Prerequisites:
Before practicing the script of this tutorial, you must complete the following tasks;
- Install the Django version 3+ on Ubuntu 20+ (preferably)
- Create a Django project
- Run the Django server to check the server is working properly or not.
Setup a Django App:
1. Run the following command to create a Django app named geturlapp.
2. Run the following command to create the user that will be used to access the Django database. If you have created the user before then you don’t need to run the command.
3. Add the app name in the INSTALLED_APP part of the settings.py file.
…..
'geturlapp'
]
4. Create a folder named templates inside the geturlapp folder and set the template’s location of the app in the TEMPLATES part of the settings.py file.
{
….
'DIRS': ['/home/fahmida/django_pro/validationapp/templates'],
….
},
]
Create and Modify the Necessary Files:
Three different HTML files were created in this part of this tutorial to display the current URL in three different formats.
Create the index.html file with the following script to display the domain name of the current URL only.
index.html
Create the index2.html file with the following script to display the domain name with the path of the current URL.
index2.html
Create the index3.html file with the following script to display the domain name with the path and http of the current URL.
index3.html
Modify the views.py file of the geturlapp folder with the following script. Three functions had been defined in the script to return the current URL value in three different formats to the template. The geturl1() function has been defined to retrieve the domain name of the current URL and send it to the index.html file. Request.get_host() function has been used to retrieve the domain name of the current URL. The geturl2() function has been defined to retrieve the domain name with the path of the current URL and send it to the index2.html file. On the other hand, request.path attribute has been used with the request.get_host() function to read the path with the domain name of the current URL. The geturl3() function has been defined to retrieve the domain name with the http and the path of the current URL and send it to the index3.html file. request._current_scheme_host attribute has been used to retrieve the domain name with http. The return value of each function will be passed to the template using the showURL tag.
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
# Read only the domain name of the current URL
def geturl1(request):
urlObject = request.get_host()
return render(request, 'index.html', {'showURL': urlObject})
# Read the domain name with the path
def geturl2(request):
urlObject = request.get_host() + request.path
return render(request, 'index2.html', {'showURL': urlObject})
# Read the domain name with the http and path
def geturl3(request):
urlObject = request._current_scheme_host + request.path
return render(request, 'index3.html', {'showURL': urlObject})
Modify the urls.py file of the geturlapp folder with the following script. Three paths had been defined in the script for accessing the three functions of the view file. The empty string(”) path will be used to call the geturl1() function. The ‘index2’ path will be used to call the geturl2() function. The ‘index3’ path will be used to call the geturl3() function.
urls.py
from django.urls import path
# Import view
from geturlapp import views
# Define paths to read current URL
urlpatterns = [
# Display the domain name in the template
path('', views.geturl1),
# Display the domain name with path in the template
path('index2', views.geturl2),
# Display the domain name with http and path in the template
path('index3', views.geturl3),
]
Output:
Run the following command to start the Django server.
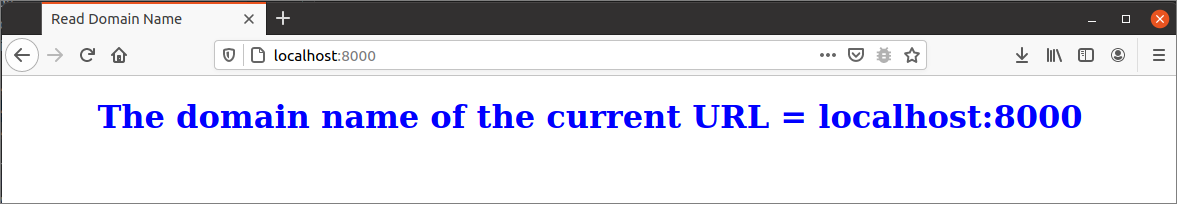
Execute the following URL from the browser to display the domain name of the current URL. The geturl1() function will be called for this URL that will send the domain name to the index.html file.
The following output will appear after executing the script.
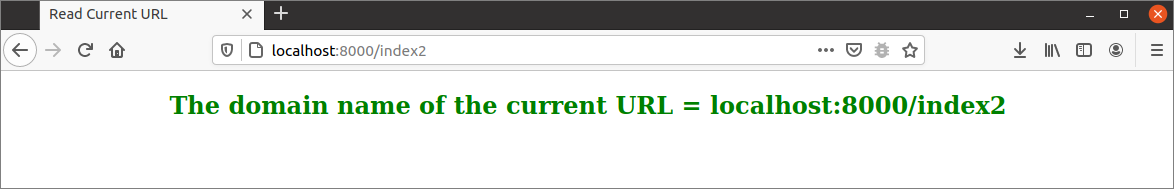
Execute the following URL from the browser to display the domain name with the path of the current URL. The geturl2() function will be called for this URL that will send the domain name with the path to the index2.html file.
The following output will appear after executing the script. Here, the path is index2.
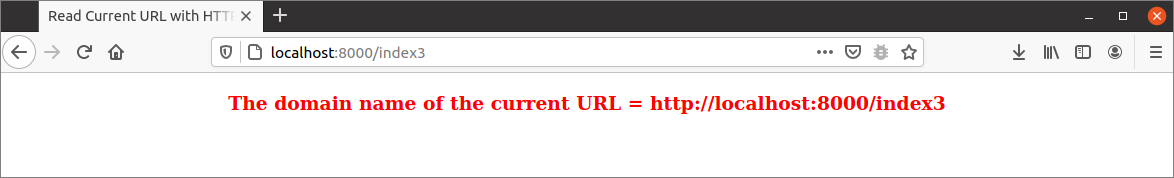
Execute the following URL from the browser to display the domain name with the http and the path of the current URL. The geturl3() function will be called for this URL that will send the domain name with the http and the path to the index3.html file.
The following output will appear after executing the script. Here, the path is index3.
Conclusion:
The current URL can be displayed in the Django template using the method and the attributes of the request object. Three templates had been created in this tutorial to display the current URL in three different ways that will help the readers to know the way of reading the current URL in the Django template.