This guide will provide in-depth information on how to show the constraints of a table in MySQL.
How to Show/Display Constraints of a Table in MySQL?
In MySQL, the constraints are utilized to set the rules to restrict or control the data to be inserted, updated, or deleted from a table. The constraints can be shown using different commands, but before that, you need to create the constraints.
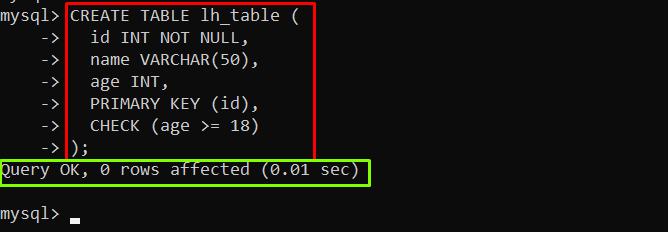
The constraints can be created while creating the table as provided below in the example:
id INT NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(50),
age INT,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
CHECK (age >= 18)
);
In the above example, the table name “lh_table” with the constraints on the “id” and “age” columns has been created.
Output
The output showed that the table and constraints have been created.
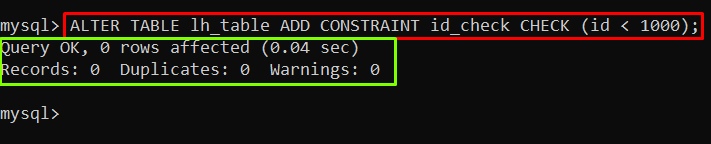
Alternatively, the constraints can also be added to the existing (already created) table utilizing the “ALTER TABLE” command as shown below:
In the above example, the new constraints name “id_check” is being created.
Output
The output showed that the constraints had been created.
After creating the constraints, there are multiple methods to show the constraints, such as by utilizing the “SHOW CREATE” command or the “information_schema”.
Method 1: Show Constraints Using the “SHOW CREATE TABLE” Command
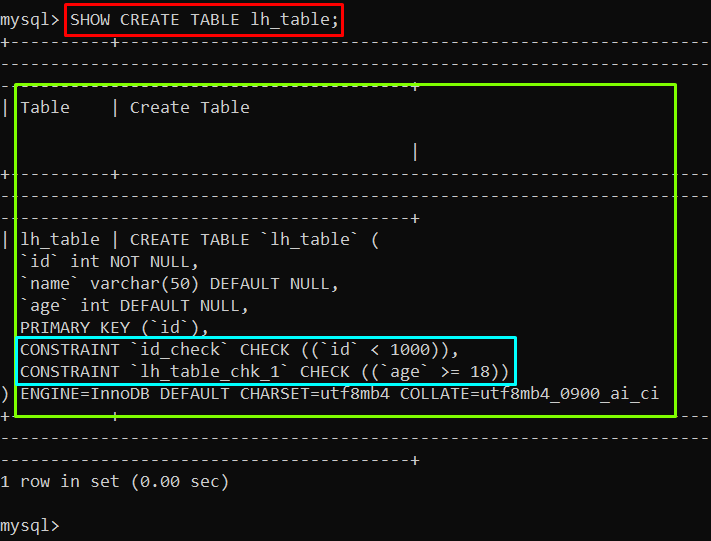
The constraints of a particular table can be displayed by utilizing the SHOW CREATE TABLE command, with the particular table name. An example of showing the constraints of the “lh_table” is given below:
Output
The output depicts the constraints of the “lh_table”.
Method 2: Show Constraints Using the information_schema
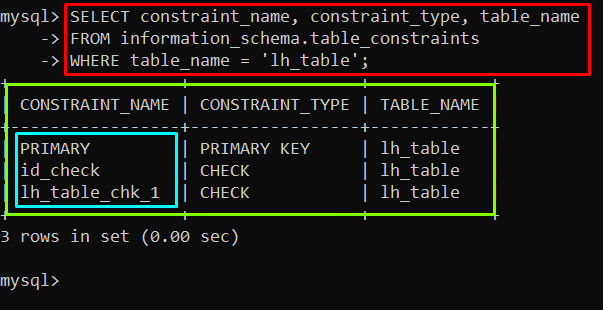
The constraints of a specific table can also be displayed by utilizing the “information schema”. The information is retrieved by using the “SELECT” statement and the table is specified with the “WHERE” clause. An example of retrieving the constraints of the “lh_table” is given below:
FROM information_schema.table_constraints
WHERE table_name = 'lh_table';
In the above example, constraint_name, constraint_type, and table_name columns of the “information_schema.table_constraints” are being retrieved.
Output
The output showed the constraints name of the “lh_table” with its type and table name.
Method 3: Show Constraints of Multiple Tables
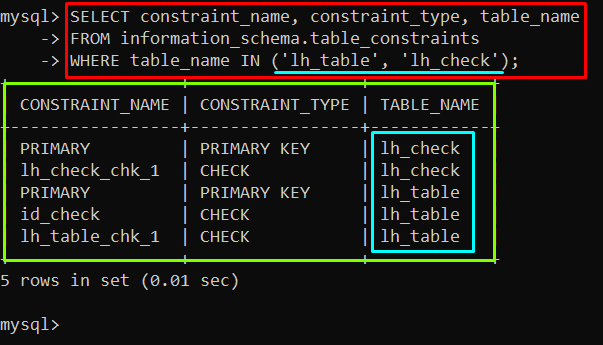
Multiple tables’ constraints can also be shown by using the information schema of the constraints table. To do that, you must utilize the “IN” operator in the “WHERE” clause to provide the table names. An example of retrieving the “lh_table” and “lh_check” tables constraints is given below:
FROM information_schema.table_constraints
WHERE table_name IN ('lh_table', 'lh_check');
Output
The output showed the available constraints of the selected tables.
Conclusion
In MySQL, constraints are used to control the data that can be manipulated in a table. They can be created while creating the table using the “CREATE” command or added to an existing (already created) table using the “ALTER TABLE” command. To retrieve the constraints, you can use multiple methods such as SHOW CREATE TABLE or querying the information_schema of table_constraints. This post presented in-depth information on retrieving the constraints of a table.