This post will provide examples:
- Export a Single Database
- Export All Databases in a Single File
- Export Only Data of a Specific Table
- Export a Database in XML Format
Prerequisite
To export a database, connect to the MySQL server where the database resides using this syntax:
Provide the Username of the MySQL Server and hit “Enter”. Type your password to login to the MySQL Server:
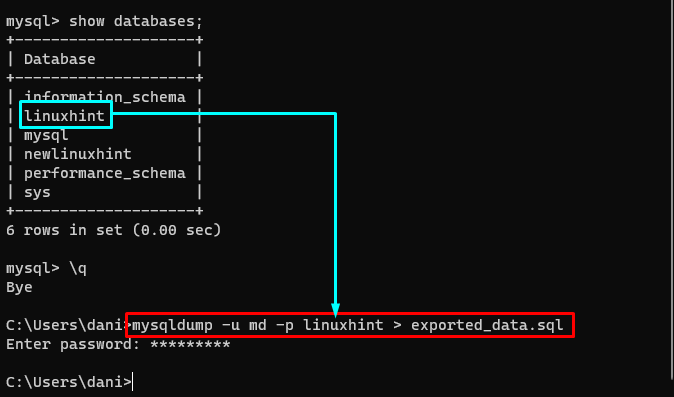
Once you have successfully logged in, run this command to see the list of all available databases:
The output will display the names of databases:
For this post, “linuxhint” database will be used to demonstrate examples of exporting MySQL database.
Export MySQL Database Using “mysqldump” Command
To export a MySQL database in the SQL file, use the mysqldump utility that is used to provide the logical backup of the database or to transfer the database from one server to another. It can be used to export single or multiple databases in a SQL file. You can also use different options in the command to export the structures, data, or multiple tables also.
Example 1: Export a Single Database
To export the single database to a SQL file using this syntax:
For example, you want to export a database named “linuxhint” to a file with name “exported_data.sql”, run this command:
The error-free message will indicate the execution of command was successful:
To verify that the file was exported successfully or not, use the “Where” command:
The output is displaying the file containing a single exported database:
Example 2: Export All Databases in a Single File
The mysqldump can be used to export multiple databases into a single SQL file using “–all-databases” option as shown in the syntax:
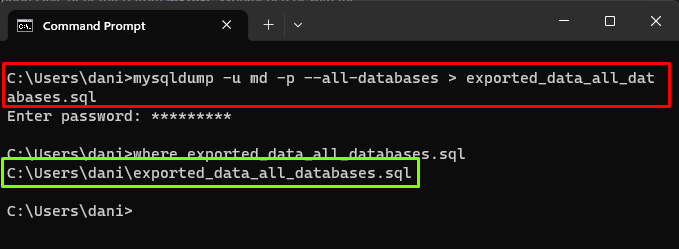
For example, to export all the databases of the MySQL server in a file named as “exported_data_all_databases.sql”, run the following command:
The error-free output will indicate the successful execution of the exporting process, to verify it use the “where” command:
Example 3: Export Only Data of a Specific Table
To export only the data of a specific table without exporting the data of “CREATE” statements, use the “–no-create-info” option as displayed in the syntax:
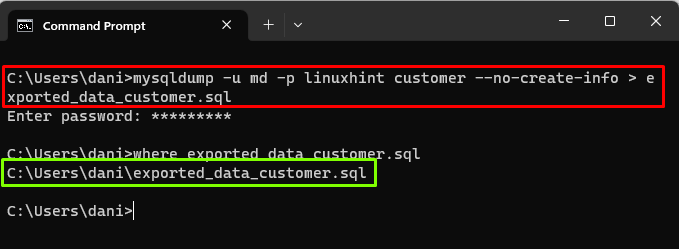
For example, to export the data of “customer” table only from the “linuxhint” database, use this command:
To verify if the file with exported data is created successfully or not run the “where” command and it is visible that the file is created successfully:
Example 4: Export a Database in XML Format
To export the database in an XML format using the “–xml” option in the mysqldump command:
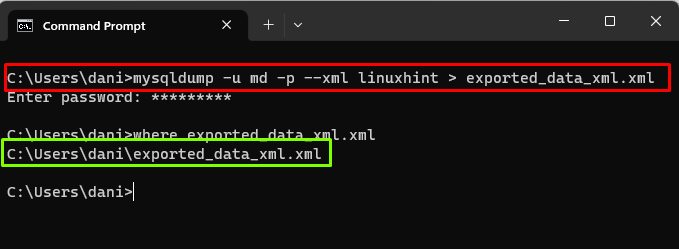
For example, to export “linuxhint” database in XML format to a file named “exported_data_xml.xml”:
Once the execution of export statement completes, verify if the file exists or not, by running the “where” command:
You learned how to export a MySQL database using mysqldump command in the command line. There are various other options available for mysqldump. Read them from the Official website of MySQL.
Conclusion
Use mysqldump to export the database in a SQL file for data backup or transfer between servers. To export a single database, use the “mysqldump -u [username] -p [db-name] > [output-file-name].sql” command. The mysqldump command can be used with other options to export all databases or specific table data. This post discussed how to export MySQL Database with examples.