Syntax:
The QUOTE() function takes a string value as the argument that will be escaped, and it returns the escaped string after executing the query. The syntax of this function is given below.
Escape Sequence Characters:
The uses of different escape sequence characters have been explained below.
| Character | Description |
| \’ | It is used to print a single quote (‘) character. |
| \” | It is used to print double quote (“) character. |
| \0 | It is used to print ASCII NULL character. |
| \b | It is used to print backspace character. |
| \n | It is used to print the newline character. |
| \r | It is used to print carriage return character. |
| \t | It is used to print tab space character. |
| \Z | It is used to print ASCII 26 (Ctrl+Z) character. |
| \\ | It is used to print backslash(\) character. |
| \% | It is used to print the ‘%’ character. |
| \_ | It is used to print the ‘_’ character. |
Use of QUOTE() function for a string value:
The uses of the QUOTE() function with different types of escape sequence characters have been shown in this part of the tutorial.
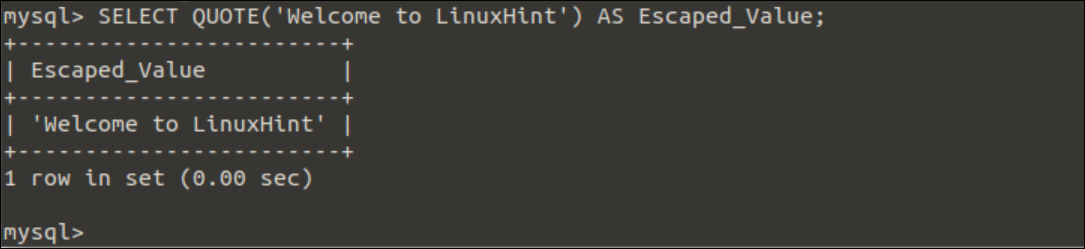
Example-1: Use of QUOTE() function to print simple string
When the string value is printed without the QUOTE() function using the SELECT statement, the string value will be printed without any quote. Run the following SELECT statement with the QUOTE() function to print a simple string with a single quote.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query.
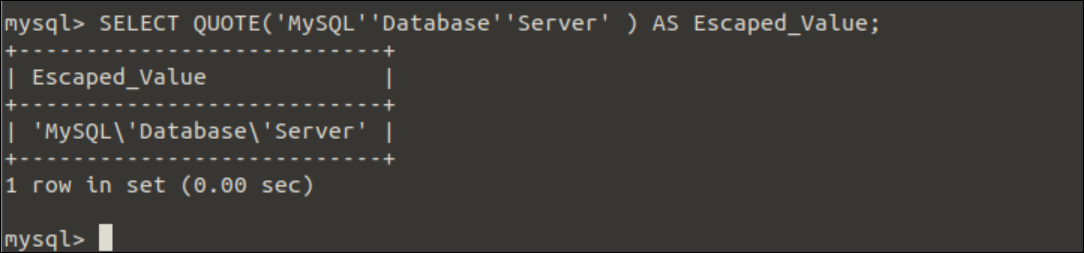
Example-2: Use of QUOTE() function to print single quote inside the string
Run the following SELECT statement with the QUOTE() function to print a string with the single quote.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query.
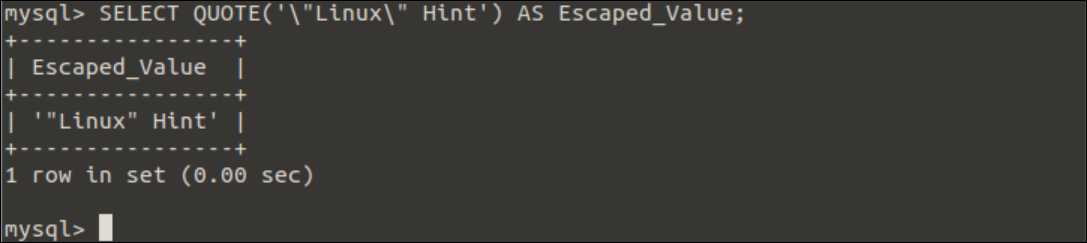
Example-3: Use of QUOTE() function to print double quote inside the string
Run the following SELECT statement with the QUOTE() function to print a string with the double-quoted string.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query.
