How to Identify and Kill the Queries Using Command Line Tool in MySQL?
To identify and kill queries in MySQL, first log in to the server by utilizing the command line tool known as “mysql”. For that, open CMD and run the command given below:
In the above command, the username is “root”.
Output
The output displayed that the connection is established with the MySQL database.
Identify Queries Using Command Line Tool
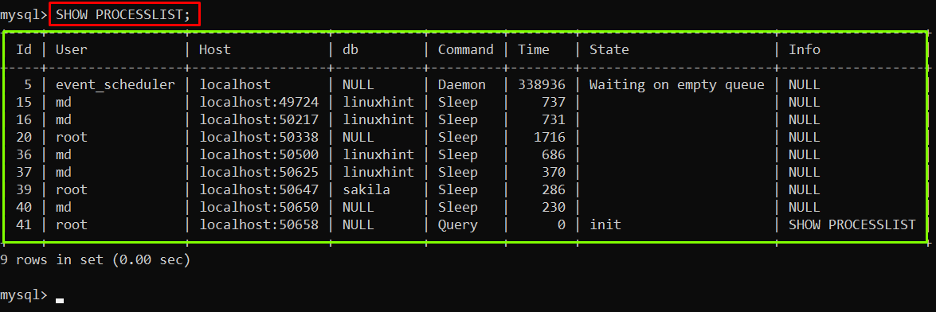
In the MySQL database, there is a table named “Processlist” which contains information about the running queries in the MySQL server. To list all the running queries for the purpose of identifying the problematic queries, execute the following command:
Output
The output portrayed the details of running queries in a tabular form.
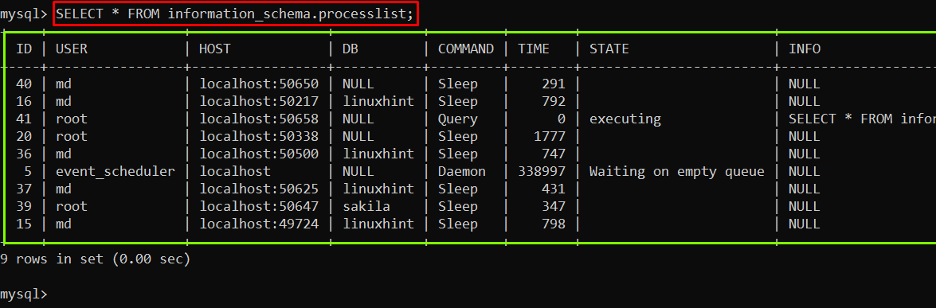
The user can also utilize this command to directly list all the columns of the “processlist” table that exists in the “information_schema” database:
Output
The output displayed the table containing information about the running queries which can be utilized to identify the problematic queries.
Kill Queries Using Command Line Tool
After identifying the problematic queries, the user has to kill or terminate them. To do so, below syntax can be used:
To kill a query, the user must specify its id in place of [pl_Id]. Moreover, the CONNECTION or QUERY keyword specifies the type of identifier utilized by the user.
However, the user can also use this short syntax for terminating the query by only specifying its id:
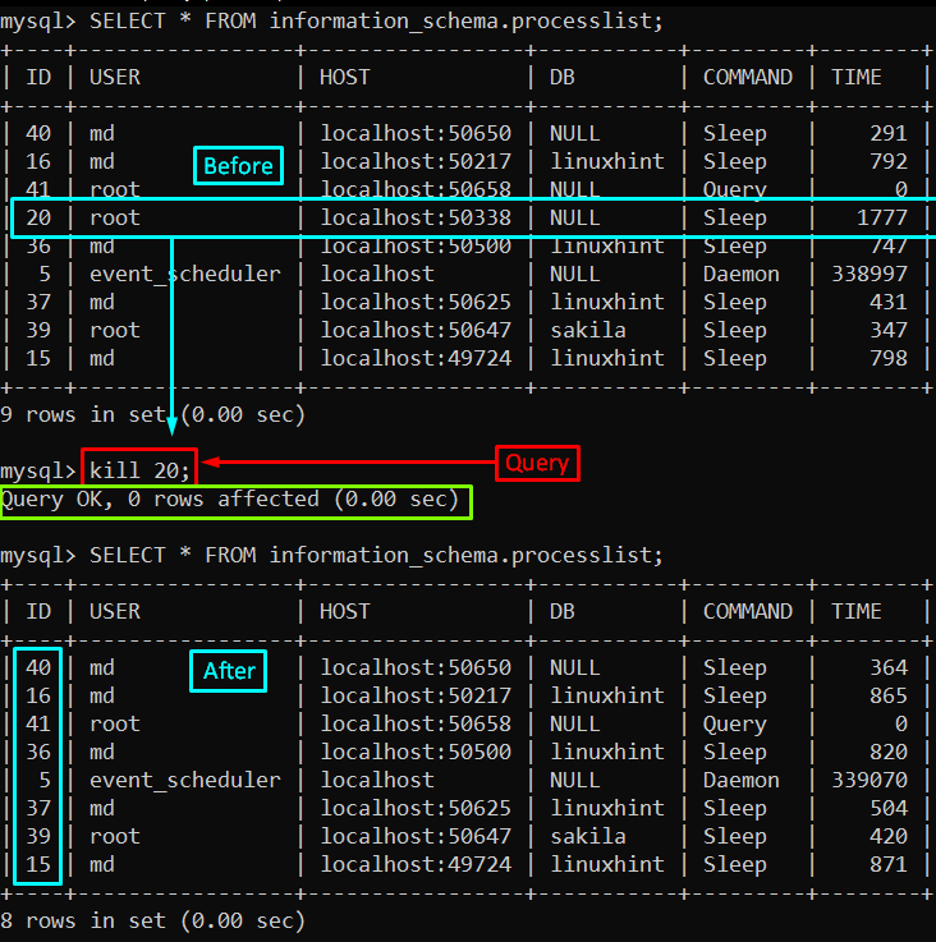
Here we will kill a query having an id equal to “20” by running this command:
Output
The output clearly displays that the mentioned query is killed successfully.
