This blog illustrated the process of the Git shallow checkout remote branch.
How to Git Shallow Checkout a Remote Branch?
To Git shallow checkout a remote branch, check out the following steps:
- Navigate to the Git particular directory.
- Check the list of remote URLs.
- Clone the remote repository with the specified depth and fetch it.
- Display all existing branches including local and remote.
- Use the “git checkout <remote-branch>” command.
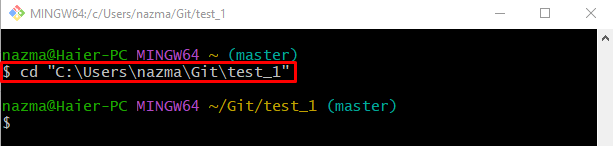
Step 1: Switch to Git Repository
First, go to the Git local repository by running the below-stated command:
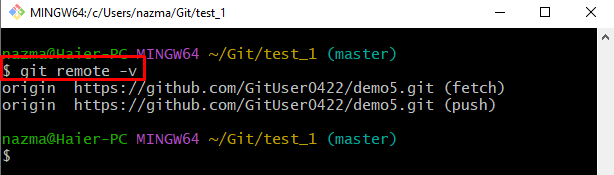
Step 2: View Remote URL List
Then, execute the “git remote” command to show the list of the remote URL:
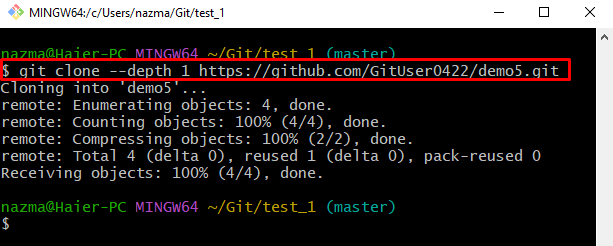
Step 3: Git Clone With Depth ‘1’
Next, clone the Git remote repository by utilizing the “git clone” command along with the desired depth “1”:
As a result, the most recent remote commit will be cloned from the GitHub server:
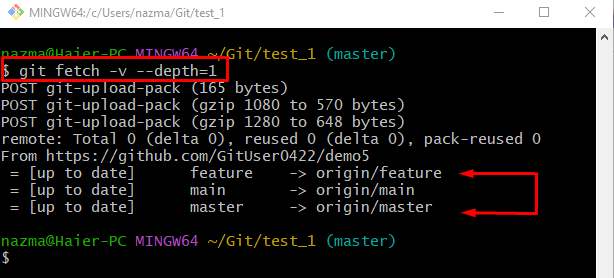
Step 4: git fetch With Depth “1”
After that, run the “git fetch” command to download the latest version of the Git remote repository:
Here, the “-v –depth=1” option is used to hold the amount of data we downloaded:
Step 5: List All Branches
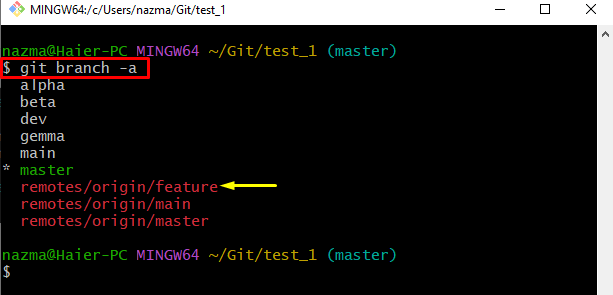
Now, show the list of all existing branches including local as well as remote by using the “git branch” command with the “-a” option for all:
As a result, all branches will be displayed. Now, select the desired remote branch. For instance, we have selected the “remotes/origin/feature” branch:
Step 6: Checkout to Remote Branch
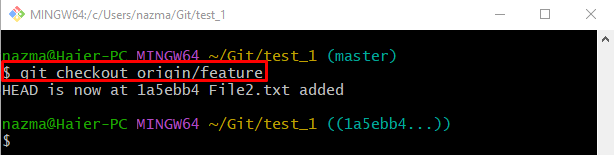
After that, execute the “git checkout” command and switch to the remote branch:
It can be seen that the HEAD is now moved to the “1a5ebb4” SHA-hash:
Step 7: View Branches List
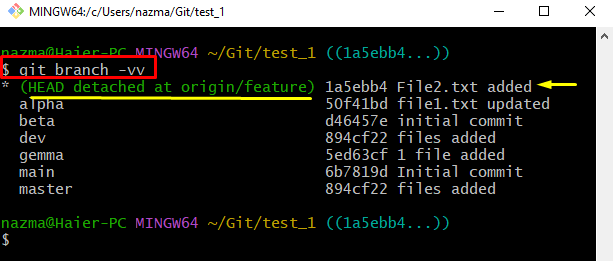
Lastly, run the “git branch” command along with the “-vv” option to view the all branches along with the HEAD pointer detail:
According to the below-provided output, the HEAD pointing to the remote “origin/feature” branch:
We have provided the easiest way to Git shallow checkout a GitHub remote branch.
Conclusion
To Git shallow checkout a remote branch, first, move to the Git particular directory and check the remote URL list. Then, clone the remote repository with the specified depth and fetch it. After that, view the list of all remote and local branches. Lastly, execute the “git checkout <remote-branch>” command. This blog illustrated the process of the Git shallow checkout remote branch.