Importing and Exporting in MySQL databases aids in ensuring data security as importing databases is used for transferring data between servers, on the other hand, exporting databases helps in data backup and recovery.
This guide will provide the procedure for:
Prerequisite: Installation of MySQL Server in Linux
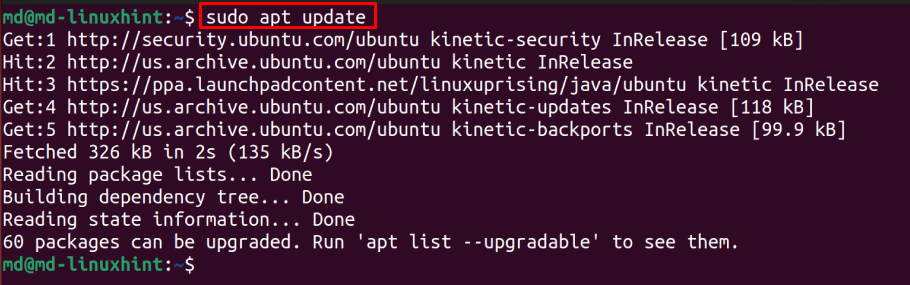
Updating your system before any installation is preferable so type:
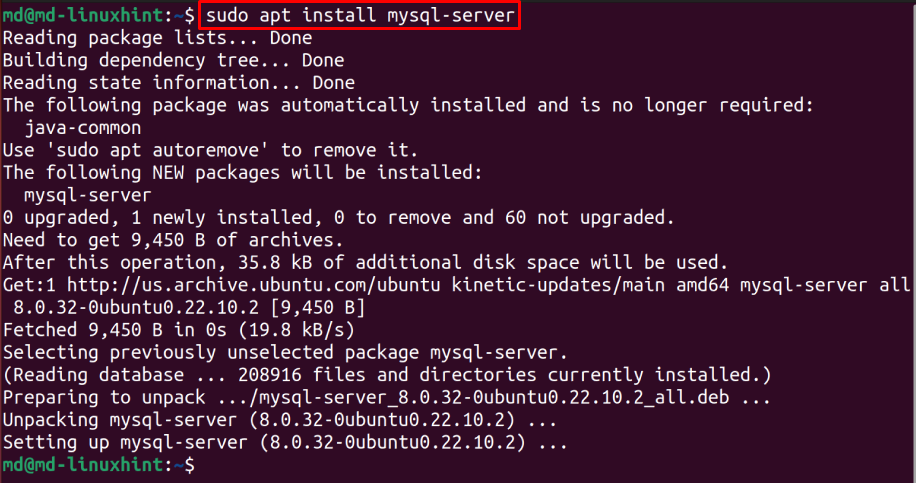
Install the MySQL server by typing:
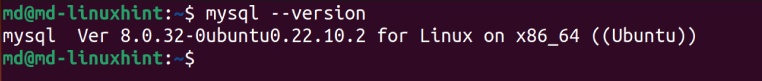
To check the installed version of MySQL, type:
For starting the services of MySQL use this command:
Exporting MySQL Databases in Linux
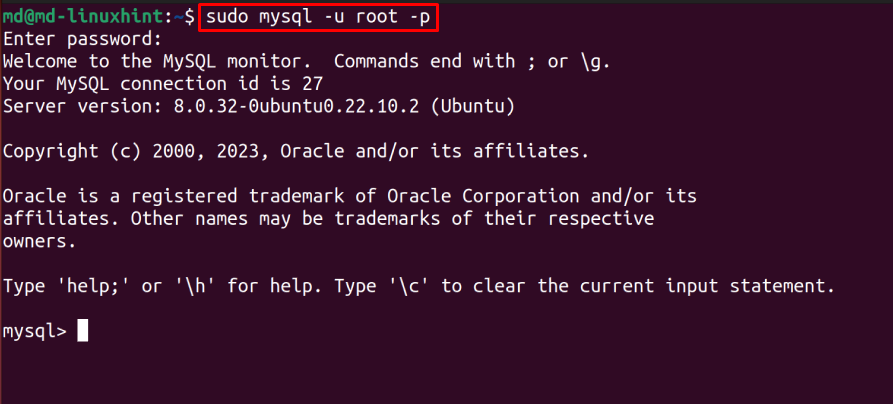
Lets export a database in Linux, but before that, you need to connect to a MySQL Server. Use this syntax to connect to a Local MySQL Server:
For this post the username is “mysql”:
As it is visible in the output above, the MySQL server is connected successfully.
