This guide will differentiate the “git pull” and “git rebase” commands and how these commands work.
Differentiate the “git rebase” and “git pull” Commands
The “git pull” command is utilized for getting the updated version of the Git remote repository and combining them into the local repository. Whereas, the “git rebase” command creates a new commit that combines the two branches and moves the local branch’s commits on top of the remote branch.
How Does the “git pull” Command Work?
To perform the “git pull” operation, follow the provided steps:
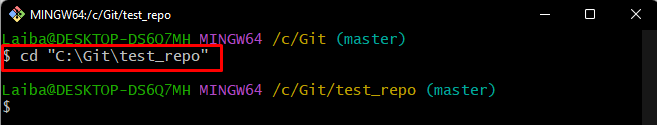
Step 1: Move to Desired Directory
Run the “cd” command along with desired directory path and navigate to it:
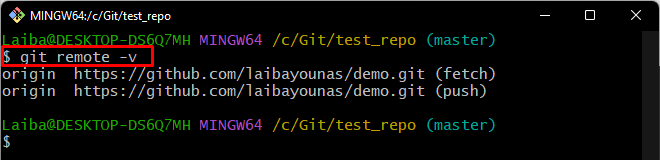
Step 2: Check Remote Origin
Verify whether the local repository is connected with the remote repository by executing the below-given command:
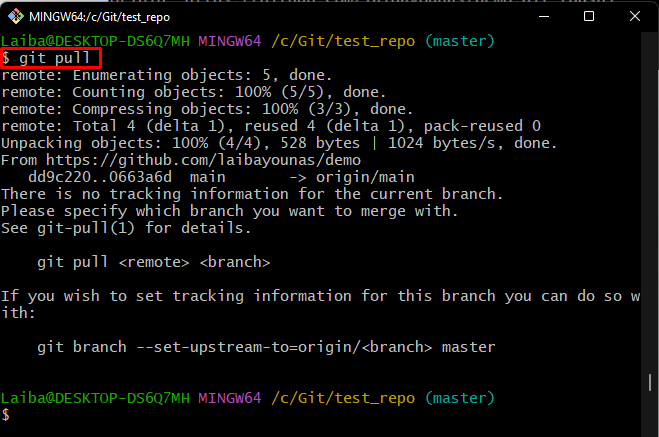
Step 3: Pull Remote Branch Content
Use the given-below command to download the latest content of the Git remote branch
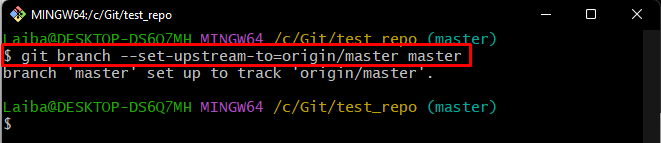
Note: When the “git pull” command is executed for the first time in a specific branch, it is required to set that branch for tracking. To do so, run the below-provided command:
As you can see, the specified branch is set as a tracking branch:
How Does the “git rebase” Command Work?
To perform the “git rebase” operation, check out the following steps:
- Go to the local Git repository.
- Check the remote URL.
- View the list of all branches.
- Execute the “git rebase” command.
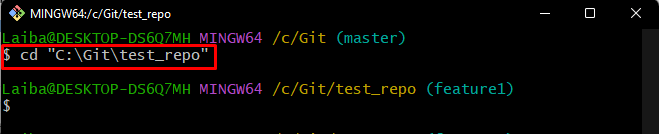
Step 1: Navigate to Particular Directory
At first, move to the desired Git directory using the “cd” command:
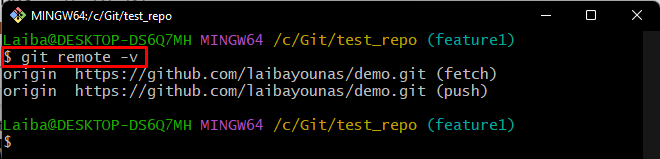
Step 2: Verify Remote Origin
Then, run the “git remote” command to ensure whether the remote URL has been added to the local directory or not:
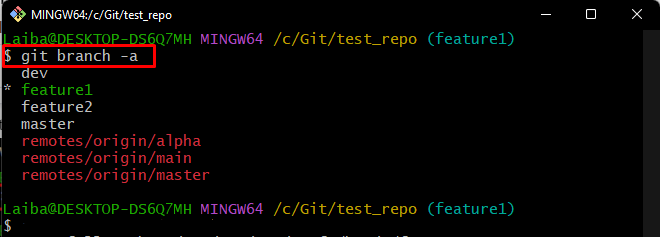
Step 3: View List of Available Branches
To check the list of all local and remote branches, execute the provided command:
The below output shows that there are four local branches and three remote branches and the asterisk “*” symbol beside the “feature1” indicates that it is the current branch:
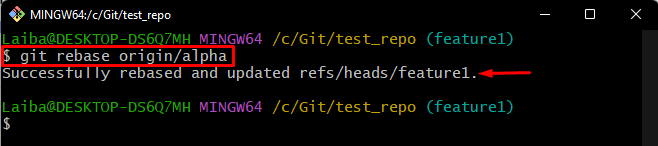
Step 4: Rebase Remote Branch
Finally, run the “git rebase” command along with the desired remote branch to perform rebase operation:
According to the below output, the rebasing process has been done successfully and changes have been integrated from the remote branch to the local branch:
Step 5: Verify Changes
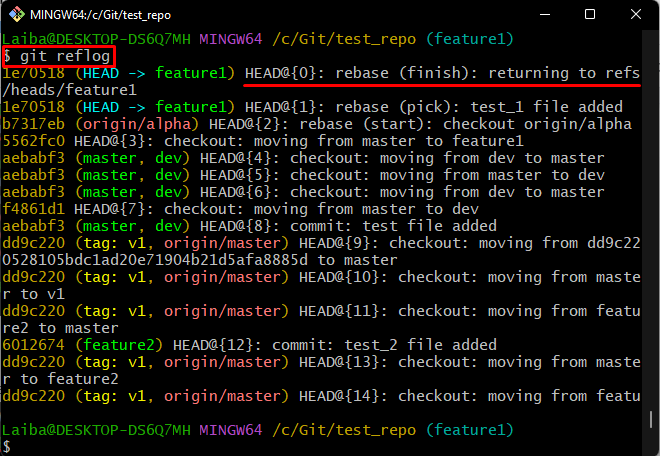
Lastly, check the Git reference log history to view the tracked changes by running the provided command:
It can be observed that the “feature1” branch has been updated with the remote branch by rebasing process:
We have efficiently elaborated the difference between “git pull” and “git rebase” operations.
Conclusion
The “git pull” command is utilized for getting the updated version of the Git remote repository and combining them into the local repository. While the “git rebase” command takes the local branch’s commits and places them on top of the remote branch’s commits. This guide elaborated the difference between “git pull” and “git rebase” commands.