By following this step-by-step guide, you will get to know how to create a superuser in MySQL.
How to Create a Superuser in MySQL?
To create a superuser in MySQL, you can follow the given below step by step guide:
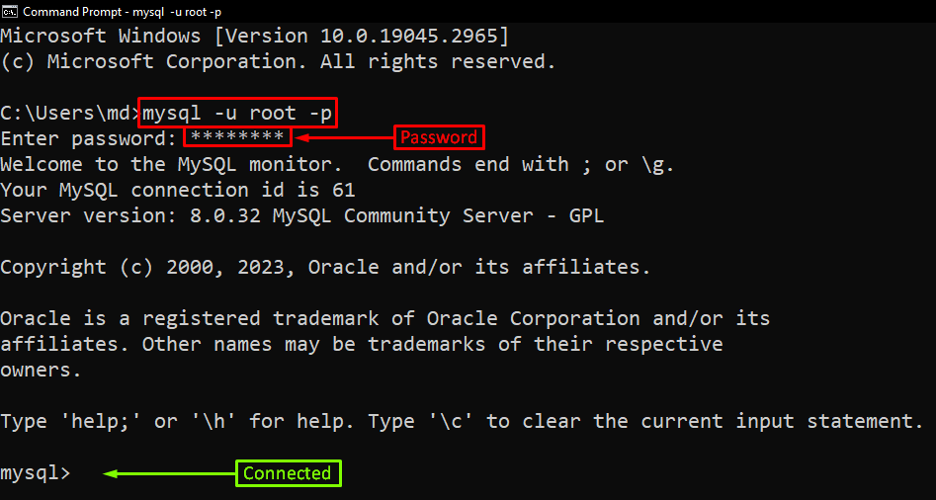
Step 1: Log in to MySQL
To create a superuser in MySQL, you need to log in to the MySQL server with the “root” user and its appropriate password as shown in the below command:
After this command, you need to type the password as shown in the output screenshot.
Output
The output showed that the MySQL server has been logged in.
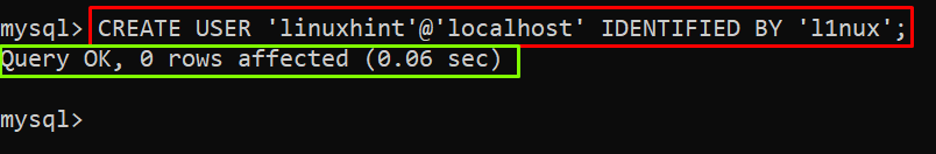
Step 2: Create a Local User
To create a regular or local user you can simply utilize the “CREATE USER” command as provided below in the example of creating the “linuxhint” user:
In the above example, the password “l1nux” of the “linuxhint” user is set by using the “IDENTIFIED BY” clause.
Output
The output displayed that the user has been created.
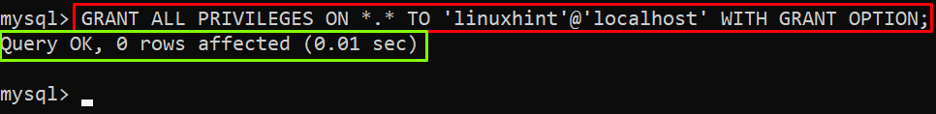
Step 3: Grant Privileges
To grant the root privileges, the “GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES” clause can be utilized with the name of the newly created user. The command to grant the superuser privileges to the “linuxhint” user on the “localhost” is given below:
In the above command, “*.*” means all databases and tables, so the “ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.*” means the user is granted all privileges on all databases and tables.
Output
The output showed that the privileges have been granted.
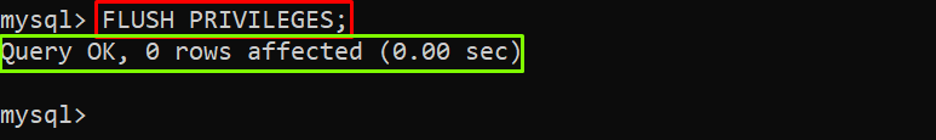
Step 4: Reload the Grant Tables
Utilize the “FLUSH PRIVILEGES” command to reload the grant tables and store user privileges information:
Output
The output showed that the user grant table has been reloaded.
Step 5: Confirmation
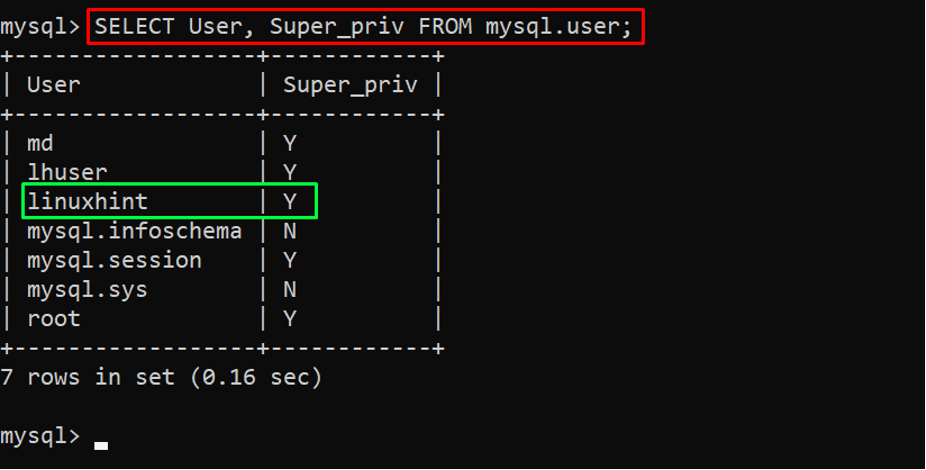
Here a new superuser has been created. To confirm if the user is a superuser or root user, you need to follow the given below command:
Output
The “Y” in the “Super_priv” column verifies that the “linuxhint” user is a superuser.
Conclusion
In MySQL, creating a superuser involves a few straightforward steps. First, log in to MySQL as the root user and create a local user with a specified username and password, then grant all privileges on all databases and tables to the newly created user. After granting the privileges, it’s important to reload the grant tables to apply the changes. All these steps have been well explained in the above article.