“getent” is a Linux command that allows users to fetch details from several text files called databases. The “getent” uses the same service name as the system, and it will display all user details and network information.
It contains various databases:

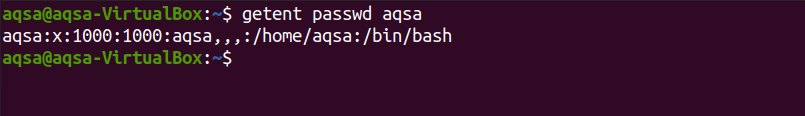
- passwd: can be used to check the user’s username, user’s ID, home folder, and full name.
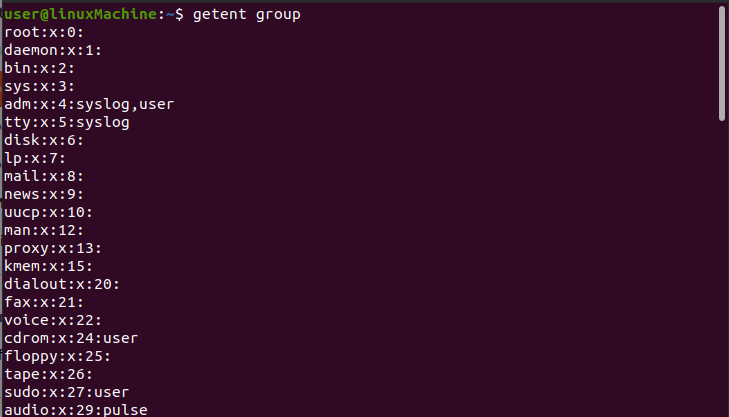
- groups: shows all the groups of your Linux system.
- services: gives information on all Linux services that are configured on your system.
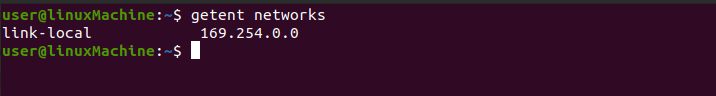
- networks: shows the networks of your system.
- protocols: tells us about our network protocols.
This post is focusing on how to fetch data from different databases.
Syntax:
Here’s the syntax of the “getent” command:
How to use the “getent” Command:
Options:
The “getent” command has various options; let’s discuss them with examples:
getent passwd:
Use “passwd” as a database to get the information of the currently logged user. It displays the username, user’s id, and folder name. Run the command:
$ getent passwd aqsa
getent group:
If you want to get all group details on Linux, use “group” with the “getent” command:
getent services:
Use “services” with the port number to find the service name and its protocol, For instance:
FTP-data server uses port no. 20 with TCP protocol.
An FTP server uses port no. 21 with TCP protocol.
SSH server uses port no. 2 with TCP protocol.
$ getent services 21
$ getent services 22
getent networks:
Use the “networks” option to check the network and IP address of your system.
getent hosts:
Use the “hosts” option to get the IP address. The hostname of my Linux system is “linuxMachine”. So, I will pass linuxMachine as a parameter and give the host’s IP address.
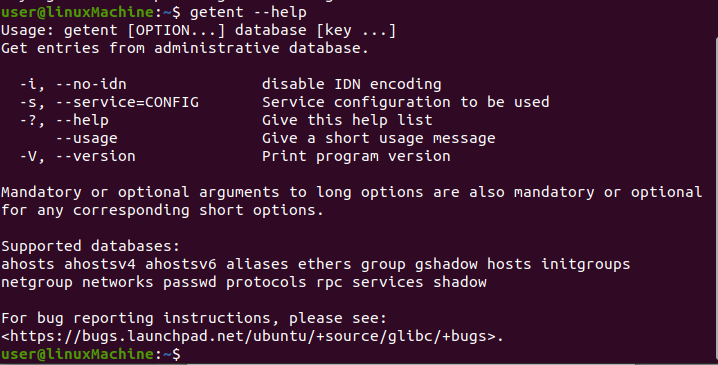
getent help:
To print the help message in the terminal, type the “–help” command. It will print all the related options, usage, and support databases of the “getent” command.
getent usage:
If you want to know how to use of “getent” command, use the below-given command:
getent version:
To get detailed information about the “getent” version, use:
Conclusion:
Getent command is used to look up the user information on Linux. The “getent” command collects data from the defined administrative database. We can get user’s account information, IP address, servers, protocols, and some other information from the specified database. Through this tutorial, we have seen how to use the “getent” command with different options.