This manual will define the procedure to remove or discard your local changes in Git.
How to Discard Your Local Changes in Git?
To discard your local changes in Git, first, move to the Git root directory and create a new Git local repository, and immediately move to it. Initialize the created directory, create new files, and check the commit reference history of the Git repository using the “$ git commit -m <message>” command and copy the commit reference to which we want to revert. Lastly, execute the “& git reset –hard <commit-id>“ command to discard your local changes in Git.
Let’s move forward to implement the above scenario!
Step 1: Open Git Bash
Launch the Git terminal by using the “Startup” menu:
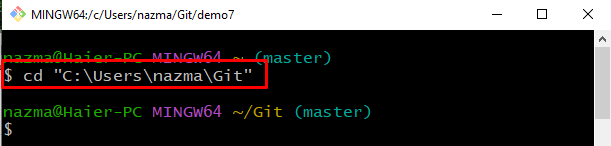
Step 2: Navigate to Git Root Directory
Move to the Git root directory using the “cd” command:
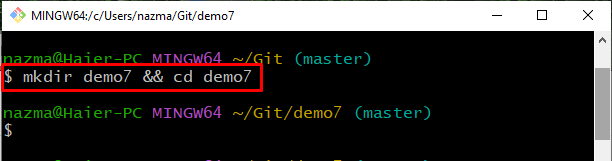
Step 3: Create Git Local Repository
Execute the below-provided command to create and navigate to the new directory:
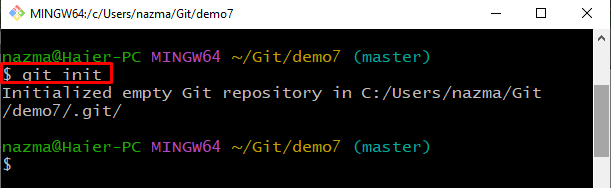
Step 4: Initialize Git Repository
Now, initialize the newly created Git local repository using the “git init” command:
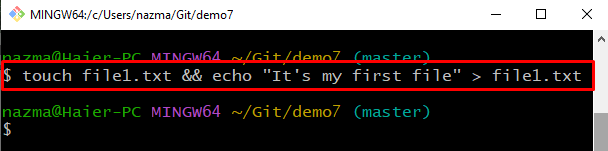
Step 5: Create and Make Changes
Next, execute the “touch” command with the “echo” command to create a file. Then, add some text to it using the redirect operator:
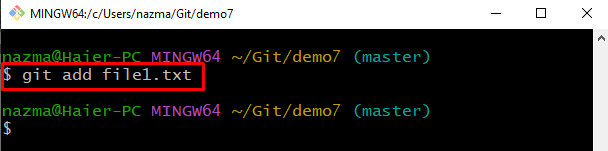
Step 6: Add File to Staging Area
Track the file using the “git add” command:
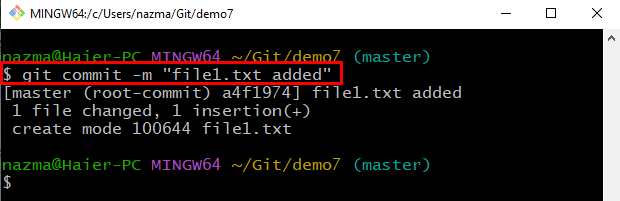
Step 7: Commit Changes
Run the “git commit” command to add the changes to the Git local repository with the specified message:
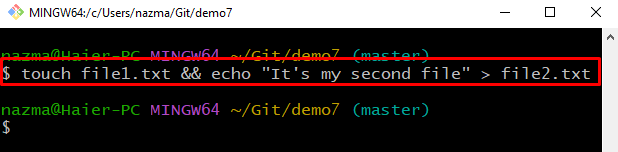
Step 8: Create and Update File
Next, create a new file named “file2.txt” and add some text to it:
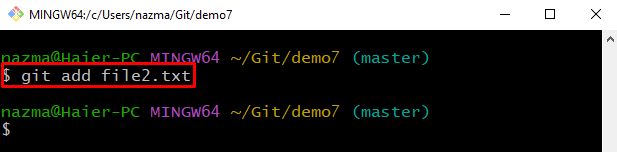
Step 9: Add file
Now, add the required file from working area to the staging area:
