To connect to the authorized client machine, we generate the SSH keys which are unique and can connect to the host machine after entering those unique SSH keys into the client machine. So, in this blog, we will explore a method by which we can generate the SSH keys on Ubuntu.
How to generate the SSH keys on Ubuntu
First, we will make sure that the SSH server is installed on both the client and host machine. If it is not installed, install it first by following our dedicated installation guide.
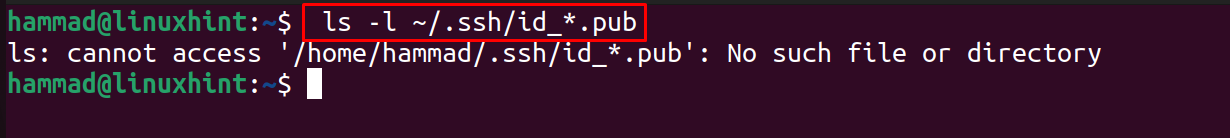
To begin with the generation of SSH keys on Ubuntu, we will start with the client machine. First, verify whether there are keys already generated or not. To verify, use the command typed below:
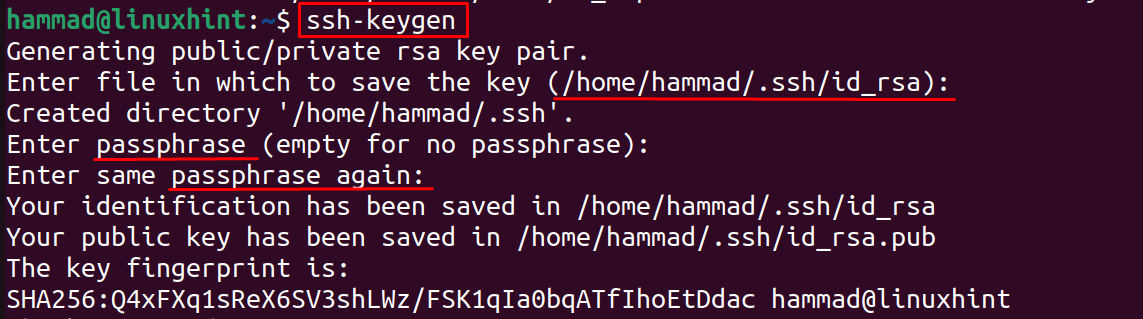
In the above figure, we can see that there is no directory which means that there is no SSH keys on the client machine, so now we will generate the SSH key on the client machine using the command:
When you run the above command:
- it will ask you to enter some directory where you want to store the SSH keys, and if you press “ENTER” key without typing any directory, then it will store the SSH keys on the default path which is displayed in next line.
- Later, it will ask you to enter a passphrase and re-type it again to confirm the passphrase, the passphrase is used to have more security.
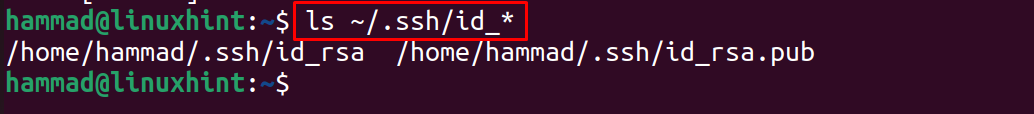
Once the key is generated, the next step is to verify the generation of SSH keys by running the command:
So, it has displayed the SSH keys file.
