Syntax
Different syntaxes of foreach loop are given below.
A. foreach var (array) {
statement(s);
}
The above foreach loop is used to iterate the array values.
B. foreach var (file_handler) {
statement(s);
}
The above foreach loop is used to read the content of a file.
C. foreach var ( ) {
statement(s);
}
The above foreach loop is used to read the user inputs.
Different uses of the foreach loop have been shown in the next part of this tutorial.
Example-1: Read a One-Dimensional Array
Create a PERL file with the following code that will iterate the values of a one-dimensional array using a foreach loop and print each value of the array in a line. An array of 5 string values has been defined in the code. In each iteration of the loop, each value of the array will be parsed and printed in the output with the newline.
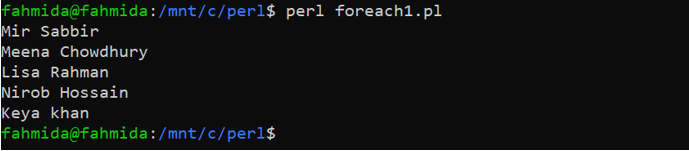
@students = ("Mir Sabbir", "Meena Chowdhury", "Lisa Rahman", "Nirob Hossain", "Keya khan");
# Iterate the array values using the foreach loop
foreach $value (@students)
{
# Print the array value
print "$value\n";
}
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
Example-2: Read a Two-Dimensional Array
Create a PERL file with the following code that will iterate the values of a two-dimensional array using a foreach loop and print each value of the array in a line. A two-dimensional array of 4 rows and 3 columns has been defined in the code. An extra newline has been added after iterating all values of a row. The values of each row have been parsed by using the object variable defined in the loop.
@students = (
{
id => '20227856',
name => 'Neha Ali',
marks => 89
},
{
id => '20224523',
name => 'Mizanur Rahman',
marks => 95
},
{
id => '20221278',
name => 'Ruhul Amin',
marks => 69
},
{
id => '20228956',
name => 'Mehrab Hossain',
marks => 70
},
);
# Iterate the array values
foreach $std (@students)
{
# Print the array values
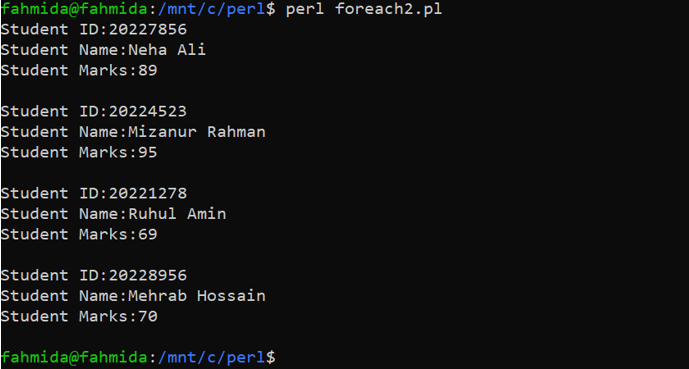
print "Student ID:", $std->{'id'}, "\n";
print "Student Name:", $std->{'name'}, "\n";
print "Student Marks:", $std->{'marks'}, "\n\n";
}
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
Example-3: Read the Range of Values
Create a PERL file with the following code that will iterate the foreach loop based on the values of a range array. In each iteration, a number value will be taken from the user and inserted into an array. The values of this array will be printed after completing the iteration of the loop.
@lines;
# Iterate the loop 4 times
foreach $numbers (1 .. 4)
{
# Print message for the user
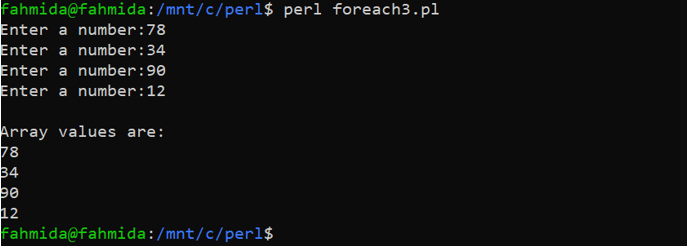
print "Enter a number:";
# Take input from the user
$line = ;
# Add the input value into the array
push @lines, $line;
}
# Print the array values
print "\nArray values are:\n", @lines;
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
Example-4: Read the Content of a File
Create a text named myfile.txt with the following content before testing the code of this example.
myfile.txt
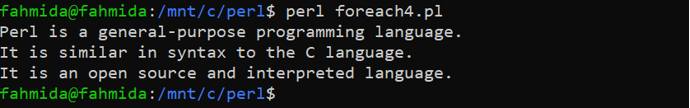
Perl is a general-purpose programming language.
It is similar in syntax to the C language.
It is an open-source and interpreted language.
Create a PERL file with the following code that will read the content of the myfile.txt file and print the file content by using a foreach loop. The open() function has been used in the code to open the file for reading. The “<” symbol is used to open a file for reading in PERL. Next, the foreach loop has been used to read and print the file content line by line.
$filename = 'myfile.txt';
# Open the file for reading
open $file_handler, '<', $filename or die "Unable to open $filename file.";
# Read each line of the file using foreach loop
foreach $line () {
# Print the line of the file
print $line;
}
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code if the myfile.txt file does not exist in the current location.
After creating the myfile.txt file, the following output will appear after executing the above script.
Example-5: Control the foreach loop Using the “last” Keyword
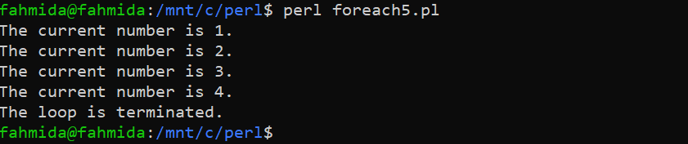
Create a PERL file with the following code in which the foreach loop will be terminated by using the last keyword based on the “if” condition. The foreach loop will iterate 10 times based on the range array. The loop will be terminated after iterating the loop 4 times.
foreach $number (1 .. 10) {
# Print the current value
print "The current number is $number.\n";
#Terminate the loop based on the 'if' condition
last if $number > 3;
}
# Print the termination message
print "The loop is terminated.\n";
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
Example-6: Read the Values of Multiple Arrays
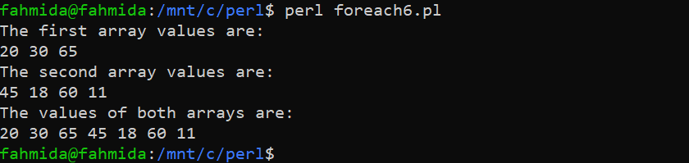
Create a PERL file with the following code that will print the values of two numeric arrays by using a single foreach loop. The values of two arrays and the merged values of these arrays will be printed after executing the code.
@array1 = (20, 30, 65);
# Define the second array
@array2 = (45, 18, 60, 11);
print "The first array values are:\n", join(' ',@array1),"\n";
print "The second array values are:\n", join(' ',@array2),"\n";
print "The values of both arrays are:\n";
# Read the values of both arrays using loop
foreach $number (@array1, @array2)
{
# Print the array value
print "$number ";
}
print "\n";
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code
Conclusion
The ways of using the foreach loop to parse one-dimensional arrays, two-dimensional arrays, multiple arrays, and the file content have been shown in this tutorial to help the PERL user to know the uses of the foreach loop in PERL properly.