Git permits developers to manage their projects and host them on a platform like GitHub and GitLab. In Git, all contributors to the particular project work in the branches and directories. While working in one repository, it is difficult for the developer to switch to another directory/branch without saving the changes. To handle such cases, Git allows the user to create multiple worktrees of different branches. So, that the user can switch between them easily, without losing the currently doing changes.
This tutorial will provide the steps-based procedure to work and manage multiple working directories using Git worktrees.
How to Work with Multiple Working Directories Using Git Worktree?
To work with multiple working directories using Git worktrees, walk through the below-provided instructions.
Step 1: Open Git Directory
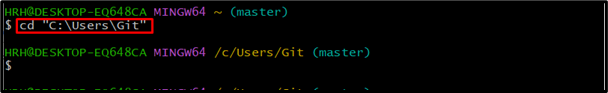
Open Git bash and move to the Git repository using the “cd” command:
Step 2: List Available Worktree
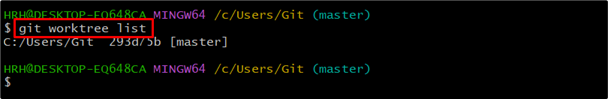
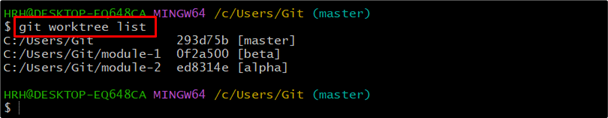
List down the available worktree using the provided command:
For now, there’s only one worktree in which we are working.
Step 3: Add Multiple Worktrees
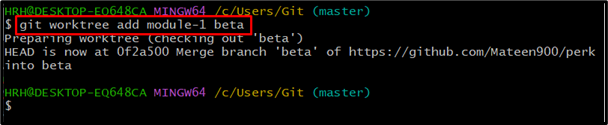
Add multiple wokrtrees in Git using the following syntax and specify the directory name and branch name:
Let’s say we want to add “module-1” in the “beta” branch, to do so, run the provided command:
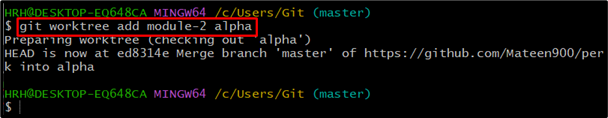
Likewise, for adding the “module-2” in the “alpha” branch, use the following command:
Step 4: Check Worktrees
Now, again list down the available worktrees using the following command:
The above image shows that the three worktrees are available.
Step 5: Switch Multiple Directories
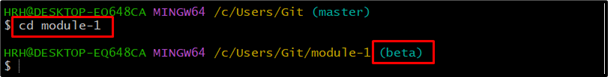
To switch to the desired working directory, use the “cd” command and specify the directory name. See the following command implementation:
The user has been switched to “module-1” under the beta branch.
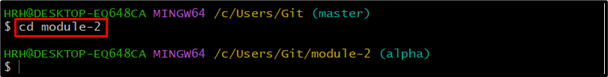
Similarly, you can switch to the “module-2” which is in alpha branch as shown:
Work in Multiple Worktrees Directories
Let’s do some work in the “module-1” worktree. To do so, consider the following steps.
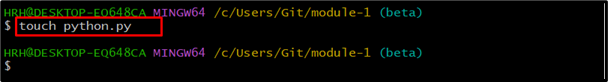
Step 1: Create a File
Create the file through the “touch” command:
Step 2: Track File
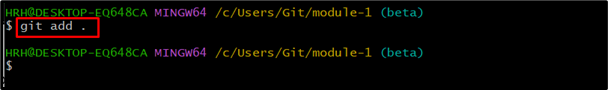
Track the created file using the provided “git add” command:
Step 3: Commit Changes
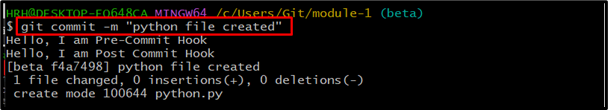
Commit the changes by running the mentioned command:
Step 4: Push Project
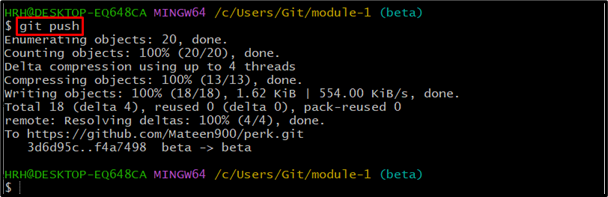
Lastly, push the project file via the “git push” command:
Conclusion
Git allows users to create worktrees and manage multiple working directories and branches simultaneously. To create a worktree use the “git worktree add <Directory Name> <Branch Name>” syntax, and specify the directory and branch name. After creating it, use the “cd” command to switch between them. This guide has provided a detailed guide on Git worktrees with multiple working directories.