This post will describe the work of the “git pull origin <branch-name>” command.
What Does git pull origin [branchname] Mean?
The “git pull origin <branch-name>” command is used to download and merge the content of the particular remote branch into the local branch.
To perform the above-stated scenario, first, redirect to the Git local repository and list its content. After that, view the remote URL list and run the “git pull <remote-name> <branch-name>” command.
Step 1: Redirect to Repository
At first, utilize the “cd” command and navigate to the desired repository:
Step 2: View Repository Content
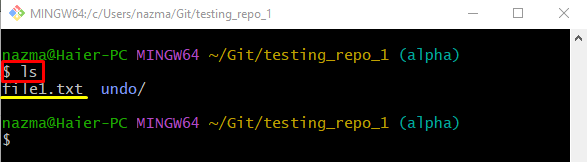
Then, list the repository content by running the “ls” command:
We have selected the “file1.txt” file from the content for further process:
Step 3: Check Remote URL
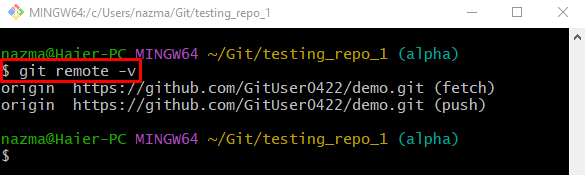
Now, execute the “git remote” command along with the “-v” option and check the list of available remote URLs:
Step 4: Pull Remote Branch
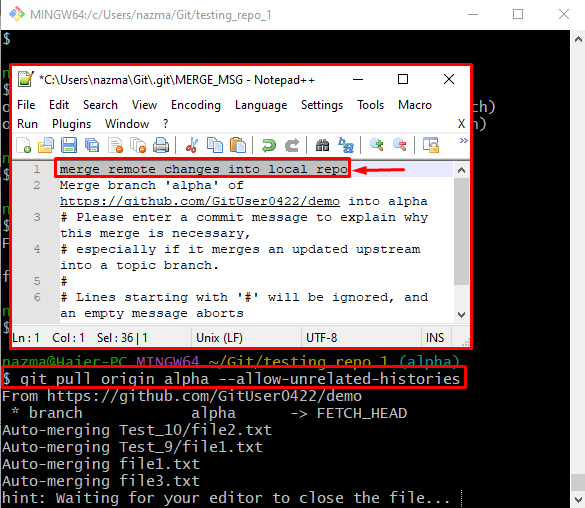
Next, pull the particular remote branch to the local repository by running the “git pull” command:
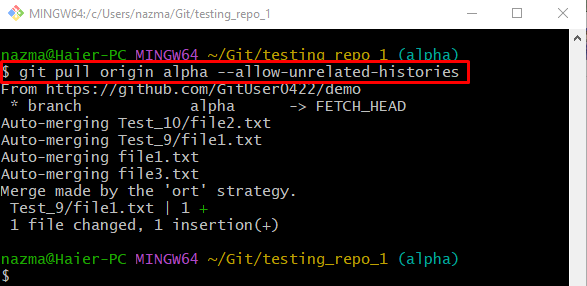
Here, the “origin” is the remote URL, and “alpha” is a local branch name. The “MERGE_MSG” text editor will open when the above-stated command is executed. Now, add a message, save changes, and close it. For instance, we have typed the “merge remote changes into local repo” pull message:
As you can see, the latest version of the specified remote branch is downloaded and merged successfully into the local repository:
That’s all! We have provided about the “git pull origin <branch-name>” in detail.
Conclusion
When the “git pull origin <branch-name>” command is executed, then the content of the specified remote branch will be downloaded and merged into the local branch. To do so, first, go to the required repository and list its existing content. Then, check the remote URL list and execute the “git pull <remote-name> <branch-name>” command. This post briefly explained the work of the “git pull origin <branch-name>” command.