As we know that the Linux distributions are designed for multi-threaded purposes. Several processes run in the background simultaneously with the assigned unique identifiers. These identifiers are assigned automatically by the kernel and are known as Process Identifiers (PIDs).
While operating a system, sometimes we need to get details on how many processes are running and what the kernel gives PIDs.
Several reasons could be listed that why we need to know the PID of running the program. When multiple programs are executing, sometimes we want their PIDs for scheduling purposes, or when a program behaves abnormally, we need its PID to kill the associated program.
You can also find the PIDs through the Graphical User Interface (GUI), but you may not get the list of hidden running processes from GUI-based tools.
To get the PID of the running processes, a command-line interface is the most effective way.
How to find process ID in Linux:
There are different approaches to find PIDs; most of the simple and possible approaches are discussed below. Select the process you want to display the PID of and follow the approach according to choose.
For example, we will show the process ID of “VLC,” but you can select another process.
How to find the process ID (PID) with the “pidof” command:
To get the PID of the running process in a terminal with the help of the “pidof” command is the most common and simplest way.
Open the terminal and follow the given syntax of the “pidof” command to display process ID:
or to get the “VLC” PID, type:
How to Find Process ID (PID) with “pgrep” Command:
The “pgrep” command is another Linux utility that helps find the PID of a running program. To get PID of the “VLC” using the “pgrep” command utility, type:
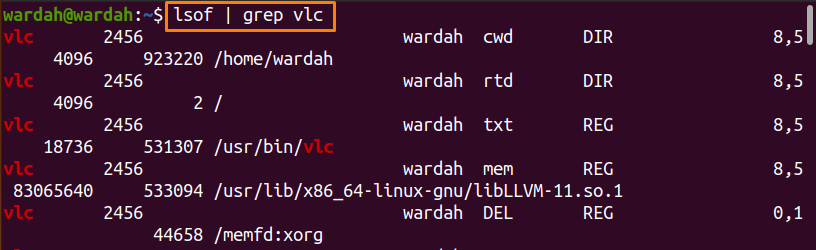
How to find the process ID (PID) with the “lsof” command:
The “lsof” command is an abbreviated form of “List Open Files.” It is used to fetch data about files opened by multiple processes.
Use it with the “grep” command to retrieve the “VLC” PID with the file data:
Keep in mind, most of the time, we use the “grep” command with multiple command-line tools. The purpose is that the “grep” command finds the file of a specified pattern of strings and displays it.
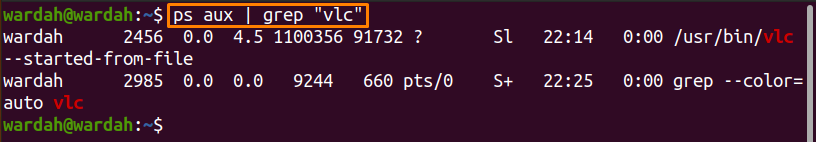
How to find the process ID (PID) with the “ps” command:
When we use the “ps” command, it lists the process ID of a running process and reads the related information from the “/proc” filesystem that contains the virtual files.
Type the given command to display PID of VLC:
(You might think why we used the “ps” command with the “aux” option. Keep that question in mind; we will use this command at the end of the article).
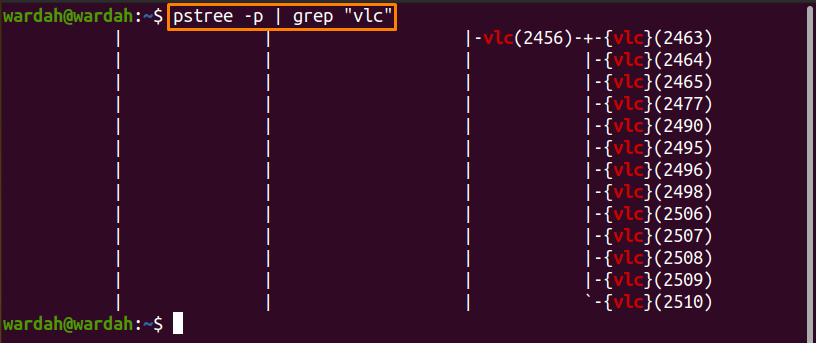
How to Find the Process ID (PID) with “pstree” Command:
The “pstree” command utility is an effective way to display the hierarchy of the running process in a tree format.
