This post will discuss the following content:
- Overview of Oracle TO_TIMESTAMP Function
- Conversion of a Character String to a Timestamp
- Conversion of System Date and Time to a Timestamp
Overview of Oracle TO_TIMESTAMP Function
The Oracle TO_TIMESTAMP is a built-in function that converts a CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, or DATE data type value to a TIMESTAMP data type.
This function takes three arguments as the input, let’s see its syntax:
Here in the above syntax:
- The “Input_value” (compulsory argument) is the value of the string or date that will convert to TIMESTAMP.
- The “Conversion_format” (Optional argument) is the format parameter specifying the input value’s format. There are many formats available for the conversion but make sure that it matches the “Input_value” style.
- The “nlsparam” (Optional argument) aids in specifying the output values (day, month names) language.
Oracle offers different formats in which you can convert your string values. Let’s enlist some of the parameters for the formatting below to understand them:
| Format Parameters | Explanation |
|---|---|
| YYYY | 4-digit Year |
| YY | 2-digit Year |
| MON | Abbreviation of the Month (Jan-Dec) |
| MM | Number of the Month (1-12) |
| DD | Number of the Day (1-31) |
| HH24 | Current Hour using 24 Hours Format (0-23) |
| HH | Current Hour using 12 Hours |
| SS | Seconds (0-59) |
| MI | Minutes (0-59) |
Now we will use the TO_TIMESTAMP function to convert the character string and current system date to a TIMESTAMP.
Conversion of a Character String to a Timestamp
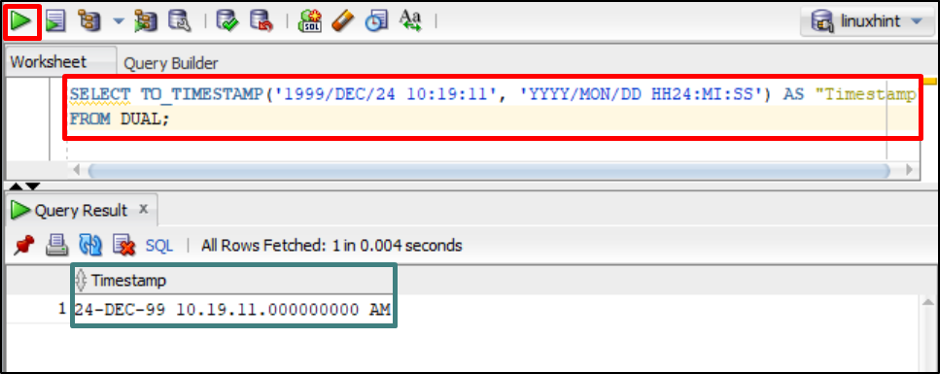
This function converts a string of any data type, such as CHAR, VARCHAR2, and NCHAR to a TIMESTAMP data type. To do so, open the Oracle database using SQL Developer or SQL PLUS utility and execute the command given below:
FROM DUAL;
Output
The output returned the TIMESTAMP after converting the provided string in the column named “Timestamp”.
Conversion of System Date and Time to a Timestamp
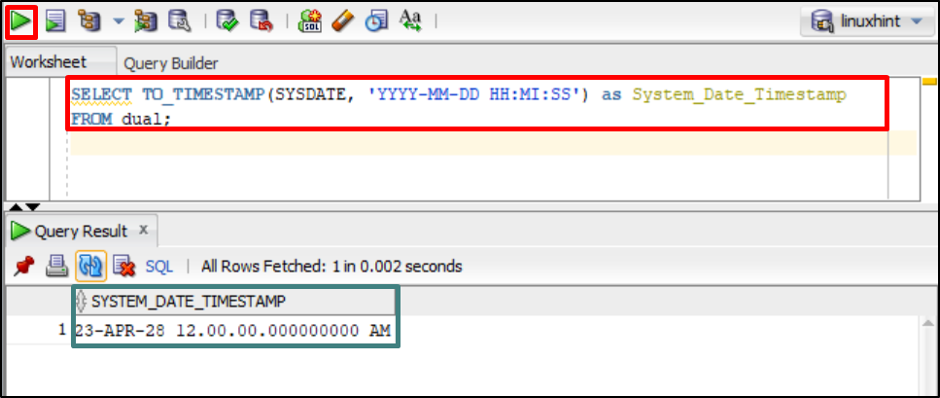
The TO_TIMESTAMP function can also call the “SYSDATE” function and use its value as the input for conversion. Let’s utilize the command given below to convert the system’s current date and time into a TIMESTAMP:
FROM dual;
In the above command, the TO_TIMESTAMP function extracts the value of the system’s current date and time and converts it to the specified format. The output will return in a column named “System_Date_Timestamp”.
Output
The output successfully returns the TIMESTAMP after converting the system’s date and time in the specified format in a column named “System_Date_Timestamp”.
Conclusion
The Oracle “TO_TIMESTAMP” function is utilized to convert the string or date value to a TIMESTAMP data type. This function takes three arguments, the input value is compulsory and two are optional arguments (format parameters and nlsparam). The post discussed the TO_TIMESTAMP function and how users can convert a string or system’s date and time into a TIMESTAMP data type.