Although this is a small API, it is a very beneficial tool, especially for developers coming from SQL databases. It can also reduce the learning curve by quickly relating the SQL queries to the corresponding search queries.
You can then explore the full capabilities of the Elasticsearch search API and the supported query languages.
It is to keep in mind that although Elasticsearch does support SQL, it does contain various limitations.
Query Syntax
The following shows the syntax of the translate API:
{
request_body
}
You can also send a post request to the translate API as shown in the following syntax:
{
request_body
}
Depending on your cluster configuration, the API may require read privileges on the index whose data you wish to query. You can also specify the target resource as an index alias or a data stream.
In the request_body, you can specify all the SQL Search API request body parameters. Explore the docs provided in the following resource to learn more:
As a response, the query should return the result corresponding to the search API with the queried data.
Example
To best illustrate how to use this API, we will assume we have an index called “netflix” containing all the data about Netflix movies and TV Shows.
Suppose we wish to fetch the top five movies from the Netflix index that we released in the year 2020 and above:
The equivalent SQL query can be expressed as shown below:
To execute the above SQL search in Elasticsearch, we can put it into the SQL Search API as shown below:
{
"query": "\n SELECT title, duration, rating, type FROM "netflix" WHERE type = '\''Movie'\'' AND release_year >= 2020\n ",
"fetch_size": 5
}'
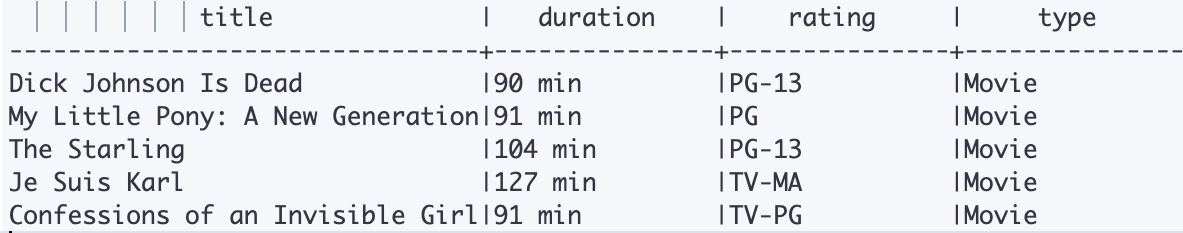
The previous request should query the index and fetch the matching records. The return output is in text format as provided below:
As we can see, Elasticsearch returns the expected output.
To return the output as JSON, we can set the format to JSON as shown below:
{
"query": "\n SELECT title, duration, rating, type FROM "netflix" WHERE type = '\''Movie'\'' AND release_year >= 2020\n ",
"fetch_size": 5
}'
Output:
Convert SQL Query Into Search Request
To convert the previous SQL search query into an Elasticsearch request, we can pass it into the translate API as shown below:
{
"query": "\n SELECT title, duration, rating, type FROM "netflix" WHERE type = '\''Movie'\'' AND release_year >= 2020\n ",
"fetch_size": 5
}'
The API should parse the input SQL input and convert it into a valid search request, as shown in the following output:
"size": 5,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"type": {
"value": "Movie"
}
}
},
{
"range": {
"release_year": {
"gte": 2020,
"boost": 1
}
}
}
],
"boost": 1
}
},
"_source": false,
"fields": [
{
"field": "title"
},
{
"field": "duration"
},
{
"field": "rating"
},
{
"field": "type"
}
],
"sort": [
{
"_doc": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
]
}
You can then use this request format to send to the Elasticsearch search API as shown below:
{
"size": 5,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"type": {
"value": "Movie"
}
}
},
{
"range": {
"release_year": {
"gte": 2020,
"boost": 1
}
}
}
],
"boost": 1
}
},
"_source": false,
"fields": [
{
"field": "title"
},
{
"field": "duration"
},
{
"field": "rating"
},
{
"field": "type"
}
],
"sort": [
{
"_doc": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
]
}'
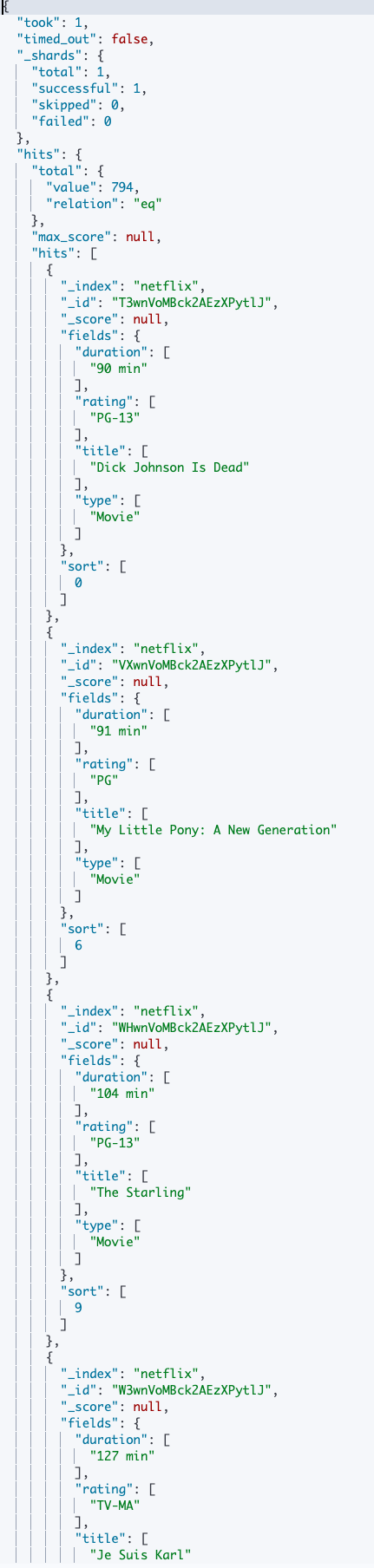
Similarly, the request should return similar data as shown below:
Conclusion
Through this post, you discovered how you could use SQL queries to fetch data from an existing Elasticsearch index. You also learned how to use the translate SQL API to convert a valid SQL query to an Elasticsearch request.