This blog will discuss the easiest way of updating all local branches with remote branches.
Can “git pull –all” Update All My Local Branches?
Yes, the “git pull –all” command is used to update all local branches with the remote repository branches. For this particular purpose, try the below-stated steps:
- Switch to the required repository.
- Check the list of all existing remote URLs.
- Run the “git pull –all” command to download the remote repository branches.
Step 1: Move to Git Local Repository
First, switch to the required repository by running the “cd” command along with its path:
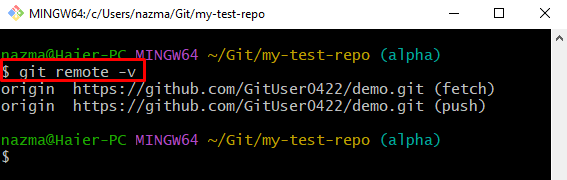
Step 2: Verify Existing Remote URL
Then, execute the “git remote” command to ensure that the remote URL is added:
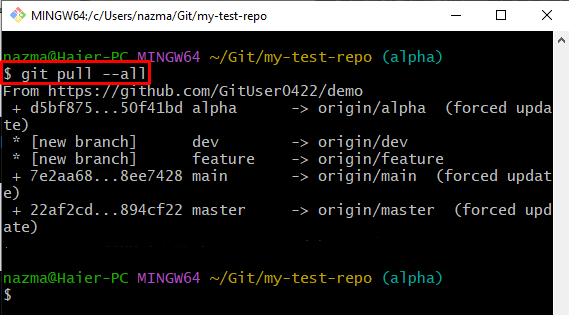
Step 3: Git Pull All Remote Branches
Lastly, execute the “git pull” command to download the entire repository including all branches:
Here, “–all” indicates for all. It can be observed that all remote branches have been pulled successfully:
That’s all! We have illustrated the process of updating all local branches.
Conclusion
To update all local branches with the remote repository branches, first, move to the required repository. Then, check the list of all existing remote URLs. Lastly, run the “git pull –all” command to download the remote repository branches. This blog illustrated the method of updating all local branches with remote branches.