Computer hardware is a combination of various components, such as motherboard, CPU, GPU, memory, and other I/O devices. It is good for Linux users to have a basic knowledge of the hardware components of the system that they are currently using. This will help administrators to manage the required devices accordingly.
This article shows you how to check the hardware information in Ubuntu using various methods. These options are discussed in the sections that follow.
Checking Hardware Information Using HardInfo
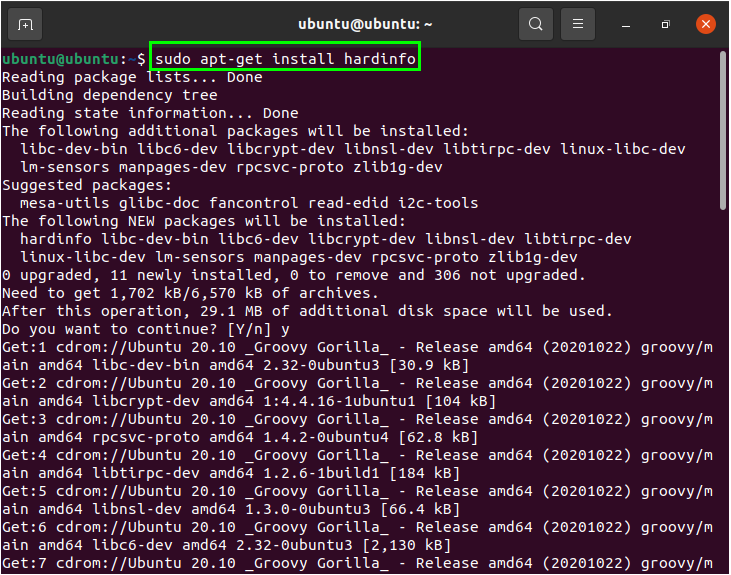
To get hardware information using HardInfo, you first need to install HardInfo on your Linux system. Start the installation process by opening the terminal and running the following command:
After installing HardInfo on your system, open the utility via the command-line to see the hardware information in the GUI. To open HardInfo, simply enter the following command:
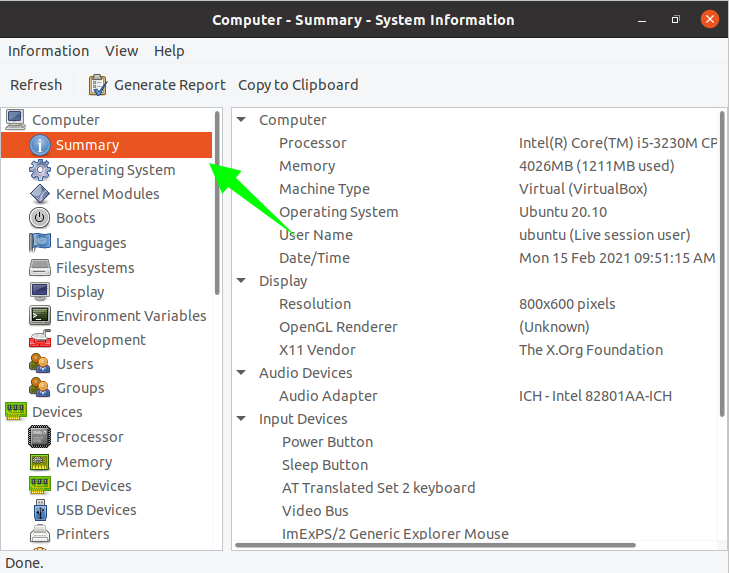
A new window will open after you run this command. If you click on “Summary,” you will get all system-related information, including the processor, OS, display, etc.
