In this guide, we will analyze the working of the double data type in C++.
Syntax
The following syntax is used to declare variables of the double type:
To declare a variable of the double data type, the keyword “double” is followed by the “variable_Name”.
How Does C++ Double Data Type Work?
The double data type in C++ contains the decimal numbers and occupies 8 bytes in the main memory. It provides a double precision to the variable as compared to the float data type. A double-type variable can store values in the range 1.7E – 308 to 1.7E + 308. Every value is by default interpreted as a double by the C++ compiler, which also conducts an implicit type conversion between other data types.
To store the value memory, the value of the double type combines a sign bit with exponent bits and fraction bits. The exponent bits show the number’s magnitude, the sign bit establishes whether it is positive or negative, and the fraction bit holds the number’s fractional component.
Let’s talk about some C++ double examples.
Example 1: Double Data Type Variables to Calculate Value with Arithmetic Operators
When using the double data type as an input value to add, subtract, multiply, or divide two numbers, the following header files must be specified:
using namespace std;
Here:
- “include<iostream>” is used for input and output functionality in the program.
- “using namespace std;” brings all std namespace members imported into the current scope.
After that, declare the “num1” and “num2” variables of double data type in the “main()” method. Then, take the value from the user for both variables to show the addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division using the “+,-,*,/” operators:
{
double num1, num2;
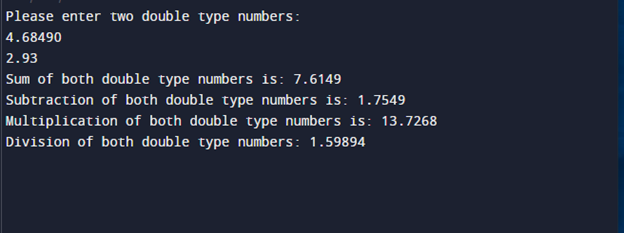
cout<<"Please enter two double type numbers: ";
cin>>num1>>num2;
cout<<"Sum of both double type numbers is: "<<(num1+num2)<<endl;
cout<<"Subtraction of both double type numbers is: "<<(num1-num2)<<endl;
cout<<"Multiplication of both double type numbers is: "<<(num1*num2)<<endl;
cout<<"Division of both double type numbers: " <<(num1/num2)<<endl;
return 0;
}
When the above code is executed, the below-stated results have been displayed on the prompt:
Example 2: Calculate the Different Precision with Double Data Type
The following program demonstrates the precision of the double data type. To do so, specify the header files:
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
In the above snippet:
- “iomanip” library is used to format operations, such as set precision and control alignments for input/output.
In the “main()” function, first, we initialized the “value” variable with the value of “3.142857142857342”. After that, used the “setprecision()” function to check the precision up to 7, and 15 decimal digits accurately. Then, print out the result values using the “cout” keyword:
{
double value = 3.142857142857342;
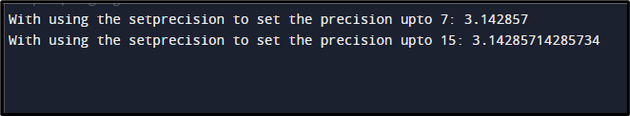
cout << "With using the setprecision to set the precision upto 7: ";
cout << setprecision(7);
cout << value << endl;
cout << "With using the setprecision to set the precision upto 15: ";
cout << setprecision(15);
cout << value << endl;
return 0;
}
When the preceding code is executed, the following result has been shown on the screen:
This guide briefly explained the working of double data types in C++.
Conclusion
Double data type in C++ is essential for managing the “double-precision” of the floating-point numbers. It is a key data type in a variety of applications due to its wide range and great precision. The above tutorial showed the double data type with the arithmetic operators in C++.