Main Features of GameMode
GameMode is being developed and maintained by “Feral Interactive”, a Linux friendly game development and publishing company that specializes in porting Windows based games to Linux, Android, iOS, macOS and game consoles. You can use GameMode to optimize performance of games on a case-by-case basis without applying it system wide. This allows you to have better control on gaming performance. GameMode optimizes gaming performance by tweaking process priority order, changing CPU and GPU governors to performance mode, optimizing I/O throughput, changing kernel scheduler settings and blocking screensaver mode. Since GameMode runs on a per-game basis, the tweaks applied are only temporary and they are disabled when a user quits a game to the desktop.
Installing GameMode in Linux
You can install GameMode in Ubuntu by using the command below:
GameMode is available in stock repositories of many Linux distributions, so you can search for it in the package manager and install it from there. You can also compile it from its full source code available here.
Verifying that GameMode has been Installed Successfully and Working Correctly
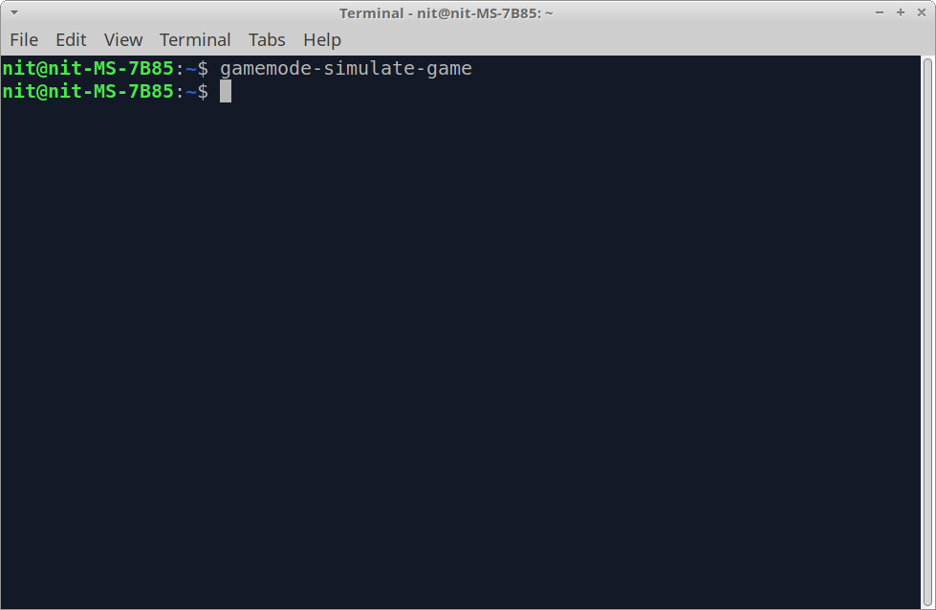
The GameMode package ships with a utility command that can be used to simulate the effects of various tweaks applied by the main GameMode command. This command can be used to verify if GameMode has been installed successfully in your Linux system and if it is working as intended. To simulate GameMode, run the following command:
If the GameMode is working correctly in your Linux PC, this command will exit without producing any output or without throwing any error after running for around 10 seconds.
In case of any issue, the simulation command will throw an error message in the terminal and you can use it to identify / debug the problem.
Using GameMode with Native Linux Games
To run linux games with GameMode optimizations, run a command in the following format:
Replace the text in quotes with either game command or with the full path to the game executable binary.
