Permission denied error in shell script execution
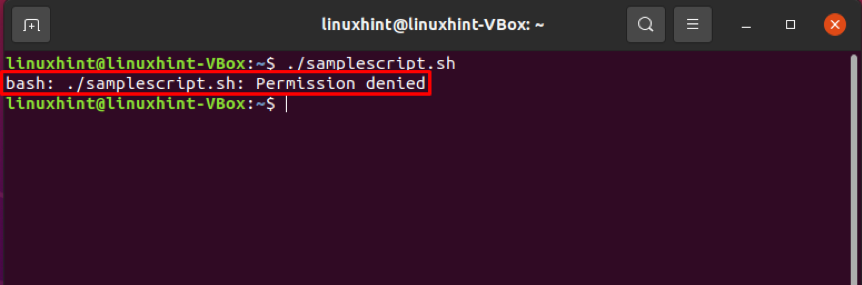
In our system, we have a shell script named “samplescript.sh”. Now, as a normal user, we will try to execute this hell script.
The output will show you the “permission denied error” because you do not have the permission to execute this script.
Fixing permission denied error
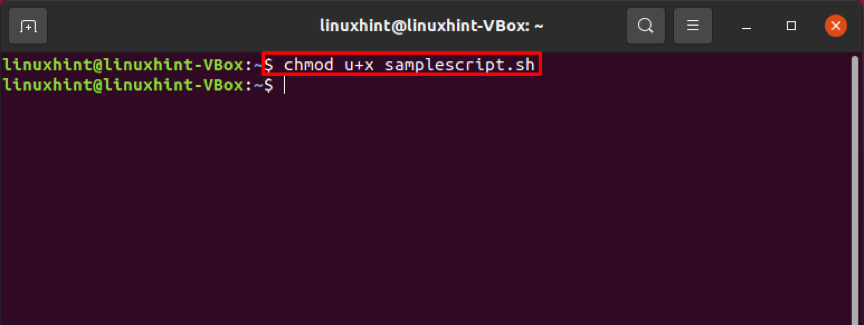
To avoid this “permission denied error,” the only thing you have to do is to add “x” or “execution” permission to this “samplescript.sh” file and make it executable for a typical user.
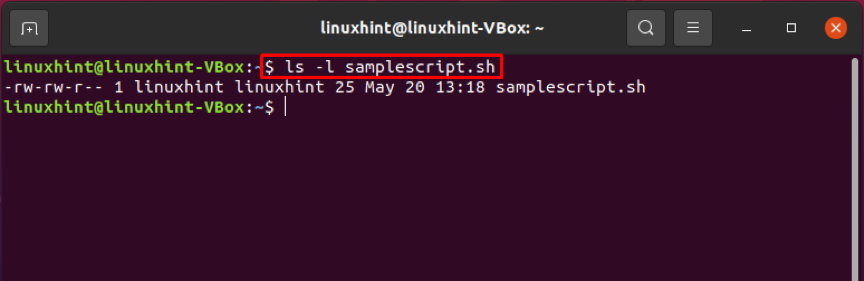
Firstly, check out the file permission of the shell script.
Using chmod command
The chmod command lets a user change permission of a file using a reference file, numeric or symbolic mode.
Syntax of chmod command:
- flags: user can set these additional options
- permissions: this part of the chmod command is used to define file permissions which include: “r” for read, “w” for write, and “x” for making it executable.
- filename: specify the filename whose permissions you want to change.
Whereas “u+x” will make the script executable for the current Linux user, though the group owner or other “users” already have access to execute it.
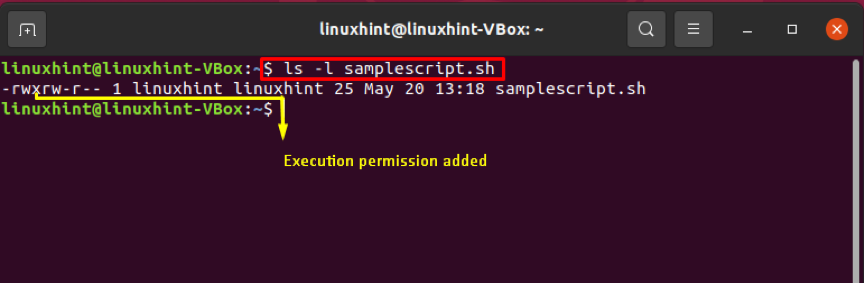
Execution of the above-given chmod command should change the “samplescript.sh” into an executable format. Now execute the “ls” command to confirm the changes we made into the permissions of this shell script.
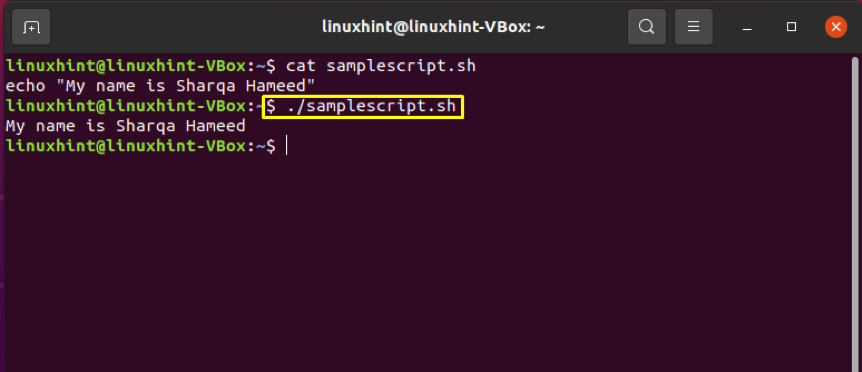
Utilize the cat command to view the content of this “samplescript.sh” script file.
Finally! It’s time to execute the shell script.
The output declares that we have successfully fixed the permission denied error of this “samplescript.sh” shell script.
Conclusion
Every Linux user should know the quick fix for the “permission denied” error encountered while executing any shell script. “chmod” command resolves this issue by changing the script’s file permissions and allowing it to in an executable format for the current user. This article has provided you a step-by-step procedure for fixing the shell script “permission denied” execution error.