Sometimes developers modify the source code files and commit these changes to the Git repository. However, they don’t want to push them to the remote server. In such a scenario, they can temporarily hold them through stash operation.
When they complete their work on the Git repository, they need to push all changes to the GitHub server. For this purpose, they are required to up-to-date the local repo with remote first. To do so, the “git pull” command can be used.
This study will discuss:
- What are git stash and git pull Commands?
- How to Perform ‘git stash’ in Git?
- How to Use ‘git pull’ Command in Git?
What are git stash and git pull Commands?
The “git stash” command is utilized to temporarily hold the changes. It can be used when the user doesn’t want to add the newly added changes to the Git repository and modify them later. On the other hand, the “git pull” command can be used to download the updated version of the remote repository.
How to Perform ‘git stash’ in Git?
Follow the steps below to keep the most recently added changes with the help of the “git stash” command.
Step 1: Redirect to Git Repository
Navigate to the Git desired repository by typing out the “cd” command:
Step 2: Make and Update File
Then, execute the “echo” command to generate and update the file immediately:
Step 3: Track Changes
Next, push the newly added changes into the staging area through the “git add” command:
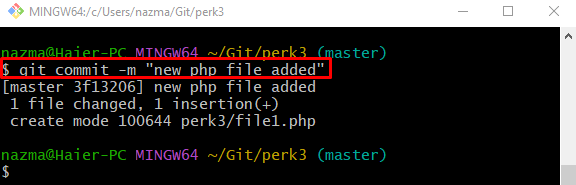
Step 4: Commit Changes
After that, run the “git commit” command to commit all changes to the Git repository:
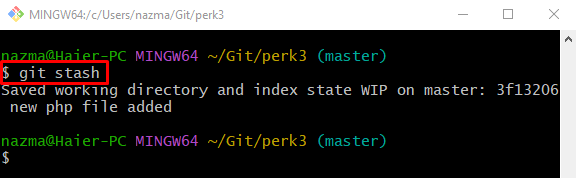
Step 5: Stash Changes
To temporarily hold all added changes, use the “git stash” command:
How to Use ‘git pull’ Command in Git?
To download the updated version of the GitHub repository, perform the below-stated steps.
Step 1: Move to Git Repository
First, switch to the particular repository by running the “cd” command:
Step 2: Create and Update File
Then, run the “echo” command to generate and update the file simultaneously:
Step 3: Push Changes to Tracking Index
Now, add all modifications into the staging area by running the “git add” command:
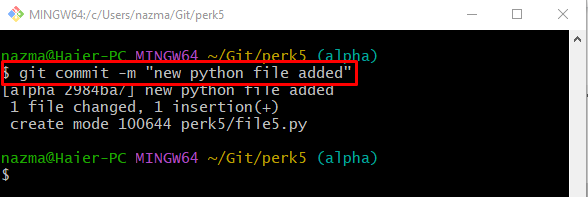
Step 4: Commit Changes
Next, execute the “git commit” command to update the Git local repository:
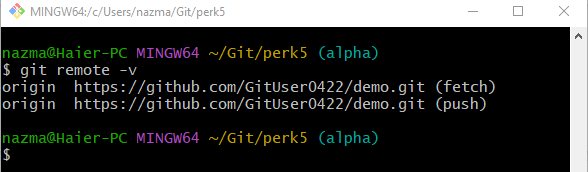
Step 5: View Remote URLs List
To check the existing remote URL list, utilize the “git remote” command:
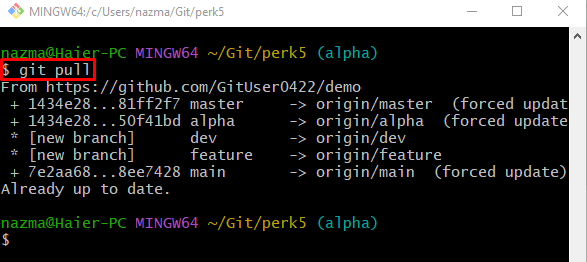
Step 6: Git Pull
Lastly, run the “git pull” command to download the updated content of the remote repository:
That’s all! We have provided the difference between the ‘git pull’ and ‘git stash’ commands.
Conclusion
The “git stash” command can temporarily hold the changes. It can be used when the user doesn’t want to add the newly added changes to the Git repository and modify them later. On the other hand, the “git pull” command can be used to download the updated version of the remote repository. This study elaborated on the “git stash” and “git pull” commands.