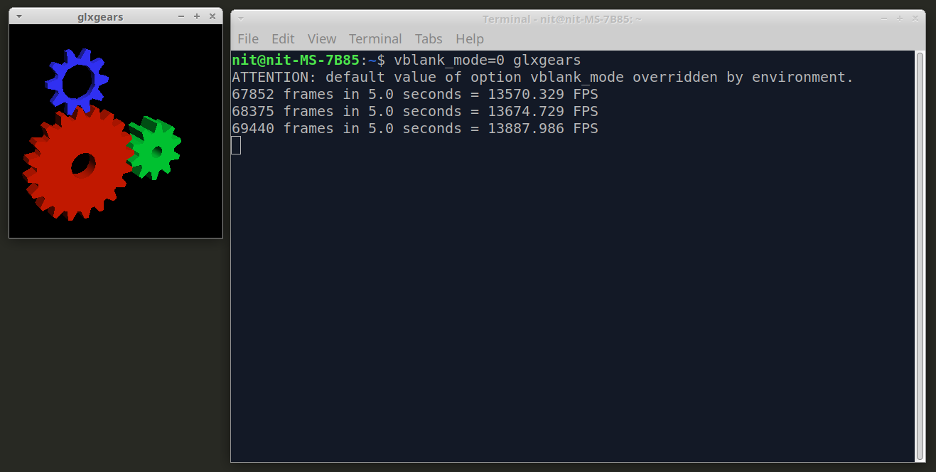
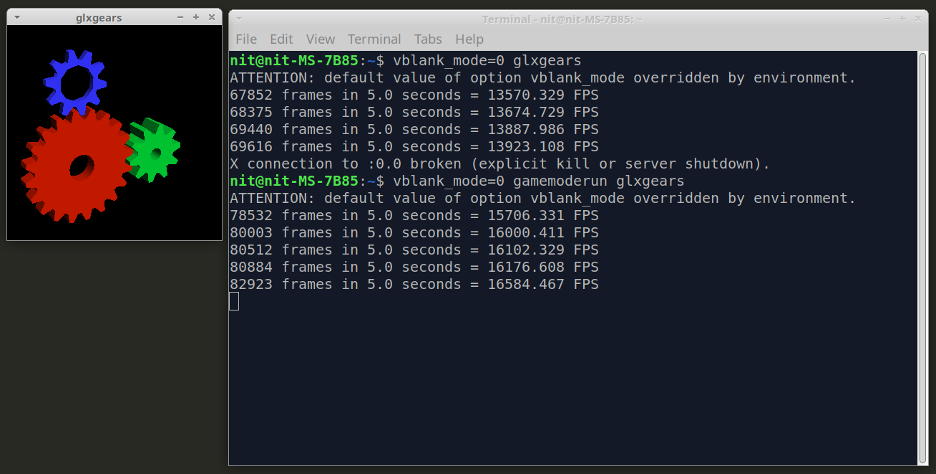
Here is a small benchmark I performed using the “glxgears” app available for Linux (command executed with vsync disabled). It shows the effect of GameMode and how it boosts FPS of GPU intensive games and apps.
Frame rate before using GameMode:
Frame rate after using GameMode (second output block):
As you can see in the output, there is over 15% increase in FPS. However, depending on the game you are running and CPU / GPU configuration of your Linux system, this gain can be higher or lower and results may vary.
Note that GameMode may increase power consumption of your Linux system and if you are running GameMode on battery power without an AC power connection, you may observe increased battery drain.
Using GameMode with Wine Games
Wine is a compatibility layer that allows you to run Windows based apps and games in Linux. To use GameMode with Wine games, add “gamemoderun” command just before the main “wine” command. Here is an example:
Using GameMode with Native and Proton Games Launched from Steam Client in Linux
Proton is based on Wine and it is being developed by Valve, creators of the Steam game store and Half-Life games. Proton comes with many additional features and optimizations over the vanilla Wine implementation and it is specially designed to further improve performance and compatibility of Windows based games in Linux. Proton, also called SteamPlay, is baked into the official Steam client for Linux.
