A scheduled task, also known as a cron job uses very time formats to determine when to run. For example, you can create a simple cronjob that runs when the system reboots.
To learn more on how to use the Crontab utility, check this tutorial. In this guide, however, we will discuss how we can implement cron tasks using the Go language.
Golang Cron Package
To create and run cron tasks using Golang, we need to install and import the Go cron package.
Start by creating a working directory to store your Golang code.
cd crons
Next, run the command below to install the package:
Once installed, create a Go file to store your code
Open the main.go file with your text editor and import the package using the line shown below:
Golang Create Cron Object
The first step is to create a cron object using the cron.New() method. You can then use this object manage and schedule tasks.
The above should return a new cron job runner with the defined time zone. If no time zone is specified, the function will use the local time zone.
Golang Add Func
The next step is to call the AddFunc method on the cron object. This allows us to add a time to the job manager. The function syntax is as shown:
It takes the duration under which the specified function will run. You can set this value to any time.ParseDuration() format. For example, to set a function to run every minute, we can specify the parameter as: @every 1m.
The second parameter is the function which to execute.
An example code is as shown below:
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/robfig/cron/v3"
)
funcmain() {
cron := cron.New()
cron.AddFunc("@every 1m", func () {
fmt.Println("Hi Every minute!")
})
}
In this example, we define a function that prints “Hi Every minute”, every minute.
The next step is to start the cron scheduler. For this, we can use the cron.Start() method. The function will take the scheduler and run it in its own go-routine.
time.Sleep(time.Minute * 5)
The above code starts the cron scheduler using the Start() method. We also include the time.Sleep() method with a parameter of 5 minutes. This is because the Start() methods runs in its own go-routine for loop detection. The sleep method prevents the go routine from exiting.
If we run the above code, we should get an output as:
Hi Every Minute!
Hi Every Minute!
Hi Every Minute!
….
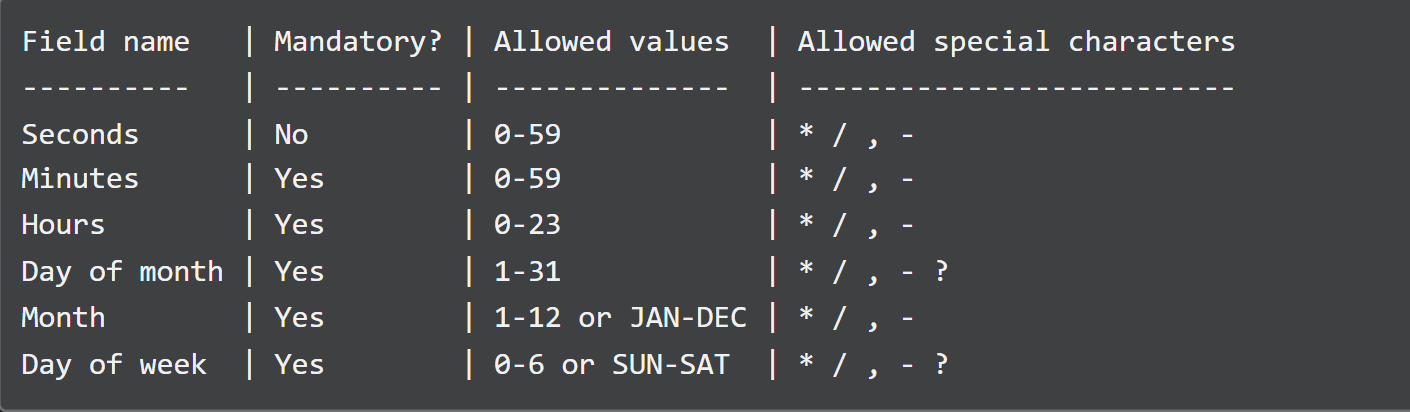
Golang Expression Formats
You can use various expression formats to define a set of times and durations under which a task will run.
The cron package supports the following expressions:
- An asterisk shows the expression matches all the values of the field.
- A forward slash describes the increment of ranges.
- Comma separates a list of items.
- Hyphen defines a set of ranges.
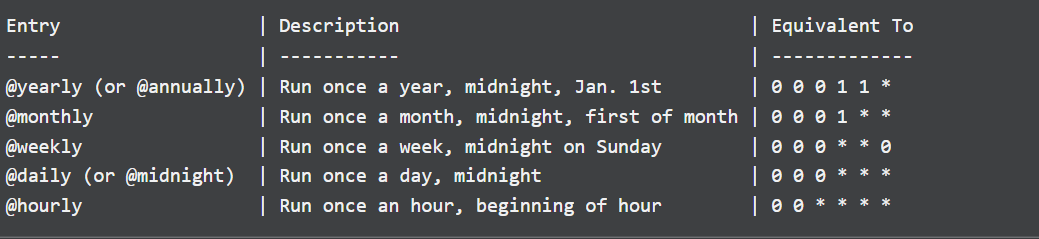
You can also use the pre-defined formats as shown:
Closing
This was an introductory tutorial on creating and scheduling tasks using cron in the Go language. Check the docs for more.