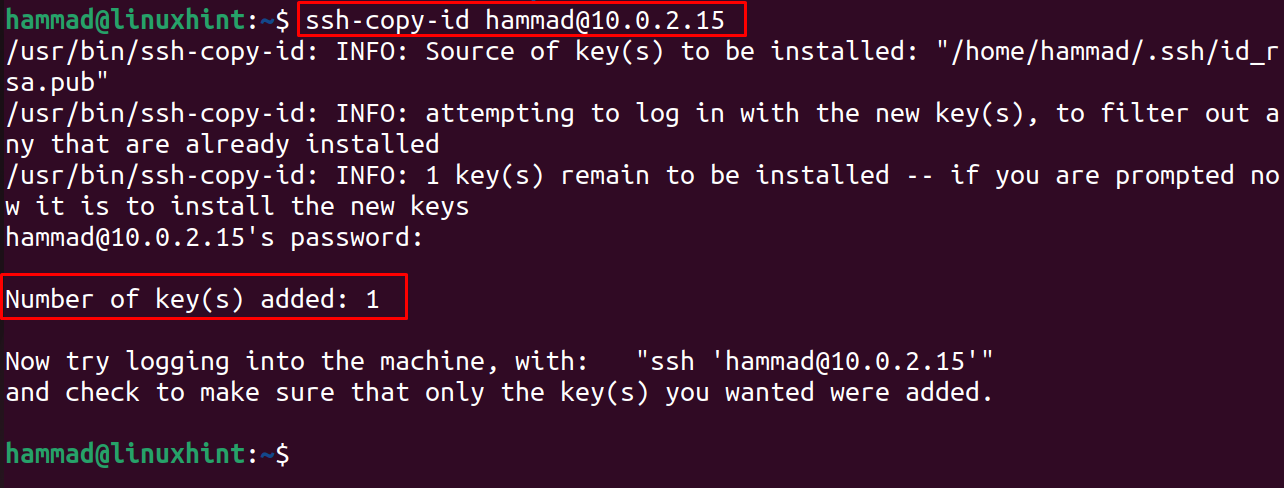
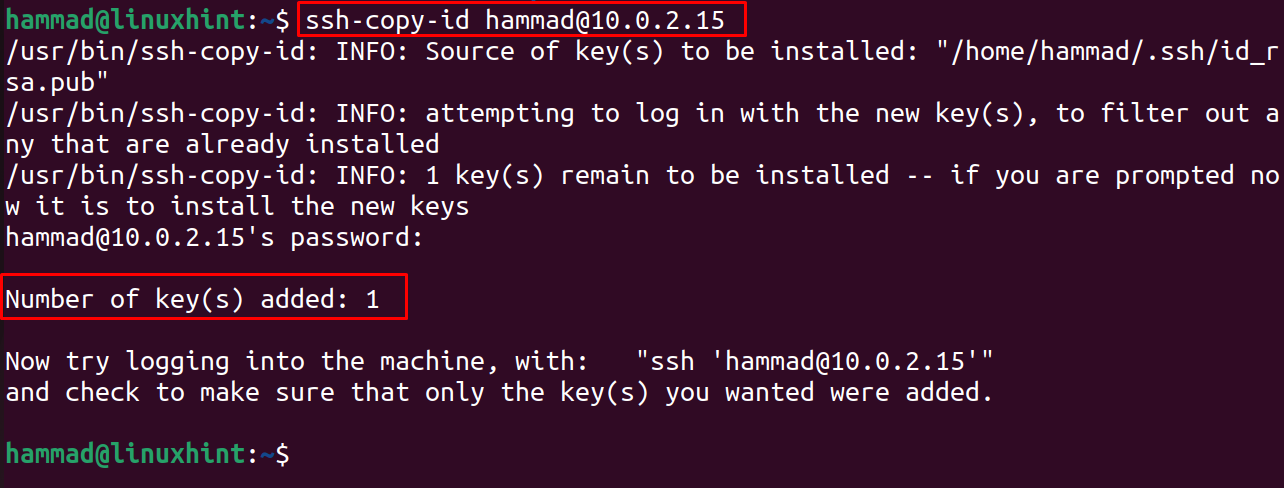
Now, to copy the SSH keys on the machine to which we want to connect remotely(host). For this, we should know the IP address as well as the username of that machine. In our case, the user name is “hammad”, the ip address is “10.0.2.15”:
It will ask you to enter the password of the remote(host) machine; enter the password and hit “Enter”:
The SSH keys are successfully copied to the Host machine.