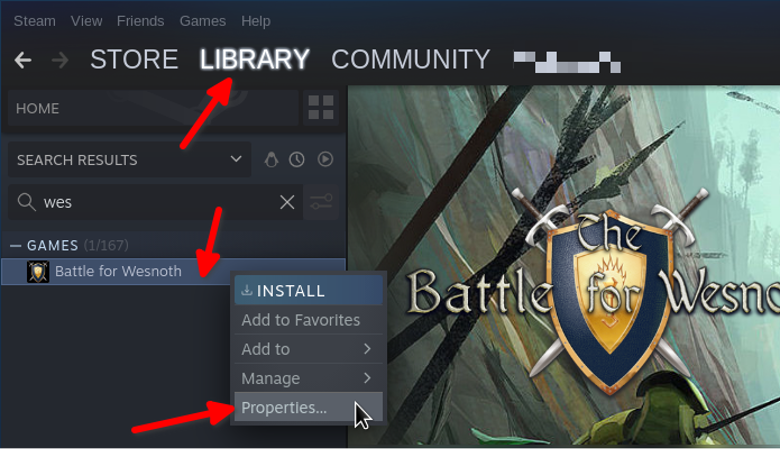
To run GameMode with both native and Windows based games installed in Steam using Proton, go to your game library in the Steam client, right click on game entry and click on “Properties” menu option, as shown in the screenshot below:
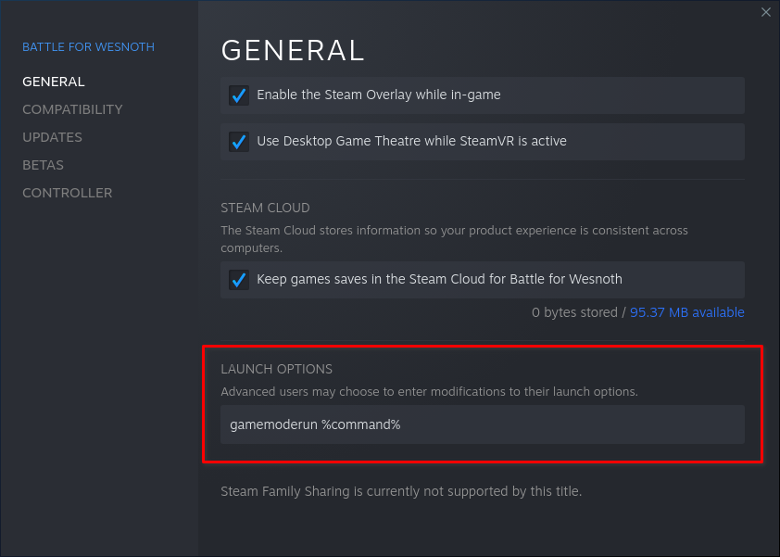
You will get a new configuration window. Under the “GENERAL” tab, enter the following command under “LAUNCH OPTIONS” input box and then run the game.
Here is a screenshot showing the final result:
Customizing GameMode Settings
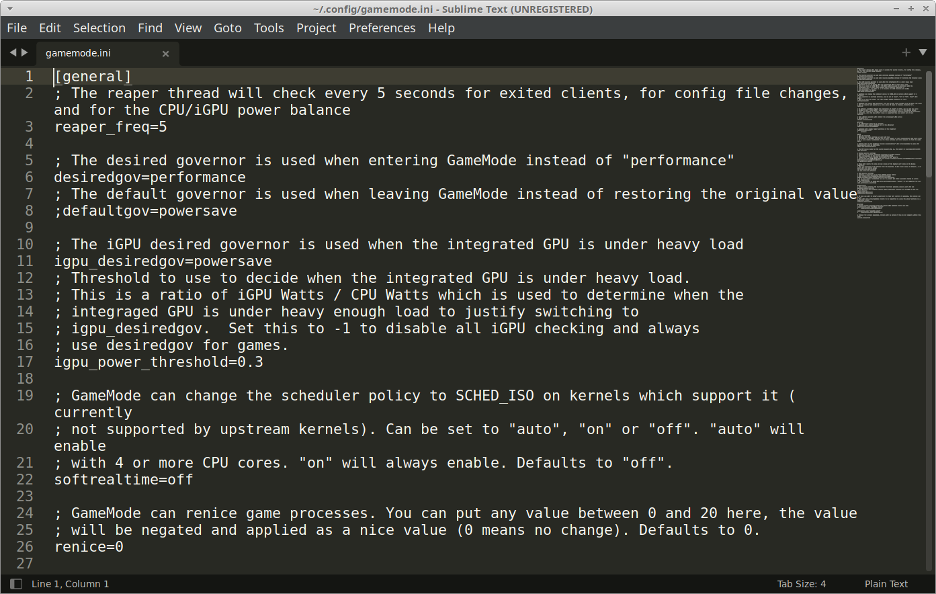
To customize GameMode settings, you will need to download and modify its configuration file in “ini” format. You can download the official configuration file from here. Once downloaded, copy it to the “$HOME/.config/” folder. Next time when you run GameMode, it will automatically pick up various configuration parameters present in this file. The configuration file is self explanatory, with detailed comments and descriptions left by developers themselves.
More information about GameMode configuration files can be found here.
Conclusion
GameMode can be used to significantly increase performance of both native and non-native games in Linux. It is also designed to be run on a per-game basis and it automatically removes optimizations when a game is closed. This allows you to resume your work on desktop and use other apps without performing a full logout or reboot.