “DESCRIBE” statement that is utilized on the “linuxhint_products” table:
Output
In the output, it can be seen that the information about a particular table has been fetched by using the “DESCRIBE” keyword.
How to Use the SHOW COLUMNS Statement in MySQL?
The “SHOW COLUMNS” statement followed by any particular table name, allows you to fetch the information of the table’s columns. To understand how to use the “SHOW COLUMNS” statement in MySQL follow the given below syntax:
By using the above syntax, you can easily get the information of the selected table.
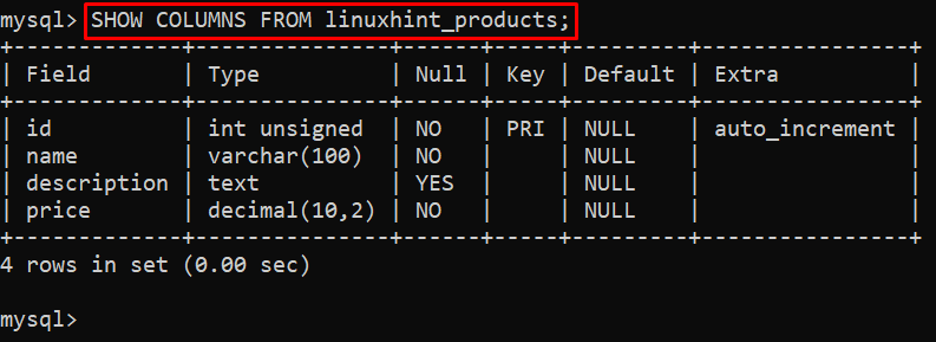
An example of getting the information of column in a “linuxhint_products” table is provided below:
Output
The output showed the information that contains the column names, datatype, whether the NULL value is allowed in that column or not, etc.
Conclusion
The “DESCRIBE” and “SHOW COLUMNS” statements in MySQL are useful tools for retrieving information about the columns in a table. By using these statements, you can obtain details such as column names, data types, nullability, key information, default values, and extra attributes. Execute these statements with the appropriate table name to easily access the desired information about a specific table in your MySQL database.