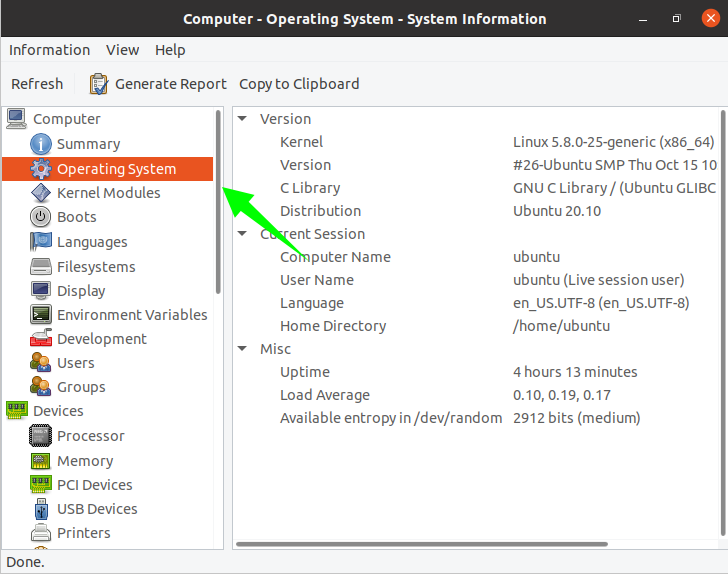
To check the status of the Operating System, including the version, PC name, distribution, etc., go to the “Operating System” window. A screen will appear with detailed information, as shown in the image below:
To check the system’s kernel version, select the “Boot” window. This window will show you the updated version information with the date and time.
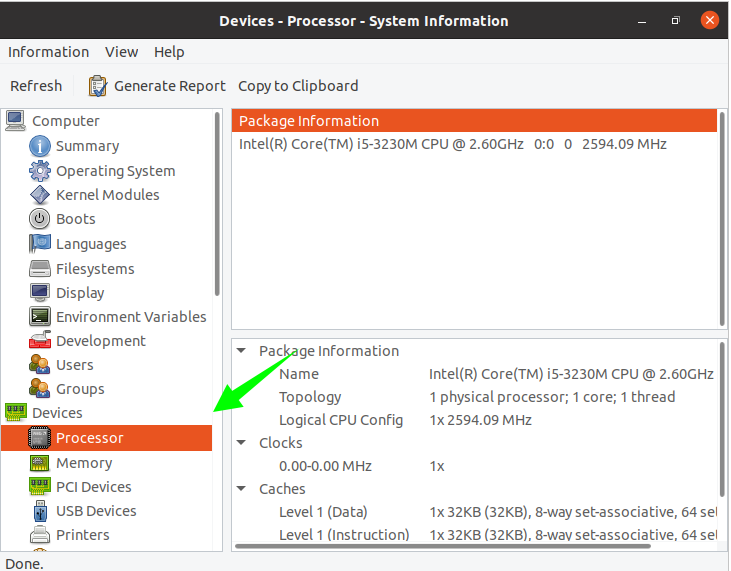
To get package information, click “Processor.”
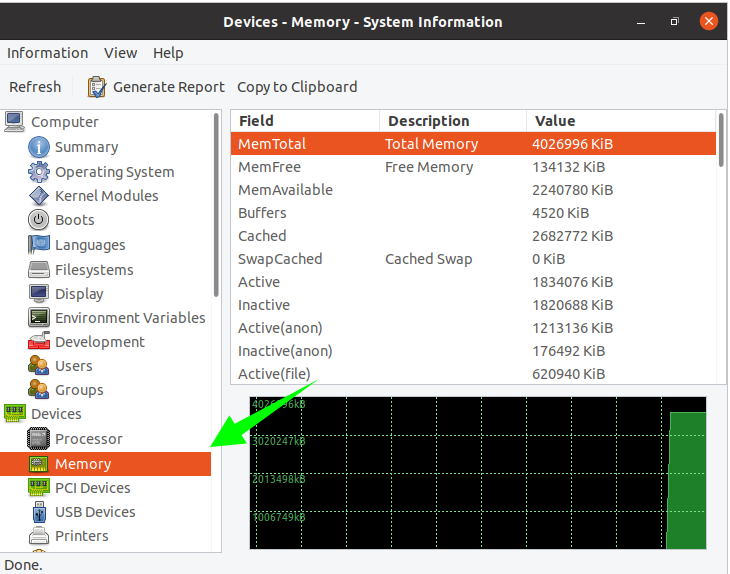
Clicking “Memory” will display the memory status, including the total memory, available memory, used memory, cache, active, inactive status, etc.
