This tutorial will explain the Git merge strategies and options.
What are Git Merge Strategies and Options?
While performing a Git merge operation in Git, users can choose different strategies and options to customize the behavior of the merge operation. Some most commonly used merging strategies are listed below:
- Fast-forward Merge Strategy
- Ort Merge Strategy
- Recursive Merge Strategy
Fast-forward Merge Strategy
It is the default strategy that is used when developers want to merge branches that have a linear commit history. It simply moves the branch pointer to the latest commit of the merged branch, resulting in a fast-forward merge.
Step 1: Navigate to Git Local Directory
First, execute the “cd” command along with the path of the Git local directory for navigating to it:
Step 2: List all Branches
Next, list all branches of the stated repository by using the “git branch” command:
The below-stated output shows that all branches have been listed successfully:
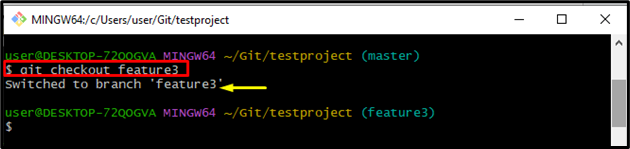
Step 3: Switch to Feature Branch
Next, switch to the feature branch by running the “git checkout” command with the specified branch name:
It can be observed that the branch has been switched successfully:
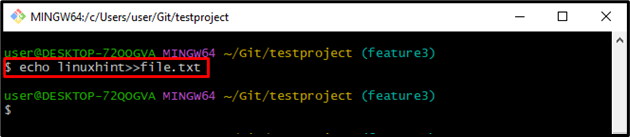
Step 4: Generate and Modify the File
Run the “‘echo” command to create a file and modify it:
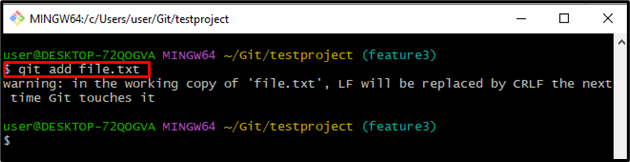
Step 5: Track File
Execute the “git add” command to track all changes from the working area to the staging area:
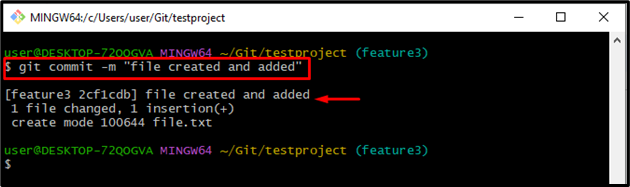
Step 6: Commit Changes
Commit all changes with the help of the “git commit” command and set the message for commit using the “-m” option:
It can be observed that all the changes have been committed successfully:
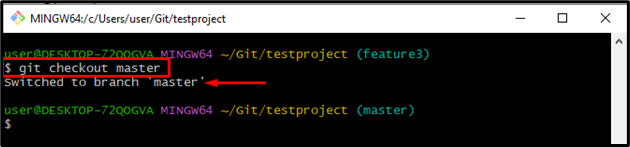
Step 7: Navigate to Master Branch
Switch to the master branch by running the “git checkout” along with the branch name “master”:
You have switched to the “master” branch successfully:
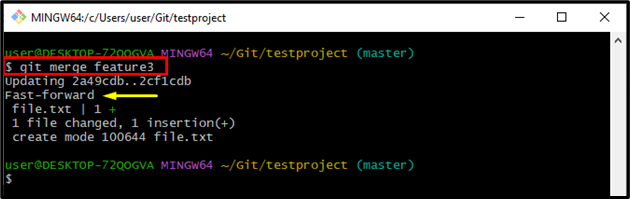
Step 8: Merge with Feature Branch
Run the “git merge” command along with the “feature3” branch to merge it with the “master” branch:
The below-stated output indicates that both branches have been merged with the help of the “Fast-forward” merge strategy:
Ort Merge Strategy
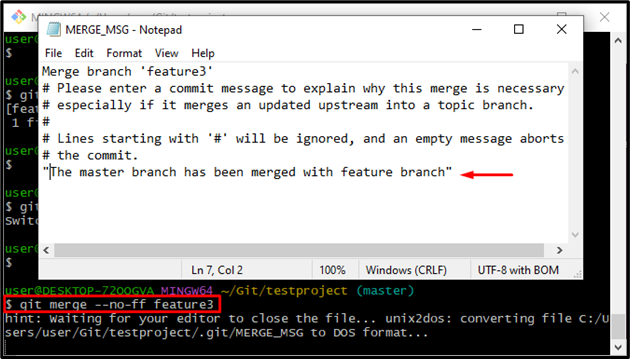
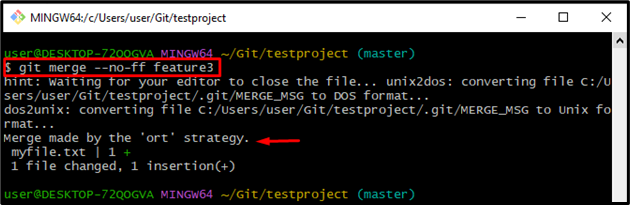
The “Ort” merge is a relatively new Git merge strategy that is significantly faster and addresses correctness problems that exist in the merge-recursive strategy. Because “ort” is the default merge strategy in the latest releases of Git, merge results are now more predictable and consistent between the local machine and GitHub. Utilize the command stated below to perform the Git merge strategy:
The resultant image shows that the default editor has been launched to make a commit message:
The merging operation through the “ort” strategy has been performed successfully:
Recursive Merge Strategy
The recursive merging strategy is the default strategy for merging branches with complex commit histories. It performs a three-way merge, considering the commonality of the branches being merged, and attempts to intelligently merge the changes from both branches. In Recursive merge, after switching branches and making some commits, there are some new original commits on the “master”. So, when it’s time to merge, git resources over the branch and create a new merge commit.
That’s all about Git merging strategies and options.
Conclusion
The Git merge strategies are used to integrate the latest modifications made in one branch into another. To do so, there are various Git merge strategies, including “fast-forward”, “ort”, “recursive” and others used for this purpose. This tutorial demonstrated the Git merge strategies and options.