In Git, commits are utilized to save changes or modifications in the Git repository. Each commit represents a snapshot of the modifications made to the repository at a certain point in time. Whenever a user makes changes to their projects, they save those changes by committing them. However, sometimes, users may want to save the modifications in the past. In this situation, Git allows them to make commits in the past.
This article will illustrate the procedure to make a commit in the past in Git.
How to Make a Git Commit in the Past?
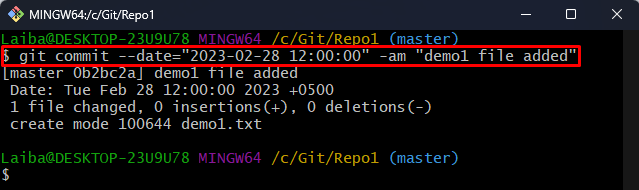
To make a Git commit in the past, the “git commit –date=”YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS” -am “<commit-message>”” command is used. Let us take a scenario to perform this operation:
Step 1: Redirect to the Local Repository
First, navigate to the particular local directory:
Step 2: Create a New File
Next, run the following command with the particular file name to create it. For instance, we are creating a “demo1.txt” text file:
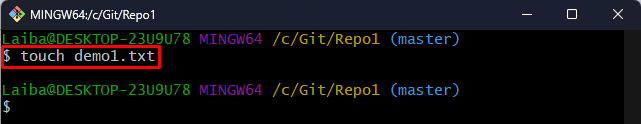
This command has created a new file named “demo1.txt”.
Step 3: Track the File
Then, stage the newly created file for tracking purposes:
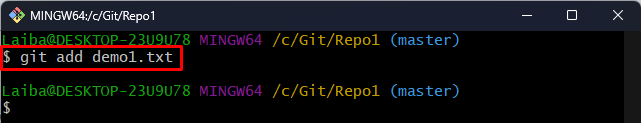
The “demo1.txt” file has been added to the Git staging area.
Step 4: Commit Changes in Past
Now, commit the file changes in the past using the “git commit” command with the “–date” format and specify the old date and time, and commit message:
This command has made the commit on “2023-02-28” at “12:00:00”.
Step 5: Verify Changes
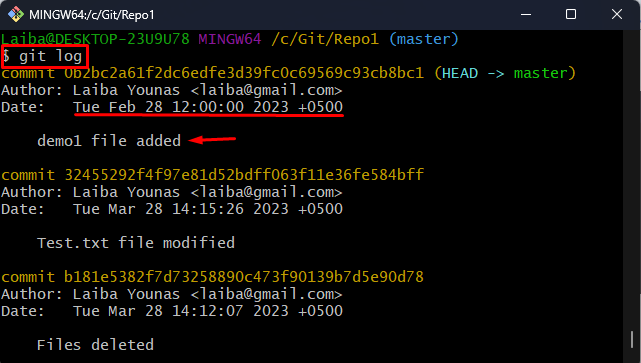
Lastly, view the commit history to verify whether the commit has been made in the past or not:
In the above output, the desired commit has been made in the past on the specified date and time.
Conclusion
To make a Git commit in the past, first, make desired changes and track them. Then, commit changes using the “git commit –date=”YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS” -am “<commit-message>”” command. To verify whether the commit has been made in the past or not, use the “git log” command. This article illustrated the method to make a commit in the past in Git.