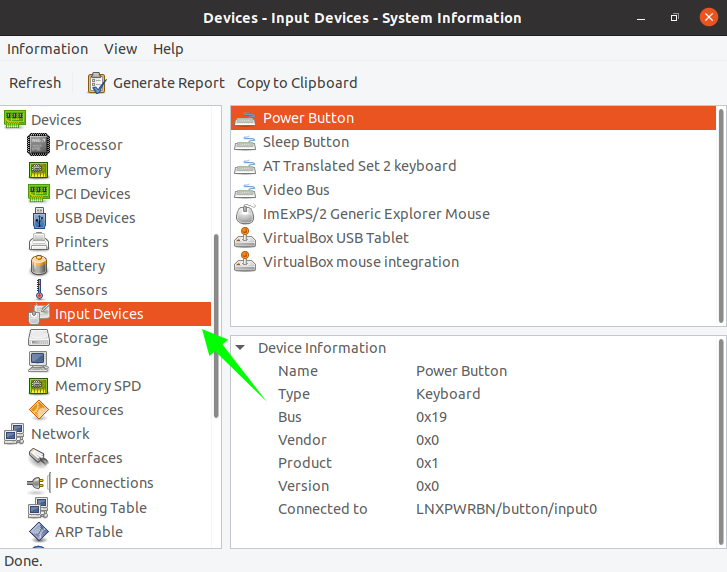
Select “Input Devices” to get more icons to view specific system details. Click a specific icon to reveal relevant details related to that icon.
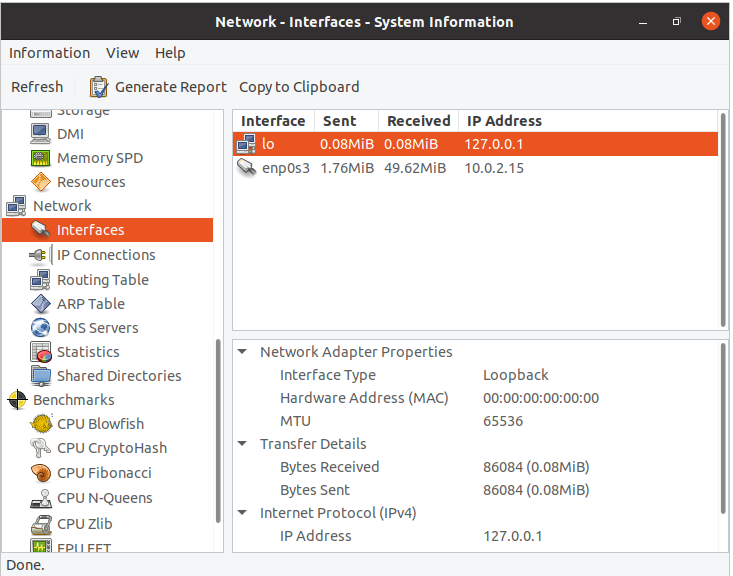
To obtain details about the system network, click the “Network” option:
So, this is how you can find hardware system details using HardInfo.
If you prefer to check the hardware information via the command-line, then follow the steps mentioned below.
Checking Hardware Information Using the Command-Line
This section covers some important commands that can be used to fetch hardware information via the terminal. The ishw command is used for this purpose.