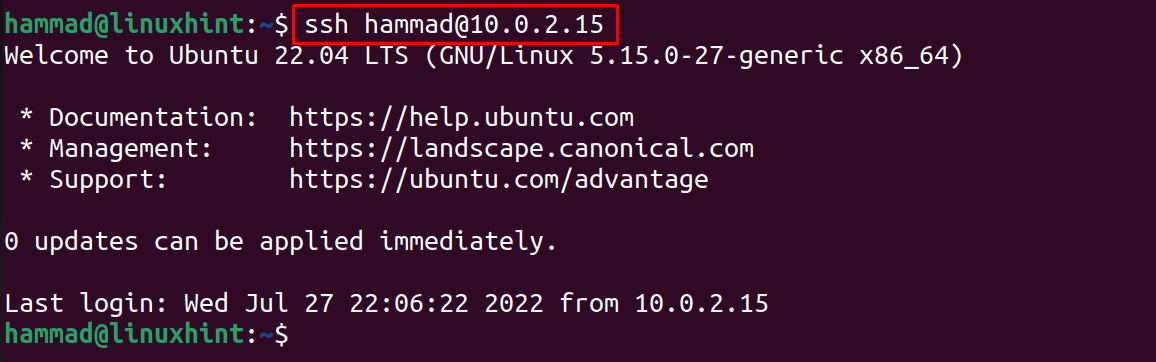
Finally, we will connect with the machine, using the command:
As you can see, we are signed into the machine.
How to configure SSH on Ubuntu 22.04?
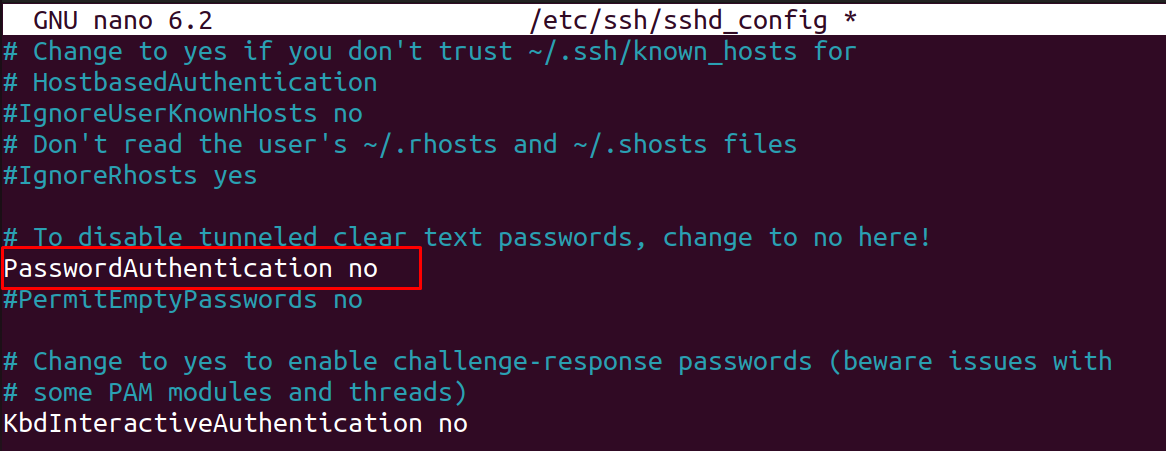
If you want to disable the identification method, then simply open the “ssh_config” file in the client machine using the nano text editor:
Find out the line “PasswordAuthentication ” and then changed the “Yes” with “no”:
Exit from the file and reload the service of ssh using the systemctl command:
The service is reloaded and status can be verified using the option of status with the systemctl command:
Conclusion
The SSH server is used to connect with the other machines remotely and to have a secure connection with them, we generate the SSH keys on Ubuntu 22.04. In this blog, the method of generating the SSH keys on Ubuntu has been explained.