This write-up will provide the easiest way of resolving the “nothing to commit” issue.
How to Resolve git add . -> Still “nothing to commit” With New Files Issue?
When the Git users tracked the changes through the “$ git add .” command, sometimes these changes are not added to the staging area. However, they exist in the repository list of content. To solve this conflict, developers need to add changes through the “$ git add –all” command.
Let’s have a look at the implementation of the above-discussed scenario!
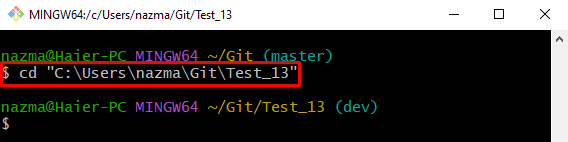
Step 1: Navigate to Git Local Repository
First, execute the “cd” command to navigate to the required local directory:
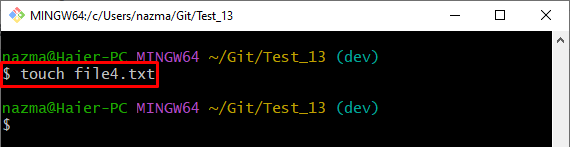
Step 2: Generate Text File
Then, create a new text file in the working area through the “touch” command:
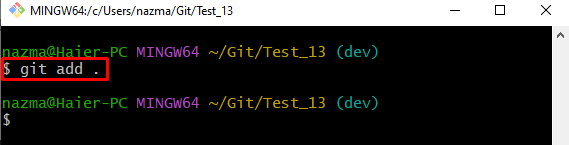
Step 3: Track Working Area Changes to Staging Index
After that, run the “git add .” command to add changes to the staging area:
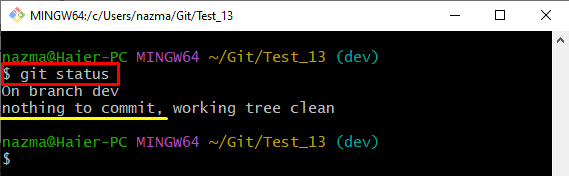
Step 4: Check Status
View the status of the current repository by running the “git status” command:
According to the below-provided output, the added changes are not pushed to the staging index:
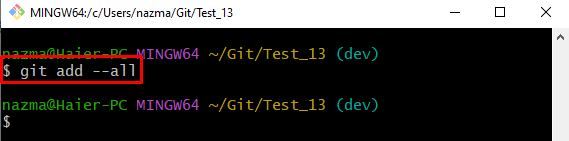
Note: To resolve the above-described issues, you need to again track the changes through the “git add” along with the “–all” flag, which will add all the performed changes to the staging index:
Step 5: Check Status
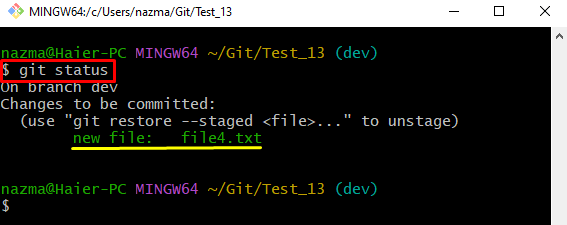
Lastly, run the “git status” command to view the current status of the repository and verify the added changes are tracked:
Here, you can see the staging area contains the tracked changes:
Here you go! You have learned the easiest way to resolve the “nothing to commit” issue.
Conclusion
Sometimes, when developers push the changes using the “$ git add .” command, these are not added to the staging area but are shown in the repository content list. To solve this conflict, developers need to add changes through the “$ git –all” command. After that, check the status to verify the tracked changes. This write-up illustrated the procedure for resolving the “nothing to commit” issue.