System Hardware Information
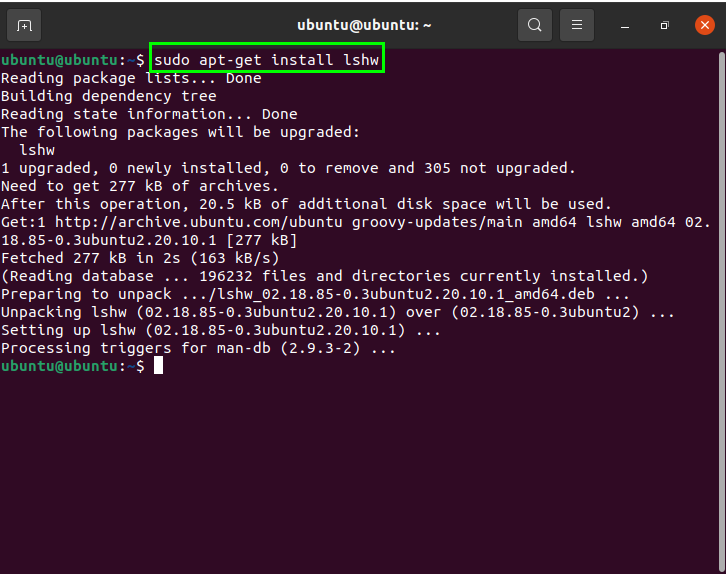
The “lshw” utility helps users to print system information such as hardware components, which can include Cpu, disks, cache, etc. Though this utility is built-in, but if your system does not have this utility, then you can install it using the following command:
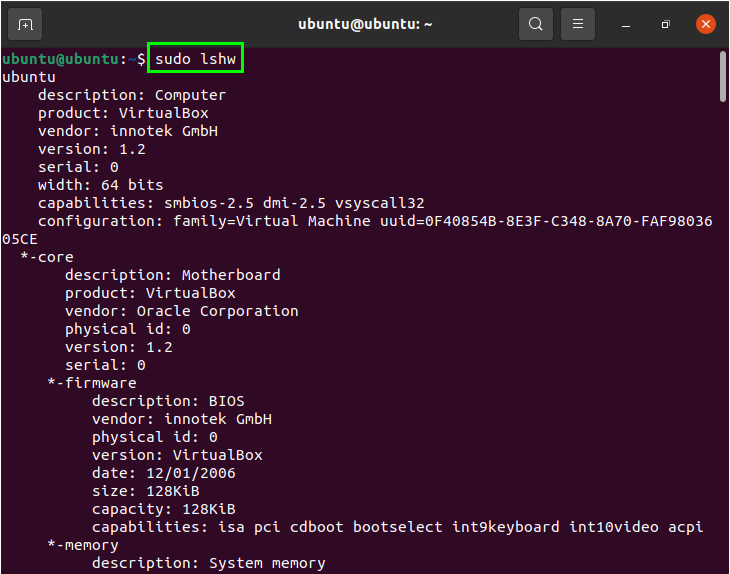
Now, to print the hardware information, use the following command:
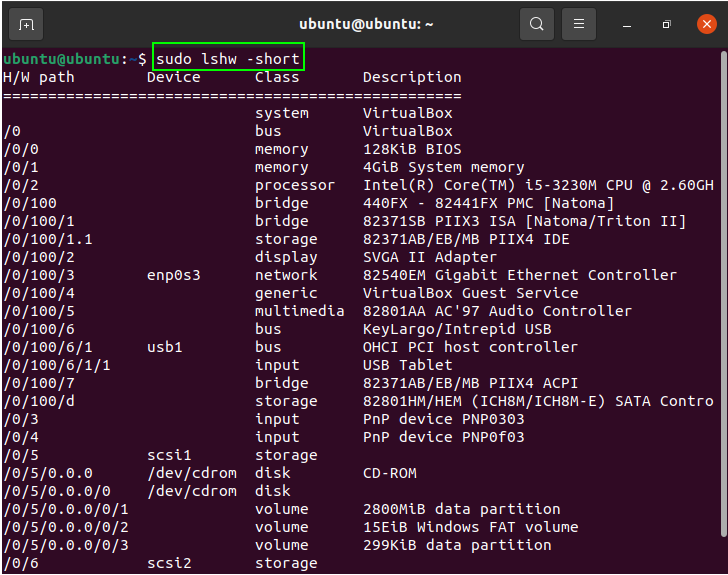
The output of this command includes every minor detail related to the system. To get a summary of this information, use the “short” command. The information will be printed in a table organized into columns:
CPU Information
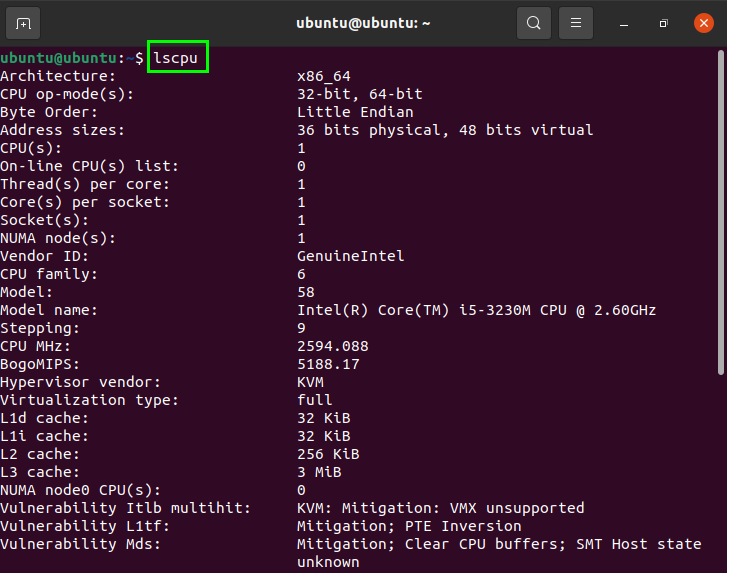
The “lscpu” command will fetch CPU details from the “sysfs” files.