Type the “pstree” command to display a hierarchy of the VLC and get its PID as well:
The image has shown the parent process with its child processes.
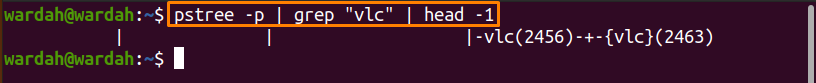
If you want to display only the parent process, use the mentioned command:
The approaches mentioned above are used to display the PID of a particular process.
If you want to display the list of all processes running in the background, use the “top” and “ps aux” command.
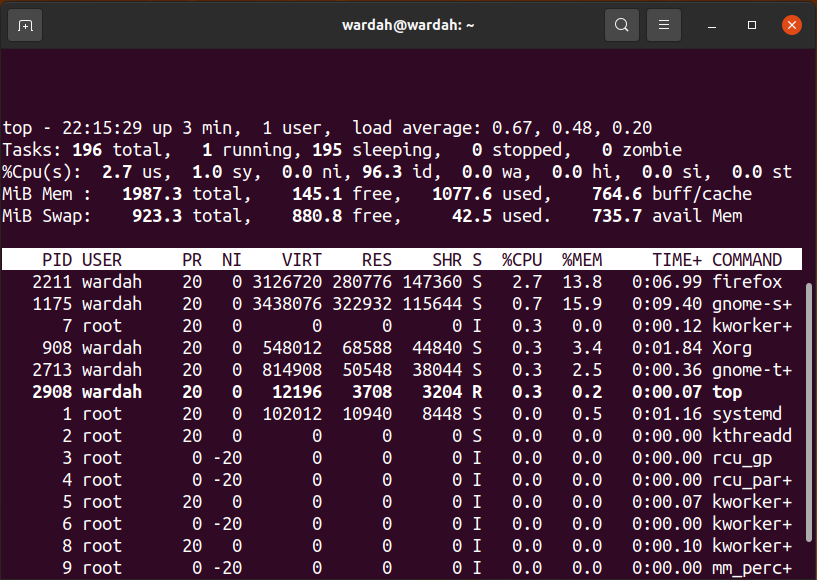
How to find PIDs using the “top” Command:
The “top” command displays the task manager, which contains the processing activity of all the running processes with their PIDs in the Linux system.
Type “top” in a terminal to get a list of processes:
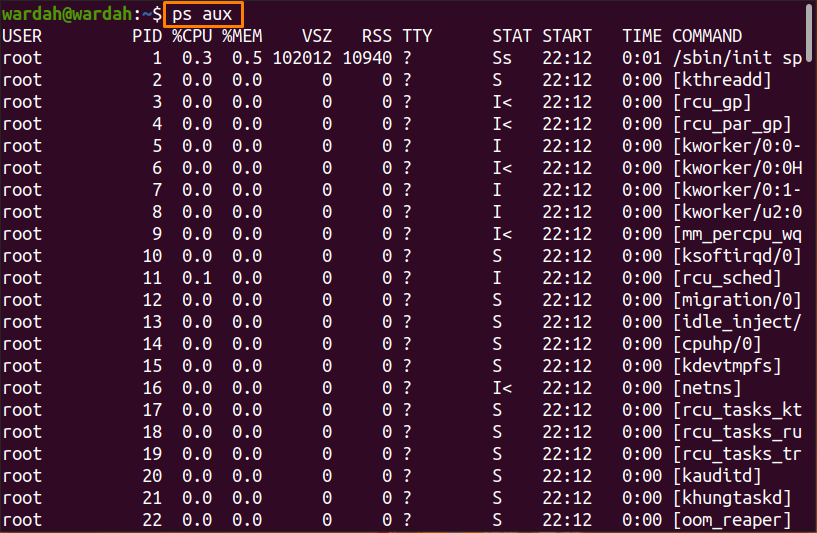
How to find PIDs using the “ps aux” command:
We have already used the “ps aux” with the “grep” command above to display the “VLC” PID. That was for the particular process as we used it with the grep command.
If we talk about the “ps aux” command, it is an efficient command-line tool to monitor all the processes running in an operating system. You can manage process-related information once the list is displayed. It shows process names with their PIDs and memory usage.
Conclusion:
Linux is a multitasking operating system; multiple processes run simultaneously with unique identifiers called PIDs. From this write-up, you have learned how to find the PID of a particular process through different approaches. We have also checked how to get the list of all running processes using the “top” and “ps aux” command-line utilities.