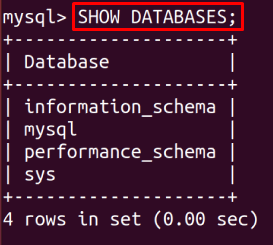
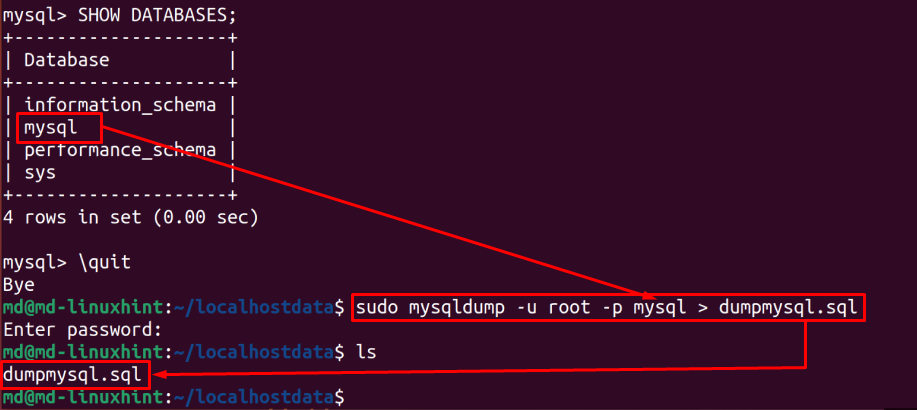
Use this SHOW command to see all the available databases:
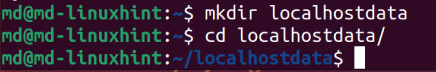
To export the “mysql” database from the available databases, first let’s create a directory using this command:
Navigate to this directory by typing:
To export the database, use this syntax:
Provide your username, database name that you want to export and the name for a file in which you want to export the database. Use this syntax and hit enter, and type the ls command to see if the database is exported successfully or not:
Here you can see that file is successfully created.
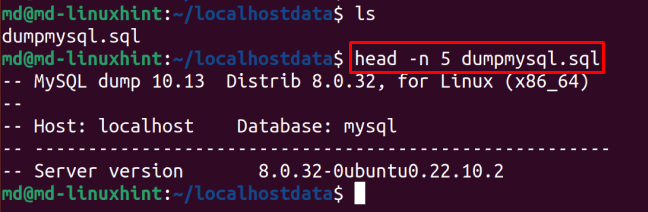
To see some data of this file, type:
Here the data of the exported database is visible.
Importing MySQL Databases in Linux
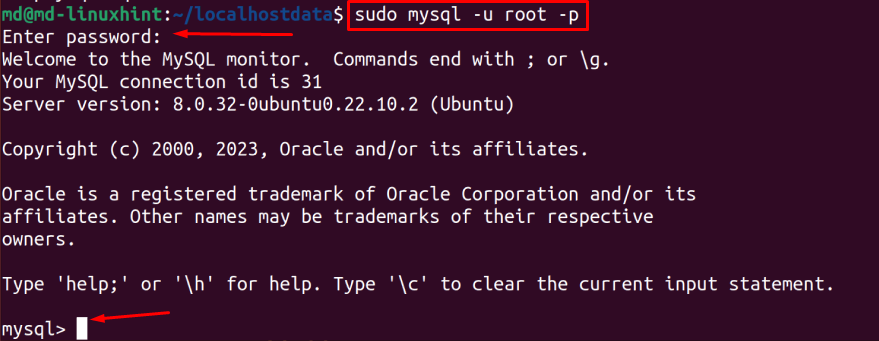
To import the database, let’s connect to the local server by using the syntax:
You have successfully logged in to your local database server.
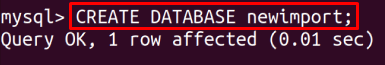
To create a database, use this syntax:
Provide the name for the database:
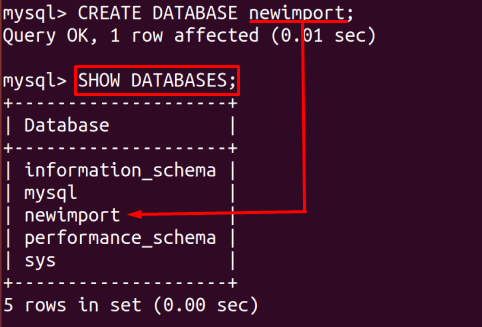
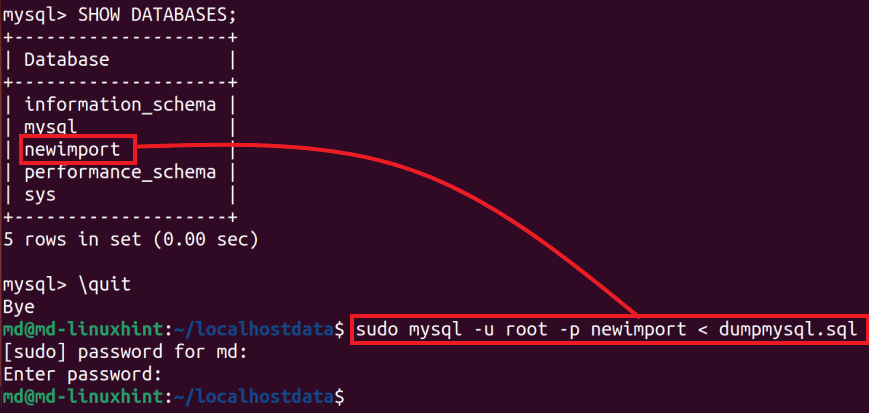
To see the available databases, type this command:
Here it is visible that the database you created is available.
Let’s import the already existing file with “.sql” extension containing the backup data of the database, using this syntax:
Provide the required values in syntax:
Your database is imported successfully as it asked for the password and gave error-free output.
Conclusion
Importing and Exporting databases is an important task for data recovery and backup, data migration, collaboration, or testing and debugging. Exporting creates a backup file, to export the database use this syntax “sudo mysqldump -u <username> -p <db-name> > <filename>.sql” whereas importing allows you to make the data transfer easy between servers, you can import database from a file by using this syntax “mysql -u <username> -p <new-database-name> < <filename>.sql”.