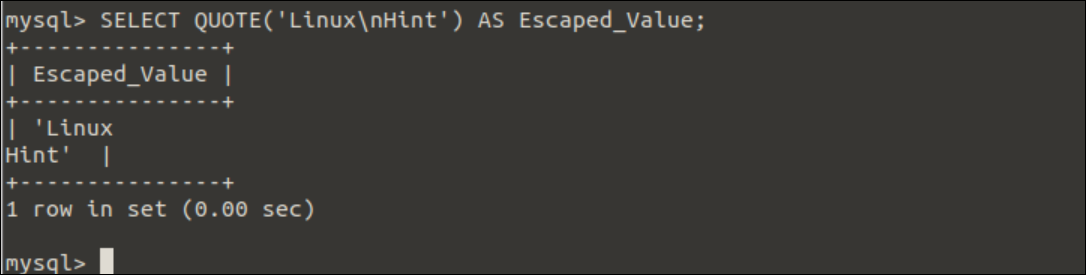
Example-4: Use of QUOTE() function to print a string with the newline
Run the following SELECT statement with the QUOTE() function to print a string with the newline.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query.
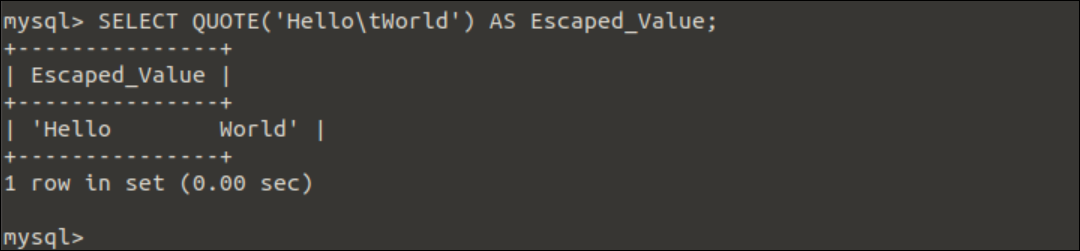
Example-5: Use of QUOTE() function to print a string with tab space
Run the following SELECT statement with the QUOTE() function to print a string with the ‘\t’ character.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query. The tab space has been generated between ‘Hello’ and ‘World’ in the output for using the ‘\t’ character.
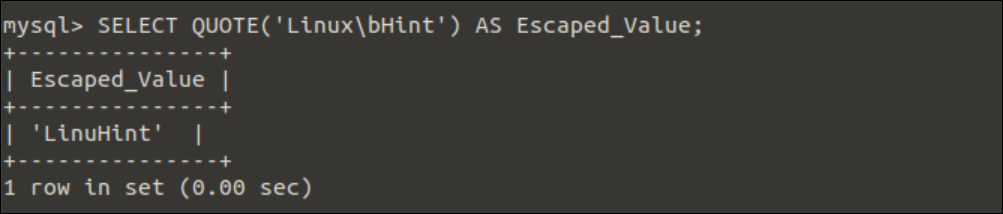
Example-6: Use of QUOTE() function to print a string with the backspace.
Run the following SELECT statement with the QUOTE() function to print a string after applying a ‘\b’ character.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query. The character ‘x’ has been removed from the main string using the ‘\b’ character inside the string.
Use of the QUOTE() function for the table data:
You have to create a table with data in a MySQL database to check using the QUOTE() function on the table data. Open the terminal and connect with the MySQL server by executing the following command.
Run the following command to create a database named test_db.
Run the following command to select the database.
Run the following query to create a table named clients with five fields.
id INTNOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(50),
address TEXT,
contact_noVARCHAR(15));
Run the following INSERT query to insert 4 records into the clients table.