Bonus: How to Identify and Kill Queries Using mysqladmin Tool
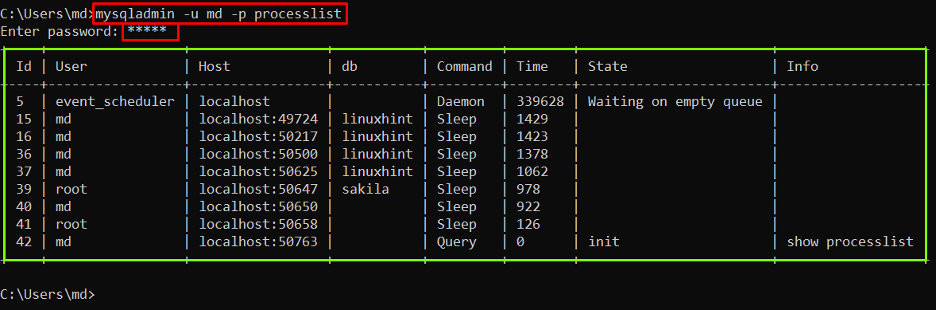
Mysqladmin is a client administrative utility that aids in performing tasks related to MySQL server. To identify the problematic queries, execute the given below command:
Here in the above command “md” is the username of the MySQL server. Replace your username in the command.
Output
The output displayed the details of running queries.
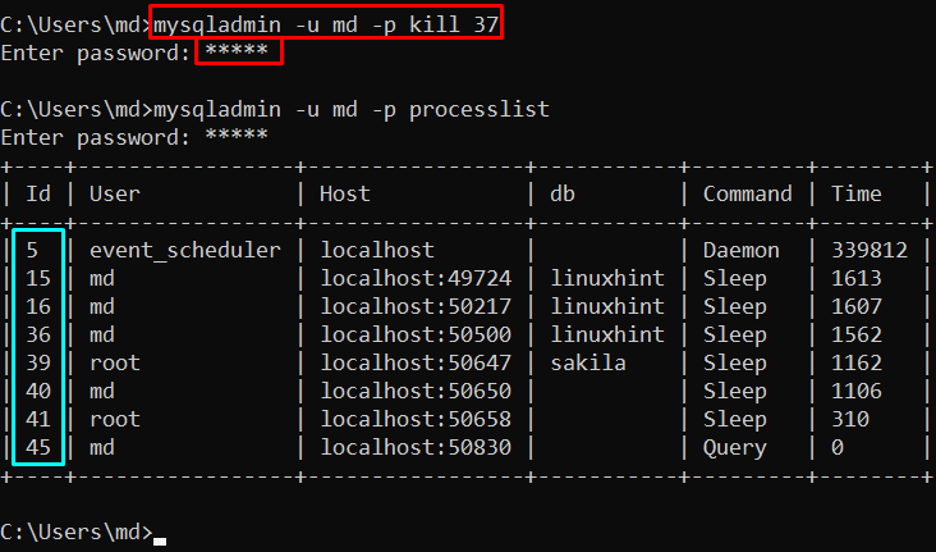
To kill the running queries, run this command:
In the above command, “37” is the number of a specific query that will be killed.
Output
The output showed that the specified query is killed.
Conclusion
To ensure that the MySQL server is running smoothly and providing high performance, it is essential that the user knows how to identify problematic running queries and terminate them. To do so, users can utilize the command line tool and execute the above-provided commands for identifying a problematic query and terminate it using its query id. This post has explained various methods to identify and kill queries using the command line tool in MySQL.