This guide will provide the usage of the “git checkout” command along with the “–theirs” option for multiple project files.
How to “git checkout –theirs” for Multiple Files?
To check out for multiple files, follow the provided steps:
- Go to the Git repository.
- List the existing content of the repository.
- Select multiple files and update them one by one without pushing them to the staging index.
- Show the status of the working repository.
- Switch to the root directory.
- Execute the “git checkout –theirs <repo-name/*>” command.
- Navigate to the target repository and view the status.
Step 1: Navigate to Git Repository
At first, execute the “cd” command along with the desired repository path:
Step 2: List Existing Content
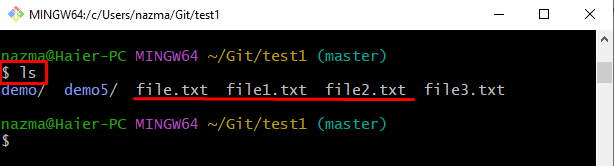
Then, display the list of current repository content by running the “ls” command:
Here, we have selected three text files which are highlighted below:
Step 3: Modify Selected File
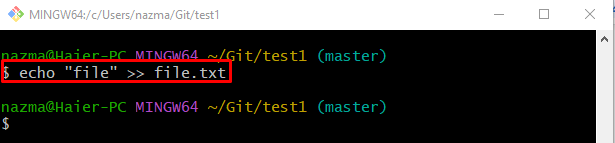
Next, modify the “file.txt” file through the “echo” command:
Step 4: Update Selected File
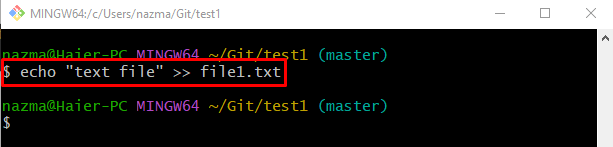
Execute the “echo” command and add the changes into the specified file:
Step 5: Edit File
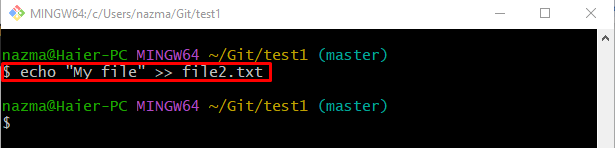
Similarly, edit another file with the help of the provided command:
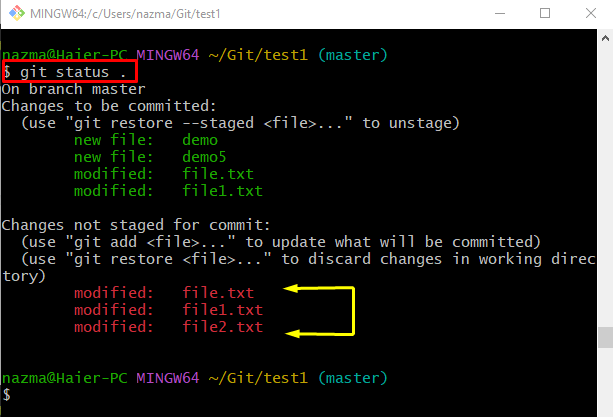
Step 6: Check Status
Now, execute the below-given command to check the status of the current working Git repository:
As you can see, all modified files exist in the Git working directory:
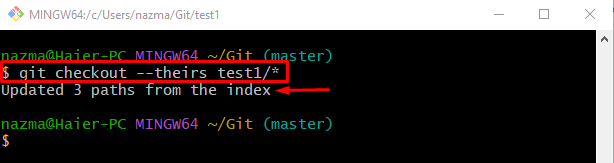
Step 7: Checkout With “–theirs”
Now, switch to the root directory and use the “git checkout” command:
In the above-stated command, the “–theirs” option signifies that the current branch is being rebased. The “test1/” is the name of the Git local repository, which contains modified untracked files and an asterisk “*” symbol after the slash “/” indicates all files.
According to the below-given output, the paths of all unstaged files are updated:
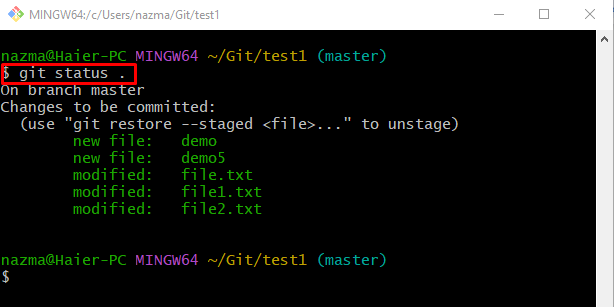
Step 8: Check Git Status
Lastly, move to the Git repository and view its status by running the “git status .” command:
It can be seen that all unmerged files are added to the staging area:
That’s all! We have demonstrated the “git checkout –theirs” process for more than one file.
Conclusion
To check out for multiple files, first, move to the Git repository and list the existing content of the repository. Then, choose multiple files and update them one by one without adding to the index. Next, check the status of the current working repository and switch to the root directory. Finally, execute the “git checkout –theirs <repo-name/*>” command. Lastly, navigate to the target repository and view the status. This guide briefly illustrated the “git checkout” command with the “–theirs” option for multiple files.