('4001', 'Laboni Sarkar', '[email protected]', '34, Dhanmondi 9/A, Dhaka.', '01844767234'),
('4002', 'Tahsin Ahmed', '[email protected]', '123/1, Jigatola, Dhaka.', '015993487812'),
('4003', 'Hasina Pervin', '[email protected]', '280, Shantibagh, Dhaka.', '01600487812'),
('4004', 'Mehrab Ali', '[email protected]', '78, Cox’s Bazar, Chottogram.', '01727863459');
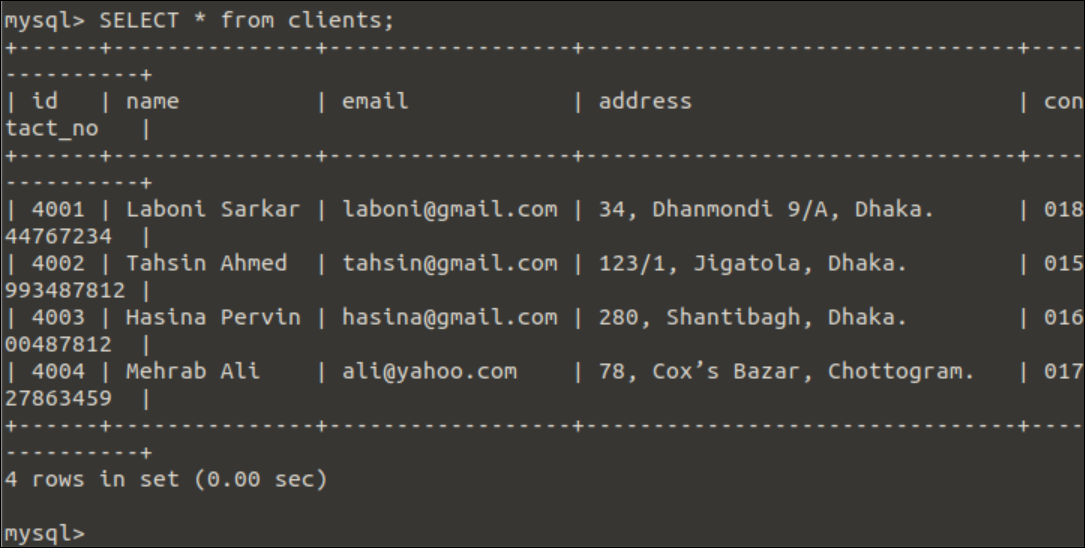
Run the following query to print all records of the clients table.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query.
Example-1: Use of QUOTE() function in a single field of a table.
When the table’s string value is printed using a SELECT query, the output will show the string value without any quote. The following SELECT query will print all records of the clients table and another extra column QUOTE (email) by enclosing the email field of the clients table with the single quote.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query.
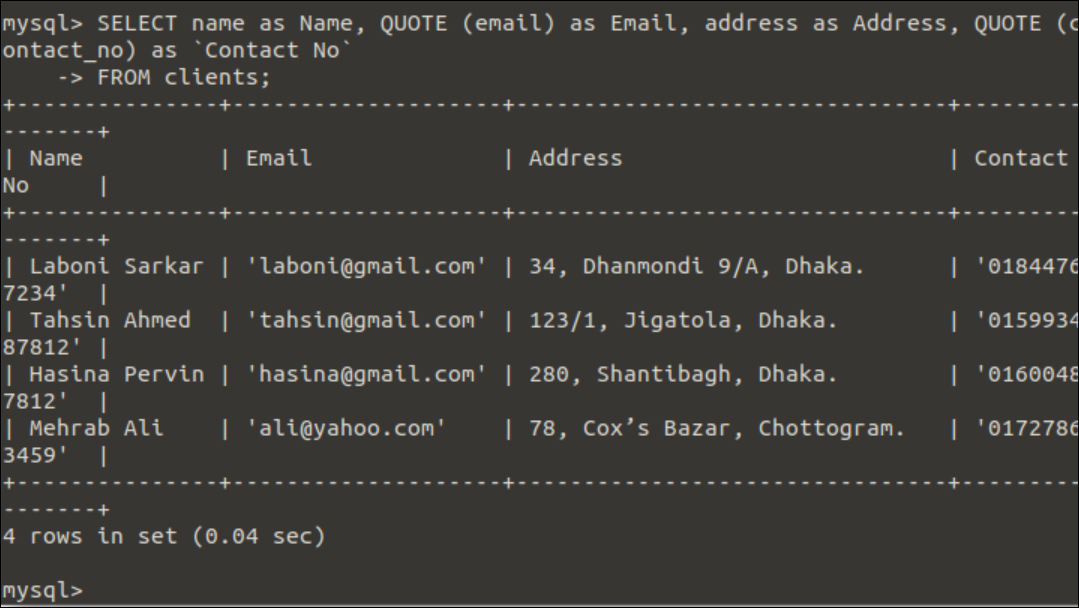
Example-2: Use of QUOTE() function in multiple fields of a table.
The following SELECT query will print the original values of the name and address fields and the single-quoted values of the email and contact_no fields of the clients table.
FROM clients;
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query.
Conclusion:
The QUOTE() function is used in the SELECT query to format the string data using different escape characters before printing. The ways of using the QUOTE() function for the simple string data and the table data have been shown in this tutorial to help MySQL users know how to escape the string in MySQL.