Secure Shell, commonly called SSH, is a network protocol used to perform remote logins in machines in a network or over the internet. SSH is very popular as it is secure and easy to use, especially if you are comfortable using the terminal.
In this quick guide, we will discuss how to install SSH using OpenSSH server on a Linux system, quick configuration, and finally, show you how to view and change the port on which SSH is running.
Let us get started:
Installing SSH on Linux
Let us start by discussing how to install SSH on Linux.
NOTE: This part of the tutorial is not all that important, and you can skip it if you already have SSH installed on your system.
That said, start by updating the system using the command:
Next, install the OpenSSH server using the simple command:
Once the command executes successfully, you should have SSH setup on your system and start configuring it.
By convention, the SSH service gets installed as ssh service, and you can manage it using systemd.
Start by checking if you have the service correctly installed using the command:
[FAIL] sshd is not running ... failed!
After confirming that you have SSH service installed, you can go ahead and start the service using the command:
[ ok ] Starting OpenBSD Secure Shell server: sshd.
To enable SSH to run on boot, use the systemctl command:
How to Change the Default SSH Port
SSH is a powerful functionality that allows remote logins on a device from anywhere in the world. This feature can also be an exploitable vulnerability if an attacker gains access to the system.
A fundamental way to secure SSH is to change the port on which it runs by default, port 22.
You will often hear the following joke: “The Universe is made of Protons, Neutrons, Electrons, and default ssh ports.” This joke is voguish in programmers’ circles because default SSH ports are susceptible to attacks, especially brute-forcing.
Let us now look at how you can start securing your system by changing the default SSH port.
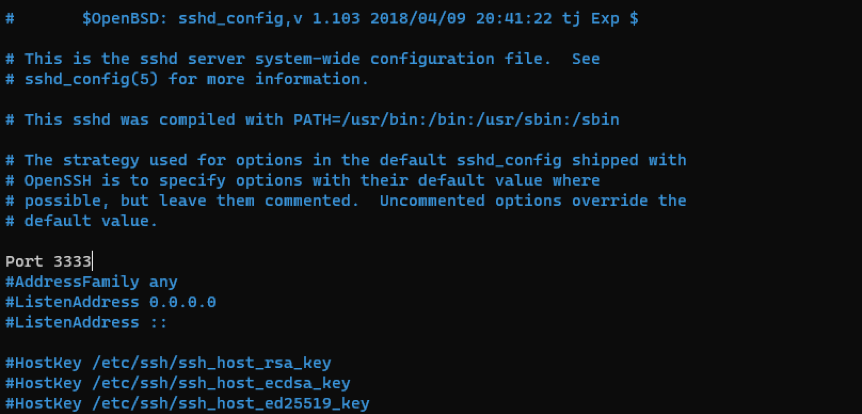
To change the default SSH port, we need to edit the SSH server configuration file in /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Edit the config file and uncomment the entry #Port and specify the port you wish to use as the default SSH port.
You can also perform other configurations in this file to enhance your server security, but we will not get into that in this tutorial.
Now, close the file and save all the changes. Next, we need to restart the service to apply the changes, which you can do using the command:
How to Find the Port On Which SSH Is Running
To view the port on which SSH is running, cat the contents of the sshd_config file and grep for port using the command:
Conclusion
In this quick guide, we have discussed how to install and quickly configure SSH on Linux. We also covered how to edit the SSH configuration file to change the default SSH port and finally looked at how to tell which port SSH is running on.