Example 01:
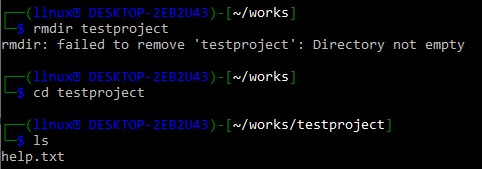
Make sure you have some git folder named “works” in your system. Within this folder, we have another folder named “test” project which is not empty right now. Let’s say we want to remove this folder permanently from our git system. For this, we have tried Ubuntu’s “rmdir” instruction on the shell followed by the name of a directory. It turns out that the directory is not empty so the command is unable to remove it. To investigate this, we have to move in within the folder using the “cd” instruction.
After that use the ls (short key for list) command which displays a list of all the files and folders in a directory or folder. To remove the folder, we need to remove all its inner files and folders first. Use the “rm” command to remove file “help.txt” and then go back to the “works” folder to remove the “testproject” directory.
Example 2: Delete Recursively
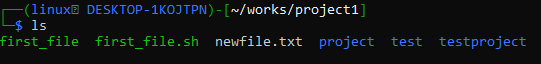
Let’s say, we have created a “project!” folder in the git “works” directory. We are currently in the project1 folder/directory and we have sub-directories and files in it as per the “ls” query.
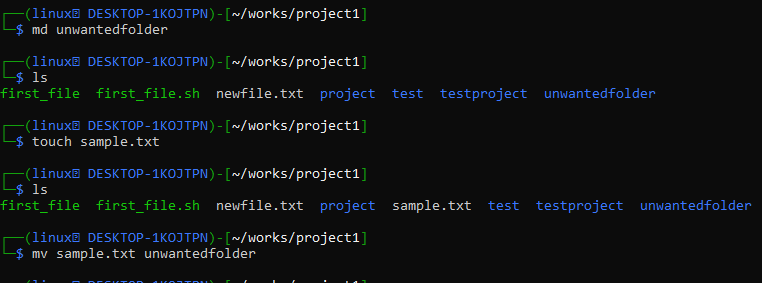
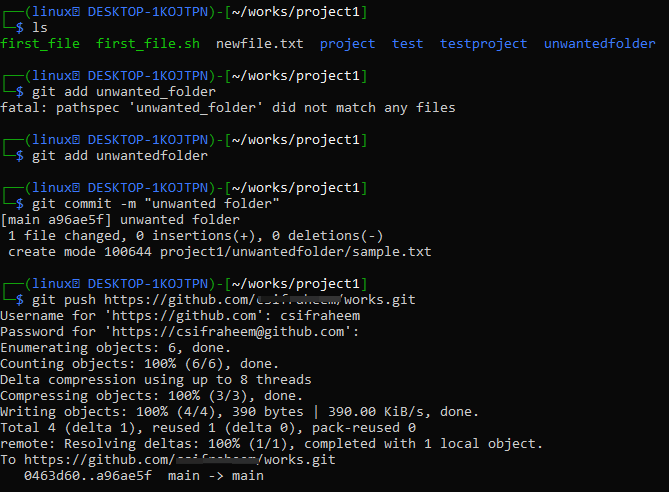
Using the “md” command, new directory called “unwanted folder” was set-up within the “project1” folder. We have created a text file with the “touch” instruction and moved it to the “unwanted folder” using the “mv” instruction on the Kali Linux shell.
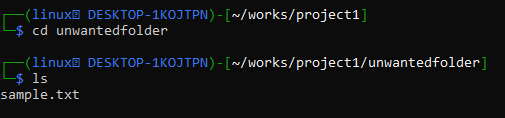
We’ve now navigated to the unwanted folder directory where we can see a list of sub-directories and files. We just have one file in the unwanted folder, sample.txt, as seen in the screenshot below.
Now move back to the “project1” git working directory and list all its folders and files.
To add a newly created folder to GitHub remote repository, we need to use the “git add” instruction along with the name of a folder. Git commit will reflect the changes made to the directory while the git push instruction followed by the remote Github link will let us reflect the changes made to the local repository reflect at remote git as well. Now, this updated version is updated at both local and remote Github.
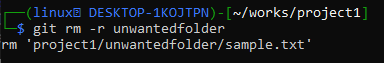
To delete the folder from the git repository recursively, we have to use the “rm” command followed by the “-r” option and the name of a folder as shown below.