To display cpu information, use the following command:
Block Device Information
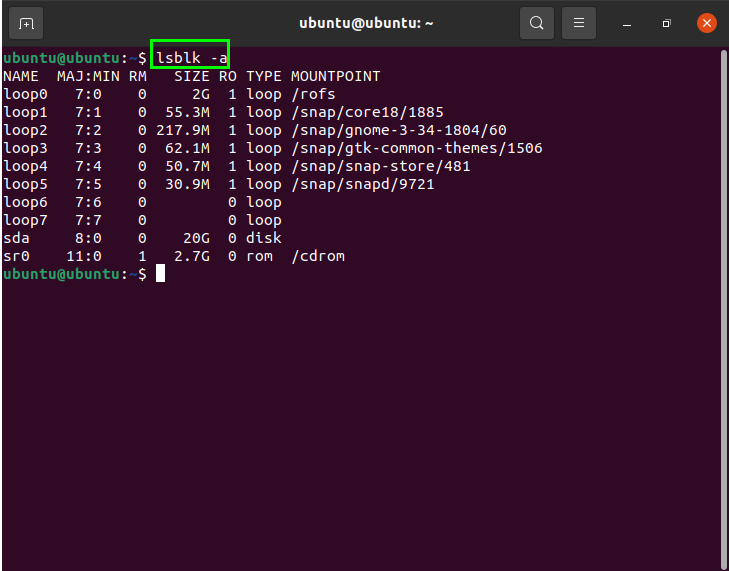
The “lsblk” command is used to collect block device, storage, and other information related to the hard disk, flash drive, etc.
To list data using this command, issue the following in the terminal:
The output will provide a list of information on the screen. To check all block devices, issue the following:
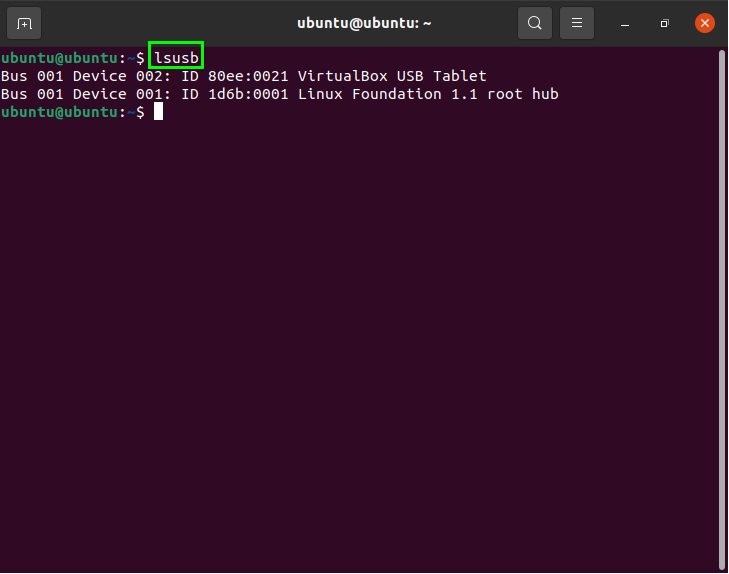
USB Controller Information
To view information about the devices that are connected to the system, including USB controllers, enter the following command:
Conclusion
This article provided a brief introduction to getting Linux system hardware information using the HardInfo utility. We have also displayed all the necessary commands for readers who want to check this through the command-line.