Implement a Do-While Loop Using the While Loop
The while loop can be used in different ways to implement the functionality of the do-while loop. Generally, the while loop checks the condition at the beginning of the loop to start the iteration. So, if the condition is set to True, the while loop will work like the do-while loop. This type of while loop will work like the infinite loop and the loop will be terminated based on the particular condition. The syntax of this type of loop is given below.
Syntax:
statements…
if condition:
break
or
while condition:
statements…
reset condition
The statements of the above loop will be executed at least once like the do-while loop and the loop will iterate until it matches the ‘if’ condition, and executes the ‘break’ statement or matches the particular condition. Different uses of the while loop to implement the logic of do-while in Python have been shown by using various examples.
Example-1: Emulate the Do-While Loop Using the While Loop
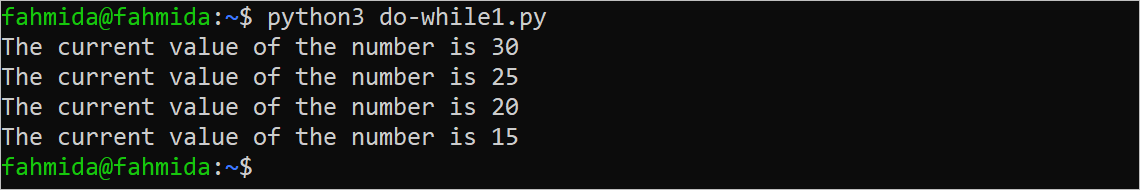
Create a Python file with the following script to print the numbers from 30 to 10 with the interval of 5 by using a while loop. Here, the condition of the loop is set to True to start the iteration of the loop. The number variable is initialized to 30 before starting the execution of the loop. The value of the number will be decreased by 5 in each iteration of the loop. When the value of the number reached 10, then the ‘break’ statement will be executed and terminated from the loop.
number = 30
#Declare infinite while loop
while True:
#Print the current value of a number
print("The current value of the number is %d" % number)
#Decrement the number value
number = number - 5
#Check the condition to terminate from the loop
if number <= 10:
break
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script.
Example-2: Emulate the Do-While Loop Using the While Loop Without the ‘If’ Condition
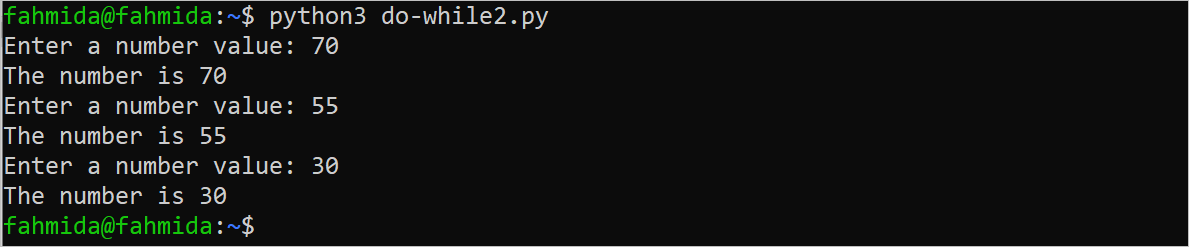
Create a Python file with the following script to take a number from the user repeatedly until the user provides a number greater than or equal to 50. The check variable is set to True to start the iteration of the while loop like the do-while loop. The value of this variable has been changed at the end of the loop to terminate the loop.
check = True
#Declare the loop
while check:
#Take a number value from the user
number = int(input("Enter a number value: "))
#Print the value taken from the user
print("The number is %d" % number)
#Reset the condition for the loop
check = number >= 50
Output:
The following output will appear for the input values of 70, 55, and 30 after executing the above script.
Example-3: Emulate the Do-While Loop Using a While Loop with Multiple Break Statements
Create a Python file with the following script to take the username and password for the authentication, and the user can provide the username and password for a maximum of three times if he/she is unable to authenticate in previous attempts. The first ‘break’ statement will be executed and terminated from the loop if the taken username and password are valid. The second ‘break’ statement will be executed and terminated from the loop if the wrong username or password is provided three times.
#Define while loop
while True:
#Take input from the user
username = input("Enter username: ")
password = input("Enter password: ")
'''Check the username and password
and terminate from the loop for the valid user
'''
if username == 'Admin' and password == 'secret':
print('Valid user.')
break
else:
#Decrement the counter value
counter = counter - 1
#Check the counter value to terminate from the loop
if counter == 0:
break
#Print the error message
print("Username or password is incorrect")
#Print the number of login attempts left
print("You have %d login attempts left." % counter)
Output:
The following output will appear for providing an invalid and valid username and password after executing the above script.
Example-4: Emulate the Do-While Loop Using the While Loop Using a Random Number
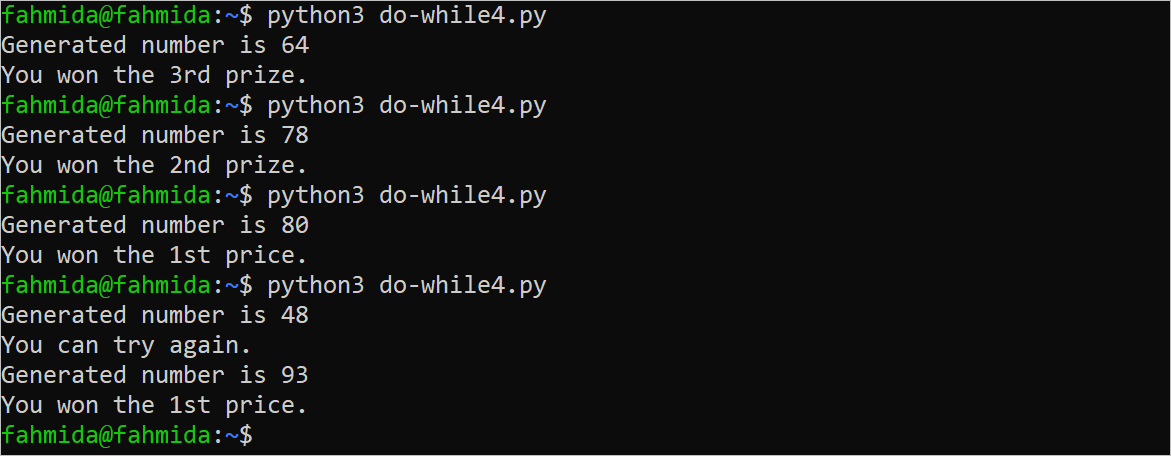
Create a Python file with the following script to generate a random integer within 10 to 99 and terminate the loop based on the random value. Three ‘break’ statements have been added in the script to terminate the loop based on three conditions.
from random import randint
#Define the loop
while True:
#Generate a random number
number = randint(10, 99)
#Print the number
print('Generated number is %d' %number)
#Continue the loop if the number is less than 60
if number < 60:
print('You can try again.')
#Terminate from the loop if the number is less than 70
elif number < 70:
print('You won the 3rd prize.')
break
#Terminate from the loop if the number is less than 80
elif number < 80:
print('You won the 2nd prize.')
break
#Terminate from the loop if the number is more than or equal to 80
else:
print('You won the 1st price.')
break
Output:
The following similar output will appear after executing the above script. The script has been executed four times and four types of outputs have been generated based on the random value.
Conclusion
Different ways of implementing a do-while loop in Python by using a while loop have been shown in this tutorial using simple examples to help the Python users. The ‘for’ loop can be used also to do the same task.