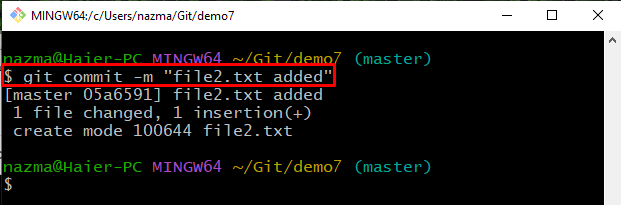
Step 10: Commit Changes
Run the provided command to commit made changes with the commit message:
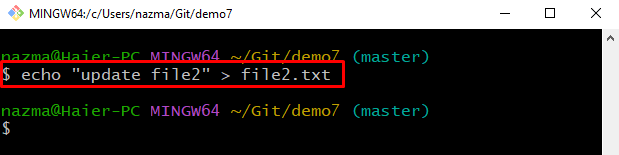
Step 11: Update File
Now, again open “file2.txt” and update it accordingly:
Step 12: Check Status
To check the Git local repository run the provided command:
As you can see that, the “file1.txt” file is modified successfully:
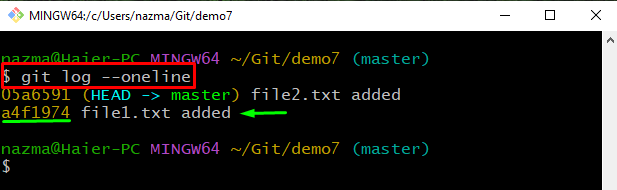
Step 13: Check Log
Check the Git local repository reference log history with the provided command:
From the displayed information, copy the commit reference number to discard local changes:
Step 14: Discard Local Changes
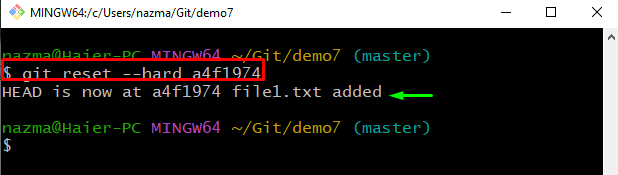
Finally, execute the “git reset” command with the “–hard” flag and the copied commit reference to discard the related changes:
As you can see, our HEAD position is moved to the stated commit reference, and most recent changes are discarded:
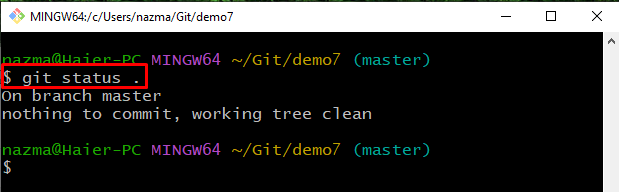
Step 15: Check Status
Next, check the status using the provided command:
Step 16: Check List Content
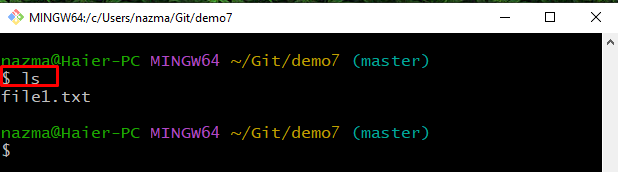
Lastly, run the “ls” command to view the existing content of the Git repository:
It can be seen that the “file1.txt” no longer exists in the repository anymore:
We have offered the procedure to discard your local changes in Git examples.
Conclusion
To discard your local changes in Git, first, move to the Git root directory, create a new Git local repository and navigate to it. Next, create new files, and open and update them. Then, commit changes to the Git repository. After that, again update the file and check the Git commit log reference, copy the commit reference and execute the “$ git reset –hard <commit-ref>” command to discard related commit changes. This manual discussed the method to remove your local changes in Git.