Let’s have a start by opening Ubuntu’s terminal shell with the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl+Alt+T”. Within the terminal shell, we will be utilizing the apt package to update the system with an update keyword. Add your system password, press Enter, and you are good to go. Within a few seconds, our system will get updated.
Before going towards the examples of using “fputs” in C, we need an empty file within our system. Therefore, we have to use Ubuntu’s touch instruction within the console terminal to create a new text file quickly. Right now, we have been naming it as “file.txt”. This file has been created within the system’s home folder. You can go towards the folders to see.
![]()
The file must be empty as we have just created it. Let’s confirm that it is empty. You have to use the “cat” instruction of Ubuntu on the console query area along with the file name. Simply type the shown below command in the image at the query area and execute it by pressing the Enter key. The output is showing nothing because the file is empty. Let’s get started with our examples now.
![]()
Example 01:
Firstly, you have to ensure that your Ubuntu system has a C compiler installed already, i.e. “gcc”. Without it, we will be unable to make our code executed.
Let’s start our first illustration with the creation of another file. This time, our file will be of the “C” type, i.e. having a C language extension. The very same “touch” query will be again utilized so far to create it. You can take a look at the home folder of your Linux system to see the empty file. We have named this file “fputs.c”.
It is time to open this file within an editor of Ubuntu to start doing code. We have preferred the “nano” editor here, i.e. use nano with the file name to open it.
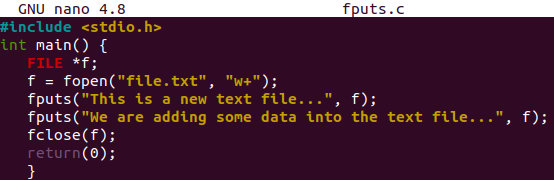
The empty file will be launched in Ubuntu’s nano editor. The code will be started by the C standard input output header library, i.e. stdio.h. This will be added by the “#include” keyword. The main() function has been started with the declaration of the pointer type File descriptor “f” using the FILE stream object.
The fopen() function of the file stream will be used to open the newly made text file, i.e. file.txt in writing mode. The function return value, i.e. true/false, will be saved to file descriptor “f”. If the file is successfully opened, we will use the fputs() function to add some data into the file using the file descriptor “f” as a file stream.
We have been adding two different lines using the fputs() function along with the file descriptor “f’. After that, the fclose() function will be using the file descriptor to close the opened file. The main() function has been completed here to execute.
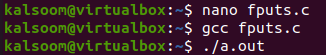
After saving our code, we have to compile it with the “gcc” compiler. Run the code file after the compilation with the “./a.out” shown below command. It will display nothing in return.
Let’s check out the file contents using the “cat” command again. You can see that two string sentences have been written to the file.
Example 02:
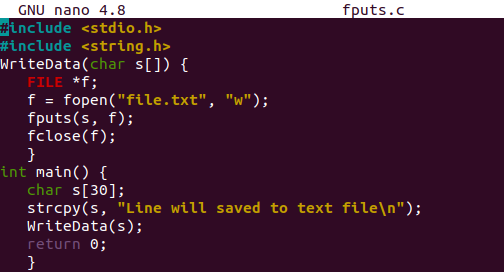
Let’s go through another example. The user-defined WriteData() function takes a character type variable in its argument. We have declared a file descriptor “f” with C Filing object FILE.
The fopen() function is here to open the text file “file.txt” in the write mode and save the response within the file descriptor “f”. The fputs() function writes the passed string “s” value to the file using the file descriptor “f”.
The main() function has been declaring a character variable “s” of size 3. The string line has been copied to the variable “s” using the “strcpy” function. The function “WriteData” has been called and passed the variable “s” in its parameters. The code has been completed here.
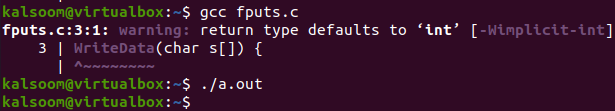
Make your file compiled with the “gcc” command and run it with “./a.out” as below.
Now, check the file.txt file via the “cat” instruction. You can see that the string has been successfully written in the file.
Conclusion:
This was all about using the fputs function of C file handling in our C code while working in Ubuntu 20.04 system. We have discussed two examples by passing a string variable to a user-defined function and directly passing a string value to the fputs function. Both are yielding the same results, i.e. writing data in the file.