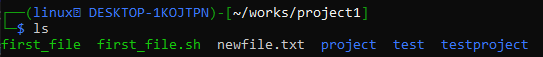
To ensure that our remove directory command worked, use the ls command to check that the unwanted folder was removed from the git repository. Now, you can use the git commit and git push instructions to reflect the change at the remote system as well.
Example 3: Delete a directory by force
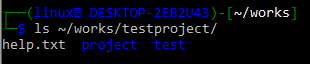
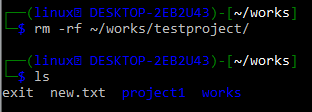
To remove a folder containing other files or folders within it, we have to use the “-rf” option along with the “rm” command. Assume you have a directory named /works/testproject/ of Git that contains the following two sub-folders and one text file i.e. help.txt, project, test.
If you use the rmdir command, you’ll get the same “Directory no empty” error on your shell.
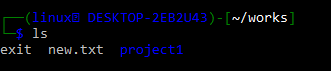
As previously stated, rmdir only deletes empty directories. Thus, to remove an entire directory in Linux without considering its internal parts, we have to use the rm command followed by the -rf option and the path to the folder. We can check that we successfully deleted the testproject by running the ls command on the works folder, which reveals that there is no directory testproject in the works folder.
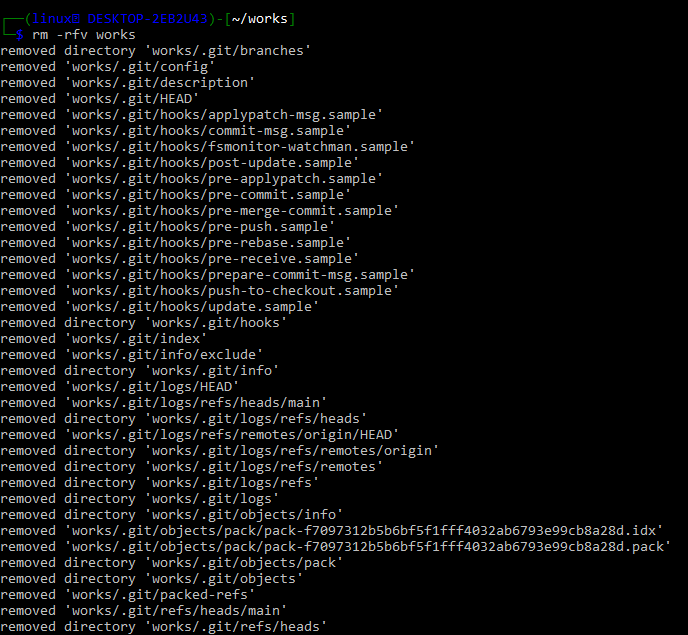
To generate a more verbose output, we have to use the -v option with the rm command. On Linux, for example, delete the entire git directory /works/works and display the output of the complete log on the screen using the rm command with the “v” parameter. This command comes in handy when we need a detailed list of the files and directories we’re removing from a directory. Each parameter in the below-shown command has a purpose, which is outlined:
- -r stands for recursive deletion.
- -f: Remove a directory with force.
- -v: It has a screen-based output, which means it displays all information about files and directories removed using the rm command.
Finally, you must ensure that the needed delete operation is completed. As can be seen, there is no folder called works in the directory (works).
Example 4: Using rmdir Command
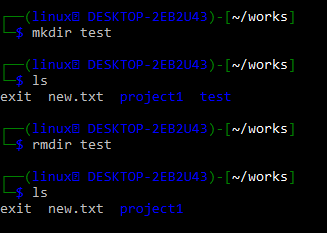
It’s beneficial when you just want to delete a folder if it’s empty rather than checking whether it’s empty or not. The command “rmdir” is used to delete empty directories. When you want to delete the empty directory, you must use the rmdir statement or explicitly remove the contents. The following is an example that shows how we created a “test” directory in git and removed it with the “rmdir” instruction.
Conclusion:
We have discussed the use of different commands to delete directories from git in bash. You need to understand that you cannot undo the action of “rm” instruction as it eliminates without regard for the concept of ‘waste.’ Some Linux and UNIX-like operating systems minimize its disruptive capabilities by typically aliasing it to rm -I, even if not all of them do.